Mediation offers a neutral third party to facilitate communication and resolve disputes amicably, while Collaborative Law involves both parties and their attorneys working together to reach a settlement without litigation. Discover the key differences and benefits of Mediation vs Collaborative Law in this article.
Table of Comparison
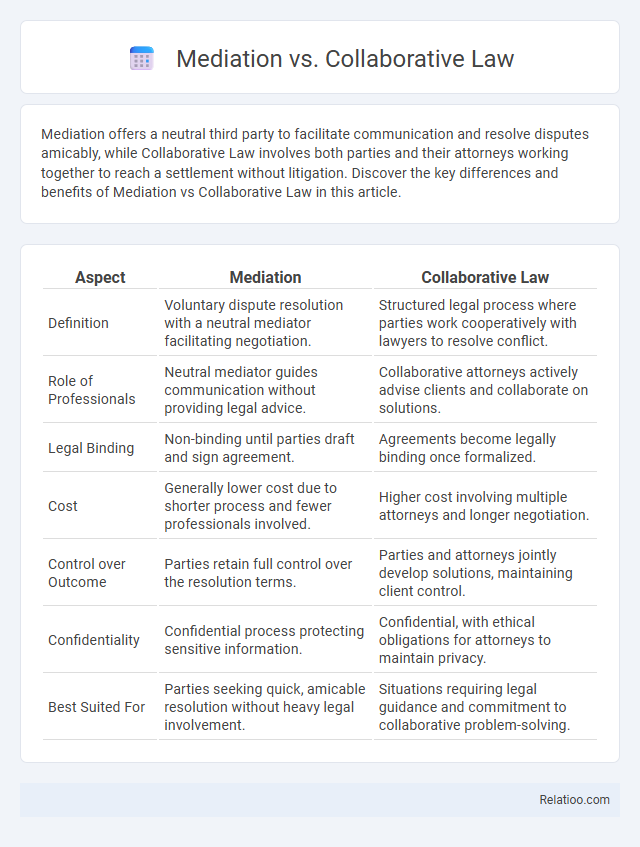
| Aspect | Mediation | Collaborative Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary dispute resolution with a neutral mediator facilitating negotiation. | Structured legal process where parties work cooperatively with lawyers to resolve conflict. |
| Role of Professionals | Neutral mediator guides communication without providing legal advice. | Collaborative attorneys actively advise clients and collaborate on solutions. |
| Legal Binding | Non-binding until parties draft and sign agreement. | Agreements become legally binding once formalized. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to shorter process and fewer professionals involved. | Higher cost involving multiple attorneys and longer negotiation. |
| Control over Outcome | Parties retain full control over the resolution terms. | Parties and attorneys jointly develop solutions, maintaining client control. |
| Confidentiality | Confidential process protecting sensitive information. | Confidential, with ethical obligations for attorneys to maintain privacy. |
| Best Suited For | Parties seeking quick, amicable resolution without heavy legal involvement. | Situations requiring legal guidance and commitment to collaborative problem-solving. |
Understanding Mediation and Collaborative Law
Mediation involves a neutral third party helping disputing parties reach a voluntary agreement by facilitating open communication and negotiation. Collaborative Law is a legal process where both parties and their attorneys commit to resolving conflicts amicably without going to court, emphasizing cooperation and mutual problem-solving. Understanding mediation and collaborative law can empower you to choose a more effective, less adversarial approach to resolving disputes.
Key Principles of Mediation
Mediation is grounded in the key principles of voluntary participation, confidentiality, and neutrality, ensuring that parties maintain control over the resolution process. Collaborative law emphasizes cooperative negotiation with legal counsel, focusing on transparency and mutual respect without court intervention. Unlike collaborative law and unassisted negotiation, mediation centers on a neutral third party who facilitates communication and helps parties explore mutually agreeable solutions without imposing decisions.
Core Concepts in Collaborative Law
Collaborative law centers on cooperative negotiation where both parties and their attorneys commit to resolving disputes without court litigation, emphasizing transparency and mutual respect. Unlike mediation, where a neutral third party facilitates communication and proposes solutions, collaborative law involves direct attorney collaboration to craft customized agreements. Core concepts include a voluntary participation framework, shared problem-solving, and an agreement to withdraw legal representation if the process shifts to litigation.
Differences in Legal Process
Mediation involves a neutral third party facilitating negotiation to help both parties reach a voluntary agreement without imposing a decision, promoting flexibility and informality. Collaborative law requires both parties and their attorneys to commit to resolving disputes through cooperative negotiations, avoiding court intervention unless the process fails. You should consider that mediation is typically less formal and quicker, while collaborative law involves structured legal representation and joint problem-solving before resorting to litigation.
Roles of Lawyers in Mediation vs Collaborative Law
In mediation, lawyers act as advisors, providing clients with legal guidance while the mediator facilitates negotiation without offering legal opinions. In collaborative law, lawyers take a proactive role by jointly working with clients and opposing counsel to reach a mutually acceptable agreement, emphasizing cooperation and transparency throughout the process. The collaborative approach requires lawyers to commit to resolving disputes without resorting to litigation, contrasting with their more advisory capacity in mediation.
Communication Dynamics in Both Approaches
Mediation emphasizes neutral facilitation where You communicate directly with the other party, fostering open dialogue and mutual understanding. Collaborative Law involves cooperative negotiation with each party's attorneys actively participating, promoting transparent and constructive communication rooted in legal collaboration. Both approaches prioritize effective communication dynamics but differ in structure; mediation relies on a facilitator's guidance, while collaborative law integrates legal experts to support resolution.
Confidentiality and Privacy Issues
Mediation prioritizes confidentiality by ensuring discussions and agreements remain private, fostering a safe environment for open communication. Collaborative Law also emphasizes privacy, with parties and their attorneys agreeing to keep information confidential throughout the process, preventing court disclosures. Your choice between these dispute resolution methods depends on how critically you value the protection of sensitive information during conflict resolution.
Cost Comparison: Mediation vs Collaborative Law
Mediation typically offers a more cost-effective resolution by minimizing attorney fees and court expenses, with average costs ranging from $3,000 to $8,000. Collaborative Law involves ongoing legal representation for both parties, resulting in higher expenses that can average between $10,000 and $20,000 or more depending on case complexity. Choosing mediation over collaborative law can lead to significant savings while still providing a structured environment for dispute resolution.
Suitability for Different Types of Disputes
Mediation suits a wide range of disputes including family, commercial, and workplace conflicts by fostering mutual agreement through facilitated negotiation. Collaborative law is particularly effective in high-conflict family law cases like divorce, where parties seek to resolve issues collaboratively without court intervention. Arbitration, distinct from both, is ideal for disputes needing binding decisions, such as contractual or business conflicts, offering a structured resolution process.
Choosing the Right Path for Conflict Resolution
Choosing the right path for conflict resolution depends on your specific situation, goals, and the relationship between parties involved. Mediation involves a neutral third party facilitating communication to reach a mutually acceptable agreement, while Collaborative Law engages attorneys who work cooperatively to resolve disputes without litigation, emphasizing settlement and preserving relationships. Understanding the nuances and benefits of Mediation, Collaborative Law, and Arbitration empowers you to select the most effective approach for a fair and efficient resolution.
Infographic: Mediation vs Collaborative Law
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com