Elite relationships often benefit from greater access to resources, exclusive social networks, and enhanced opportunities for influence and stability. Explore more about how these differences shape social dynamics and personal connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
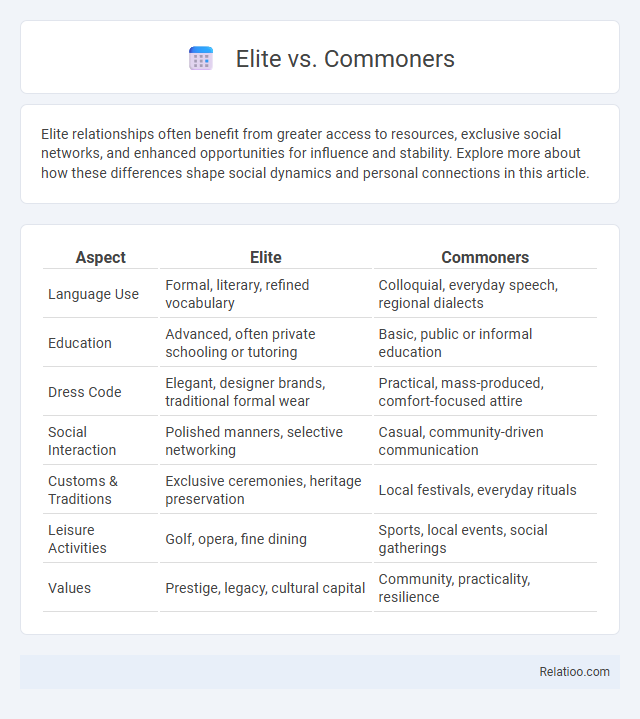
| Aspect | Elite | Commoners |
|---|---|---|
| Language Use | Formal, literary, refined vocabulary | Colloquial, everyday speech, regional dialects |
| Education | Advanced, often private schooling or tutoring | Basic, public or informal education |
| Dress Code | Elegant, designer brands, traditional formal wear | Practical, mass-produced, comfort-focused attire |
| Social Interaction | Polished manners, selective networking | Casual, community-driven communication |
| Customs & Traditions | Exclusive ceremonies, heritage preservation | Local festivals, everyday rituals |
| Leisure Activities | Golf, opera, fine dining | Sports, local events, social gatherings |
| Values | Prestige, legacy, cultural capital | Community, practicality, resilience |
Understanding the Divide: Elite vs. Commoners
The divide between elites and commoners is deeply rooted in differences in wealth, power, and access to resources, which create distinct social hierarchies and opportunities. Elites typically possess control over economic capital, political influence, and cultural institutions, enabling them to maintain and reproduce their status across generations. Commoners, conversely, often face structural barriers that limit social mobility and reinforce class distinctions, perpetuating inequality within society.
Historical Roots of Social Stratification
Historical roots of social stratification reveal deep divisions between elites, commoners, and various classes, shaped by land ownership, wealth accumulation, and political power. Centuries of institutionalized inequality entrenched distinct privileges for elites, while commoners faced limited access to resources and opportunities. Understanding these origins helps you grasp how systemic barriers continue to influence social mobility and class dynamics today.
Economic Disparities: Wealth, Power, and Opportunity
Economic disparities between elites and commoners manifest through concentrated wealth, disproportionate political power, and unequal access to opportunities. Elites often control major financial resources, influencing market dynamics and policy decisions that perpetuate systemic advantages. Commoners face limited mobility due to restricted educational, employment, and capital access, reinforcing class divisions and economic inequality.
Education: Gateways and Barriers
Elite education systems create gateways to prestigious universities and high-paying careers by providing advanced resources, personalized mentorship, and extensive networking opportunities. In contrast, commoners often face barriers such as underfunded schools, limited access to quality teachers, and fewer extracurriculars, which restrict social mobility and perpetuate class disparities. These educational inequities reinforce systemic class differences by shaping access to opportunities and economic outcomes.
Political Influence: Who Shapes Policy?
Elite groups hold disproportionate political influence, often shaping policies through lobbying, campaign financing, and access to decision-makers. Commoners have limited direct influence, primarily engaging through voting, grassroots activism, or local representation. Class differences significantly affect political power, with elites leveraging economic resources to dominate policy agendas while lower classes face structural barriers to participation.
Cultural Distinctions and Social Norms
Elite groups often uphold exclusive cultural traditions and sophisticated social norms that distinguish them from commoners, emphasizing prestige and heritage. Commoners typically adhere to more practical and community-focused customs, reflecting everyday experiences and local values. Your understanding of social stratification deepens by recognizing how cultural distinctions reinforce class differences through rituals, language, and behavioral expectations.
Access to Resources: Privilege vs. Restriction
Access to resources significantly distinguishes elites from commoners, as elites benefit from exclusive privileges such as superior education, healthcare, and networking opportunities, ensuring sustained wealth and influence. Your ability to advance socially and economically often depends on overcoming systemic restrictions faced by commoners, who encounter limited access to quality education, employment, and capital. This disparity entrenches class differences, perpetuating cycles of privilege for elites and barriers for marginalized groups.
Media Representation and Public Perception
Media representation often amplifies class differences by portraying elites as powerful, wealthy, and influential, while commoners are depicted as struggling or aspirational. Public perception is shaped by these portrayals, reinforcing stereotypes and social hierarchies that emphasize wealth and status as markers of success. This dynamic creates a feedback loop where media narratives influence societal attitudes and reinforce class divisions.
Social Mobility: Bridging the Gap
Social mobility remains a critical factor in bridging the gap between elites, commoners, and class differences, as it determines your ability to move beyond preconceived social strata. Access to quality education, economic opportunities, and inclusive policy reforms empower individuals from lower classes to ascend social hierarchies previously dominated by elites. Reducing systemic barriers and fostering equitable resource distribution enhances social cohesion and diminishes the entrenched disparities between social classes.
Prospects for Equality and Inclusion
Elite groups often hold disproportionate access to resources, creating structural barriers that limit your prospects for equality and inclusion. Commoners face systemic challenges in opportunities for education, employment, and political participation, which reinforces class differences over generations. Addressing these disparities requires targeted policies aimed at redistributing wealth, expanding access to quality education, and promoting social mobility to foster a more inclusive society.
Infographic: Elite vs Commoners
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com