Collectivism emphasizes the priority of group goals over individual desires, fostering shared responsibility and social cohesion, while Communitarianism highlights the importance of community values and individual relationships within a social framework. Explore the distinctions and impacts of these philosophies on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
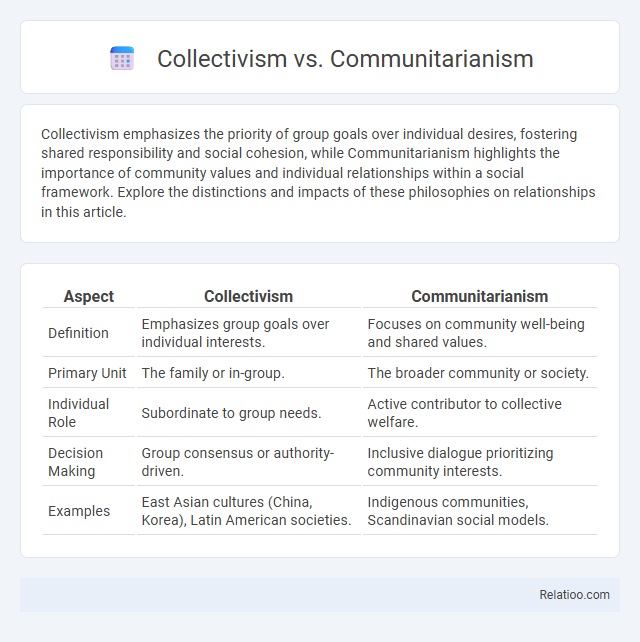
| Aspect | Collectivism | Communitarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emphasizes group goals over individual interests. | Focuses on community well-being and shared values. |
| Primary Unit | The family or in-group. | The broader community or society. |
| Individual Role | Subordinate to group needs. | Active contributor to collective welfare. |
| Decision Making | Group consensus or authority-driven. | Inclusive dialogue prioritizing community interests. |
| Examples | East Asian cultures (China, Korea), Latin American societies. | Indigenous communities, Scandinavian social models. |
Defining Collectivism: Core Principles
Collectivism centers on prioritizing the group's goals and needs over individual desires, emphasizing shared ownership, collective responsibility, and social cohesion. Its core principles include the subordination of personal interests to community welfare, cooperative decision-making, and the belief that the group's well-being ensures individual security. Understanding collectivism helps you appreciate how communal efforts and mutual support drive societal harmony.
Understanding Communitarianism: Key Concepts
Communitarianism emphasizes the role of community values and social cohesion in shaping individual identity, prioritizing the common good over individual interests. Unlike collectivism, which focuses on the collective ownership and control of resources, communitarianism centers on shared responsibilities and moral obligations within a community. Key concepts include social solidarity, participatory citizenship, and balancing individual rights with communal duties.
Historical Origins and Philosophical Roots
Collectivism, rooted in 19th-century socialist and Marxist thought, emphasizes the primacy of the group over the individual, advocating for shared ownership and collective decision-making to achieve social equality. Communitarianism emerged in the late 20th century as a response to liberal individualism, drawing on classical philosophy from Aristotle and Confucius, focusing on the importance of community values, social cohesion, and moral responsibilities within a political society. Both concepts differ from individualism by prioritizing communal welfare but diverge on state intervention, with collectivism often linked to centralized control while communitarianism stresses decentralized community engagement.
Collectivism vs Communitarianism: Main Differences
Collectivism emphasizes the primacy of the group over individual interests, advocating for shared ownership and collective decision-making to achieve common goals. Communitarianism, while also valuing the community, prioritizes the balance between individual rights and social responsibilities, stressing the importance of cultural traditions and social cohesion. Your understanding of these ideologies highlights that collectivism focuses on collective control and uniformity, whereas communitarianism promotes community-based values with respect for individual diversity.
Social Structures and Group Identity
Collectivism emphasizes the primacy of the group over the individual, shaping social structures that prioritize shared goals and collective ownership. Communitarianism balances individual rights with community responsibilities, promoting social cohesion through mutual obligations and shared values within groups. Both frameworks reinforce group identity but differ as collectivism often subordinates personal interests to the collective, while communitarianism seeks harmony between personal autonomy and community well-being.
Individual Rights within Collective Societies
Collectivism emphasizes the subordination of individual rights to the goals of the group, often prioritizing social harmony and shared responsibilities over personal freedoms. Communitarianism balances individual rights with community values, advocating for mutual obligations that support both individual well-being and collective cohesion. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate how individual rights are negotiated and protected within various collective societies.
Community Values in Communitarian Frameworks
Community values in communitarian frameworks emphasize the importance of shared responsibilities and social cohesion, fostering a collective identity that balances individual rights with social obligations. Unlike collectivism, which often prioritizes group goals over individual preferences, communitarianism integrates personal autonomy within the context of communal well-being and ethical norms. This approach cultivates mutual support and participatory decision-making, highlighting the role of cultural traditions and social institutions in sustaining community bonds.
Political Implications and Governance Models
Collectivism emphasizes the primacy of the group over individual interests, often manifesting in centralized governance models that prioritize state control and resource distribution. Communitarianism balances individual rights with community responsibilities, promoting decentralized governance structures that encourage civic participation and social cohesion. These differing frameworks shape political implications, where collectivism may lead to authoritarian tendencies, while communitarianism supports inclusive policies fostering local empowerment and shared values.
Impact on Modern Society and Policy
Collectivism emphasizes the prioritization of group goals over individual interests, shaping policies that foster social welfare systems and wealth redistribution in modern societies. Communitarianism balances individual rights with community responsibilities, influencing policies that promote civic engagement and social cohesion while preserving cultural values. By contrast, authoritarian collectivism often leads to centralized control, affecting modern governance through restrictive political frameworks and limited personal freedoms.
Future Perspectives: Bridging Collectivism and Communitarianism
Future perspectives on collectivism and communitarianism emphasize integrating individual rights with collective responsibilities to create balanced social frameworks. Your understanding of these concepts highlights the potential for collaborative governance models that foster community well-being while respecting personal autonomy. Emerging approaches aim to bridge collectivism's focus on shared ownership with communitarianism's emphasis on social cohesion and cultural identity.
Infographic: Collectivism vs Communitarianism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com