High-context relationships rely heavily on implicit communication, shared experiences, and unspoken understandings, while low-context relationships depend on explicit verbal communication and clear, direct messages. Explore this article to understand how these cultural communication styles impact relationship dynamics.
Table of Comparison
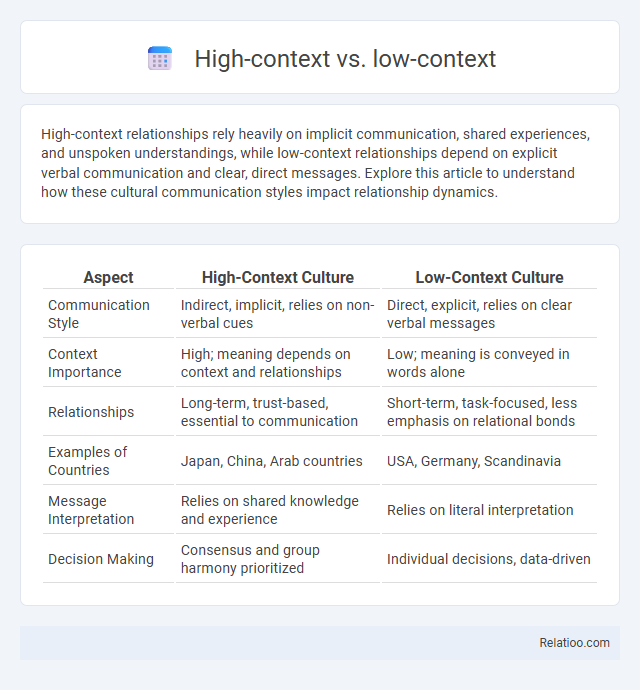
| Aspect | High-Context Culture | Low-Context Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Style | Indirect, implicit, relies on non-verbal cues | Direct, explicit, relies on clear verbal messages |
| Context Importance | High; meaning depends on context and relationships | Low; meaning is conveyed in words alone |
| Relationships | Long-term, trust-based, essential to communication | Short-term, task-focused, less emphasis on relational bonds |
| Examples of Countries | Japan, China, Arab countries | USA, Germany, Scandinavia |
| Message Interpretation | Relies on shared knowledge and experience | Relies on literal interpretation |
| Decision Making | Consensus and group harmony prioritized | Individual decisions, data-driven |
Understanding High-Context and Low-Context Cultures
High-context cultures rely heavily on implicit communication, nonverbal cues, and shared experiences, making emotional expression subtle and indirect. Low-context cultures prioritize explicit verbal communication and clear messages, often favoring direct emotional expression to convey meaning. Understanding these differences enhances cross-cultural communication by aligning emotional expression with cultural expectations in diverse social interactions.
Key Characteristics of High-Context Communication
High-context communication relies heavily on implicit messages, nonverbal cues, and shared cultural understanding, making context essential for interpreting meaning. This style emphasizes relationships, social hierarchies, and group harmony, often using indirect language to convey emotions and intentions subtly. Emotional expression in high-context cultures tends to be restrained, as individuals prioritize maintaining social cohesion over explicit disclosure.
Defining Features of Low-Context Communication
Low-context communication is characterized by explicit, clear, and direct verbal messages where most information is conveyed through words rather than situational context. Your interactions rely heavily on detailed explanations, precise language, and unambiguous expressions to avoid misunderstandings. This style contrasts with high-context communication, which depends on shared experiences, nonverbal cues, and implicit meanings to transmit messages effectively.
Examples of High-Context Cultures Around the World
High-context cultures such as Japan, China, and Arab countries rely heavily on implicit communication, nonverbal cues, and shared experiences to convey meaning. In these societies, understanding context, relationships, and social hierarchy is crucial for interpreting messages accurately. Emotional expression tends to be subtle, as maintaining harmony and avoiding direct confrontation are valued communication strategies.
Typical Low-Context Societies and Their Communication Styles
Typical low-context societies, such as the United States, Germany, and Scandinavia, emphasize direct, explicit communication where clarity and precision are paramount. Your interactions often rely on spoken or written words to convey meaning, minimizing the need for interpreting nonverbal cues or shared cultural knowledge. This communication style contrasts with high-context cultures, focusing on straightforwardness and emotional restraint in emotional expression.
Impact on Business Interactions and Negotiations
High-context cultures rely on implicit communication, shared experiences, and nonverbal cues, which can lead to misunderstandings in low-context business environments that favor direct, explicit communication. Emotional expression varies significantly, with high-context cultures often valuing subtlety and restraint, while low-context cultures may prioritize clarity and openness, impacting negotiation strategies and trust-building. Recognizing these differences enables businesses to tailor their communication styles, improve cross-cultural negotiations, and foster stronger international partnerships.
Navigating Cross-Cultural Misunderstandings
High-context communication relies heavily on implicit messages and shared cultural knowledge, often leading to misunderstandings when interacting with low-context cultures that prioritize explicit and direct language. Emotional expression varies across cultures, with some emphasizing restraint and others promoting open displays, complicating cross-cultural interpretations of intent and sincerity. Navigating these differences requires cultural sensitivity and adaptive communication strategies to bridge gaps in understanding and foster effective intercultural dialogue.
Strategies for Effective Communication Across Contexts
High-context communication relies heavily on implicit messages, cultural cues, and shared understanding, while low-context communication prioritizes explicit, clear, and direct language to convey information effectively. Emotional expression varies significantly, with high-context cultures often using subtle, non-verbal cues to signal feelings, whereas low-context cultures typically favor overt and verbal emotional expressions for clarity. Effective communication across these contexts requires adapting strategies such as active listening, cultural sensitivity, and contextual awareness to interpret underlying meanings and emotions accurately within diverse interactions.
The Role of Context in Digital and Remote Communication
High-context communication relies heavily on implicit messages and shared understanding, which often gets lost in digital and remote environments where nonverbal cues are limited. Low-context communication, emphasizing clear and explicit information, becomes essential in virtual settings to prevent misunderstandings and ensure Your message is accurately conveyed. Emotional expression in remote communication can be challenging, requiring intentional use of tone, emoticons, and timing to compensate for the lack of face-to-face interaction and maintain effective interpersonal connections.
Adapting to Diverse Communication Environments
High-context communication relies heavily on implicit messages and shared cultural understanding, requiring adaptation to nonverbal cues and context clues for effective interaction. Low-context communication emphasizes explicit, direct information where clarity and precision in verbal expression are crucial for diverse environments. Emotional expression varies culturally and impacts how feelings are conveyed and interpreted, necessitating sensitivity to emotional norms to foster clear and respectful communication across different cultural contexts.
Infographic: High-context vs Low-context
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com