Judaism emphasizes a covenantal relationship with God based on laws and traditions, while Christianity centers on a personal relationship with Jesus Christ as the path to salvation. Explore the key differences and similarities between these faiths in this article.
Table of Comparison
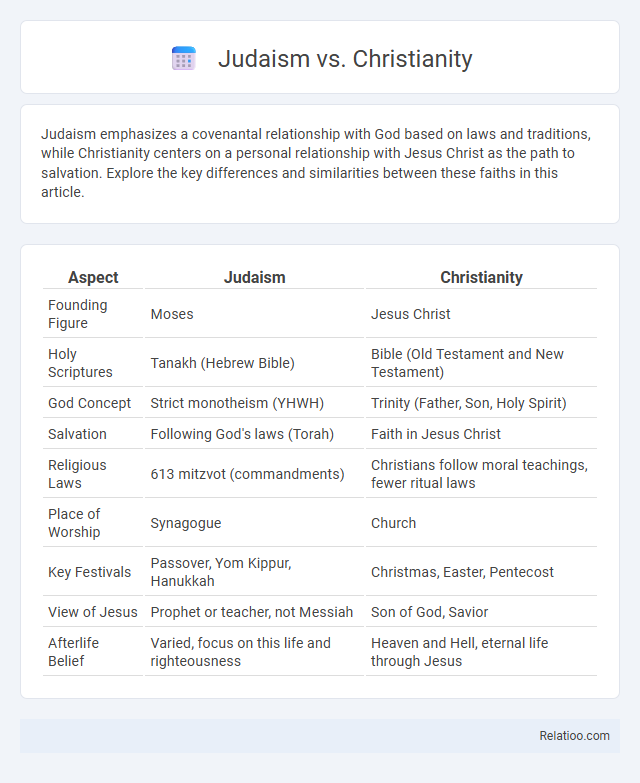
| Aspect | Judaism | Christianity |
|---|---|---|
| Founding Figure | Moses | Jesus Christ |
| Holy Scriptures | Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) | Bible (Old Testament and New Testament) |
| God Concept | Strict monotheism (YHWH) | Trinity (Father, Son, Holy Spirit) |
| Salvation | Following God's laws (Torah) | Faith in Jesus Christ |
| Religious Laws | 613 mitzvot (commandments) | Christians follow moral teachings, fewer ritual laws |
| Place of Worship | Synagogue | Church |
| Key Festivals | Passover, Yom Kippur, Hanukkah | Christmas, Easter, Pentecost |
| View of Jesus | Prophet or teacher, not Messiah | Son of God, Savior |
| Afterlife Belief | Varied, focus on this life and righteousness | Heaven and Hell, eternal life through Jesus |
Introduction to Judaism and Christianity
Judaism, one of the oldest monotheistic religions, centers on the belief in a single, omniscient God and follows the Torah as its sacred text, shaping ethical and ritual practices. Christianity emerged from Judaism, emphasizing the life and teachings of Jesus Christ as the Messiah and incorporating the Bible, consisting of the Old and New Testaments, as the foundation of faith. Both religions influence global culture and morality while differing in theological concepts such as the nature of God, salvation, and scripture interpretation.
Historical Origins and Development
Judaism originated around 2000 BCE with the covenant between Abraham and God, developing through ancient Hebrew scriptures and the Torah, while Christianity emerged in the 1st century CE, centered on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ and the New Testament. Both religions share roots in the Hebrew Bible but diverge in beliefs about the Messiah and salvation, influencing their distinct theological frameworks. Your understanding of religious belief is enriched by recognizing how historical contexts shaped these faiths' doctrines and practices over millennia.
Core Beliefs and Doctrines
Judaism centers on the belief in one God, the importance of following the Torah's laws, and the covenant between God and the Jewish people, emphasizing ethical conduct and communal responsibility. Christianity builds upon Jewish teachings, highlighting the divinity of Jesus Christ, salvation through his sacrifice, and the Trinity concept, shaping doctrines of grace and redemption. Your understanding of religious belief reflects how these core doctrines define faith practices, moral codes, and spiritual goals across both traditions.
Sacred Texts: Torah vs. Bible
The Torah, central to Judaism, consists of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible and contains laws, commandments, and teachings foundational to Jewish faith and practice. Christianity's Bible includes both the Old Testament, which overlaps with the Hebrew Bible, and the New Testament, which chronicles the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Your understanding of religious beliefs is enriched by recognizing how these sacred texts shape the doctrines, rituals, and values distinct to Judaism and Christianity.
Concept of God and the Trinity
Judaism emphasizes the strict monotheism of one indivisible God, rejecting any division of the divine nature. Christianity introduces the concept of the Trinity, describing God as three distinct persons--Father, Son, and Holy Spirit--united as one essence. Your understanding of religious belief can deepen by exploring these fundamental differences in how each tradition conceptualizes the nature of God.
Jesus Christ: Messiah or Prophet?
Judaism views Jesus Christ primarily as a historical figure or prophet but rejects the claim of him being the Messiah, emphasizing the awaited Messiah's role in fulfilling specific prophecies. Christianity centers on Jesus Christ as the Messiah and Son of God, whose life, death, and resurrection are foundational to salvation and divine redemption. Your understanding of religious belief and Christ's identity influences the theological perspectives on his role as either a prophet in Judaism or the Messiah in Christianity.
Salvation and Afterlife Views
Judaism emphasizes a collective responsibility and righteous living in this life with varied beliefs about the afterlife, often focusing on Olam Ha-Ba (the World to Come) and resurrection, while salvation is closely linked to covenantal faithfulness and ethical deeds. Christianity centers on salvation through faith in Jesus Christ's atoning sacrifice, promising eternal life in Heaven, with doctrines of resurrection and judgment shaping its afterlife views. Religious beliefs broadly interpret salvation and afterlife differently, ranging from karmic consequences and reincarnation in Eastern traditions to existential unity or annihilation, reflecting diverse metaphysical understandings across cultures.
Rituals, Worship, and Practices
Judaism emphasizes rituals such as circumcision, kosher dietary laws, and Sabbath observance grounded in the Torah, while worship centers around synagogue services and prayer with a strong communal aspect. Christianity primarily practices the sacraments, including baptism and Eucharist, with worship expressed through church services, hymns, and prayer, highlighting the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Religious beliefs in both traditions shape ethical behavior and community identity, though Christianity focuses on salvation through faith in Christ, whereas Judaism emphasizes covenantal relationship and adherence to divine commandments.
Major Holidays and Observances
Judaism centers on major holidays like Passover, Yom Kippur, and Hanukkah, which commemorate historical events, spiritual reflection, and miracles. Christianity's primary observances include Easter, celebrating the resurrection of Jesus, and Christmas, marking His birth, both pivotal to Christian faith. Your understanding of religious beliefs can be enriched by recognizing how these holidays embody distinct theological principles and cultural traditions within each faith.
Contemporary Interfaith Relations
Contemporary interfaith relations between Judaism and Christianity emphasize mutual respect, dialogue, and collaboration on social justice issues, highlighting shared ethical values and historical connections. Efforts such as joint prayer services, educational programs, and interfaith councils foster understanding and reduce religious tensions in diverse societies. These initiatives promote peacebuilding by addressing theological differences while celebrating common spiritual heritage and fostering cooperative community engagement.
Infographic: Judaism vs Christianity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com