German communication in relationships is direct and explicit, emphasizing clarity and honesty, while Japanese communication values indirectness and harmony, often relying on non-verbal cues and context. Explore this article to understand how these contrasting styles shape relationship dynamics and effective cross-cultural interactions.
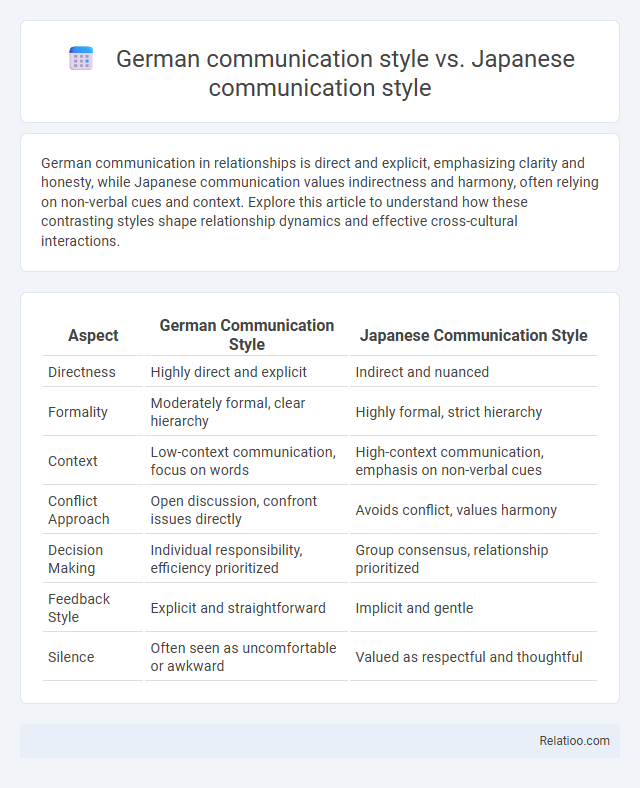
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | German Communication Style | Japanese Communication Style |
|---|---|---|
| Directness | Highly direct and explicit | Indirect and nuanced |
| Formality | Moderately formal, clear hierarchy | Highly formal, strict hierarchy |
| Context | Low-context communication, focus on words | High-context communication, emphasis on non-verbal cues |
| Conflict Approach | Open discussion, confront issues directly | Avoids conflict, values harmony |
| Decision Making | Individual responsibility, efficiency prioritized | Group consensus, relationship prioritized |
| Feedback Style | Explicit and straightforward | Implicit and gentle |
| Silence | Often seen as uncomfortable or awkward | Valued as respectful and thoughtful |
Introduction to German and Japanese Communication Styles
German communication style emphasizes clarity, precision, and directness, often prioritizing logical arguments and explicit verbal expression. Japanese communication style values harmony, indirectness, and context, relying heavily on non-verbal cues and implied meanings to maintain social cohesion. Direct communication contrasts these by favoring straightforwardness and unambiguous language, often minimizing contextual or relational considerations.
Historical and Cultural Influences
German communication style is shaped by a historical emphasis on clarity, efficiency, and formality, reflecting their cultural value for order and precision. Japanese communication style, influenced by centuries of Confucianism and group harmony, prioritizes indirectness, politeness, and context sensitivity to maintain social cohesion. Direct communication, often rooted in Western individualism and Enlightenment ideals, values transparency and explicitness to convey intentions clearly and avoid misunderstandings.
Directness vs. Indirectness
German communication style emphasizes directness, clarity, and precision, often valuing straightforward expressions and explicit messages. Japanese communication style prioritizes indirectness, using context, non-verbal cues, and implicit meanings to maintain harmony and avoid confrontation. Direct communication typically involves unambiguous language and candid exchanges, contrasting with the nuanced and subtle approach found in cultures favoring indirect communication.
Verbal and Nonverbal Communication
German communication style emphasizes directness and clarity, with precise verbal expressions and moderate use of gestures to reinforce messages. Japanese communication style prioritizes indirectness and harmony, relying heavily on context, subtle verbal cues, and nonverbal signals such as silence, bowing, and eye contact to convey meaning. Direct communication involves straightforward verbal messages with explicit language and minimal reliance on nonverbal cues, aiming for unambiguous and efficient exchange of information.
Hierarchical Structures in Communication
German communication style emphasizes clarity and directness within relatively formal hierarchical structures, where roles and ranks guide interaction but open dialogue is encouraged. Japanese communication prioritizes harmony and indirectness, maintaining strict hierarchical respect with subtle cues and non-verbal signals to navigate social status and group dynamics. Direct communication bypasses hierarchical sensitivity, favoring explicit, straightforward exchanges that minimize ambiguity regardless of organizational rank or social position.
Attitudes Toward Silence and Pauses
German communication style often values clarity and precision, treating silence as a moment for reflection or careful word choice, while Japanese communication embraces silence as a meaningful part of interaction, signaling respect, contemplation, and harmony. Direct communication, commonly found in Western contexts, tends to minimize pauses, viewing silence as a potential discomfort or sign of disengagement. Understanding these differing attitudes toward silence and pauses enhances cross-cultural communication by recognizing silence's distinct roles in conveying thoughtfulness, politeness, or urgency.
Approaches to Conflict Resolution
German communication style in conflict resolution emphasizes directness and clarity, favoring explicit expression of issues to reach logical solutions efficiently. Japanese communication style prioritizes harmony and indirectness, often using non-verbal cues and context to avoid confrontation and maintain group cohesion. Direct communication approaches value transparency and straightforward dialogue, promoting quick problem-solving but risking perceived bluntness in cultures that prefer subtlety.
Business Etiquette and Protocol
German communication style in business emphasizes clarity, directness, and precision, ensuring your message is conveyed efficiently without ambiguity. Japanese communication prioritizes harmony, indirectness, and non-verbal cues, requiring you to interpret subtle signals and maintain respect through polite language and formal protocols. Direct communication cuts through formality, favoring straightforwardness and transparency, which can enhance decisiveness but may require sensitivity to cultural contexts to avoid offending business partners.
Importance of Context and Formality
German communication style emphasizes clarity and precision, often favoring direct communication that values explicit messages with less reliance on contextual cues. Japanese communication style prioritizes high-context interactions, where formality and subtle non-verbal signals convey meaning, reflecting cultural respect and group harmony. Understanding these differences helps you navigate varied communication approaches effectively, balancing context sensitivity and formality according to the cultural setting.
Tips for Effective Cross-Cultural Communication
Mastering cross-cultural communication requires understanding that German communication style is characterized by directness and clarity, valuing precision and structured arguments, while Japanese communication style emphasizes indirectness, harmony, and context to avoid conflict. To enhance Your communication effectiveness, adapt by balancing clarity with sensitivity--use straightforward language when dealing with Germans and practice patience, reading between the lines, and non-verbal cues with Japanese counterparts. Recognize these differences and adjust Your message delivery to bridge gaps, ensuring mutual respect and comprehension across diverse cultural settings.
Infographic: German communication style vs Japanese communication style
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com