Justice ensures equal treatment under the law, while equity addresses fairness by considering individual circumstances. Explore how balancing justice and equity shapes effective relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
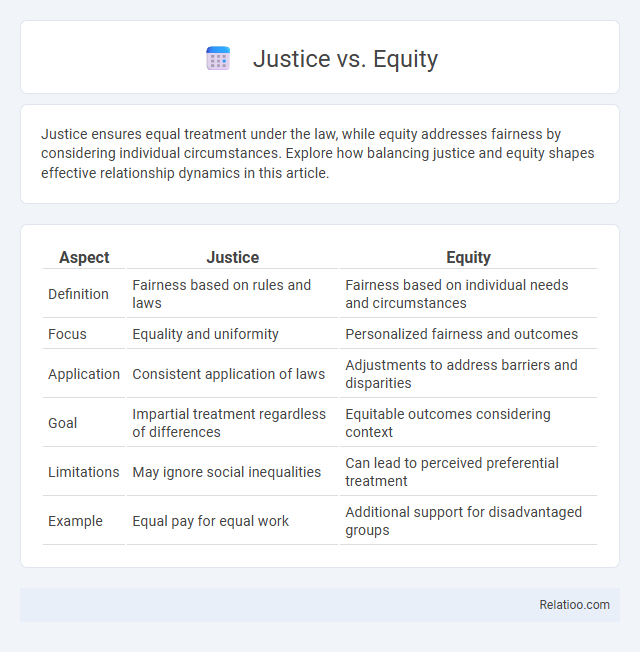
| Aspect | Justice | Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fairness based on rules and laws | Fairness based on individual needs and circumstances |
| Focus | Equality and uniformity | Personalized fairness and outcomes |
| Application | Consistent application of laws | Adjustments to address barriers and disparities |
| Goal | Impartial treatment regardless of differences | Equitable outcomes considering context |
| Limitations | May ignore social inequalities | Can lead to perceived preferential treatment |
| Example | Equal pay for equal work | Additional support for disadvantaged groups |
Understanding Justice: Definitions and Principles
Justice involves the fair and impartial treatment of individuals according to established laws and moral principles, ensuring that rights are protected and wrongs are righted. Equity, in contrast, emphasizes flexibility and fairness by considering individual circumstances to achieve just outcomes when strict application of laws may result in injustice. Understanding these concepts helps you navigate legal systems and ethical dilemmas by recognizing when to apply universal principles of justice or adapt to unique situations with equity.
Defining Equity: Meaning and Core Concepts
Equity involves fairness and impartiality in the distribution of resources, opportunities, and treatment, aiming to address systemic inequalities by considering individual circumstances and needs. Unlike justice, which often refers to the legal system and the administration of laws, equity ensures that outcomes are fair by implementing adjustments that account for historical and social disparities. Core concepts of equity include recognizing structural barriers, promoting inclusivity, and striving for proportional access rather than equal treatment.
Key Differences Between Justice and Equity
Justice ensures the fair treatment of individuals according to established laws and rules, focusing on impartiality and consistency in legal outcomes. Equity, on the other hand, emphasizes fairness by considering unique circumstances to achieve a more personalized and just resolution, often through remedies like injunctions or specific performance. Your understanding of these key differences highlights that while justice applies uniform standards, equity adapts to individual cases to address potential rigidity in the law.
Historical Perspectives on Justice and Equity
Historical perspectives on justice emphasize the consistent application of laws and fairness to all individuals, rooted in ancient philosophies such as those of Aristotle and Confucius. Equity emerged as a complementary principle to justice, addressing rigid legal rules by considering individual circumstances to achieve fairness in unique cases. Your understanding of these concepts is enhanced by recognizing how equity evolved to balance justice where strict legal interpretations fall short, ensuring more personalized and fair outcomes.
Justice in Legal Systems: A Traditional Approach
Justice in legal systems traditionally emphasizes fairness through consistent application of established laws and principles, ensuring that similar cases receive similar treatment. This approach prioritizes impartiality and adherence to precedent, promoting societal order and predictability in legal outcomes. While equity allows flexibility to address unique circumstances, justice maintains the foundational role of legal norms in upholding rights and responsibilities.
The Role of Equity in Social Policy
Equity in social policy emphasizes fairness by addressing systemic inequalities and ensuring resources and opportunities are tailored to individual needs. Unlike justice, which often focuses on uniform application of laws, equity recognizes historical and social contexts that affect marginalized groups. Implementing equity-driven policies leads to more inclusive societies by actively reducing disparities in education, healthcare, and economic access.
Real-World Examples: Justice vs Equity in Practice
Justice in practice ensures laws are applied uniformly, such as equal sentencing for similar crimes regardless of background, while equity addresses individual circumstances, like providing additional resources to underprivileged students to achieve fair educational outcomes. For instance, a court may deliver justice by upholding legal rights equally, whereas equity might involve tailoring remedies to balance disparities, such as affirmative action policies. Real-world differences emerge as justice focuses on fairness through consistent treatment, and equity prioritizes fairness through personalized support.
Ethical Implications of Justice and Equity
Justice ensures fair treatment through impartial application of laws, emphasizing equality in rights and responsibilities. Equity addresses ethical concerns by recognizing individual circumstances and providing tailored solutions to achieve substantive fairness. Ethical implications arise as justice may enforce uniformity, while equity demands empathy and flexibility to correct systemic imbalances and promote moral fairness.
Achieving Social Change: Balancing Justice and Equity
Achieving social change requires balancing justice and equity to address systemic inequalities and ensure fair treatment for all individuals. Justice focuses on upholding laws and rights, while equity emphasizes providing resources and opportunities tailored to diverse needs, promoting fairness beyond uniform application. Your efforts toward social reform must integrate both principles to create lasting, inclusive impact that recognizes historical and social contexts.
Future Directions: Integrating Justice and Equity
Future directions in social policy emphasize integrating justice and equity to create fairer systems that address both legal rights and resource distribution. Advancements in data analytics and AI enable more precise identification of disparities, allowing your organization to tailor interventions that promote systemic fairness. Prioritizing policies that balance procedural justice with equitable outcomes fosters sustainable social progress and inclusive growth.
Infographic: Justice vs Equity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com