Hinduism emphasizes the sacred duty (dharma) and spiritual union in relationships, often linked to karma and reincarnation, while Buddhism focuses on detachment and compassion to overcome suffering within relationships. Explore how these distinct spiritual frameworks shape interpersonal connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
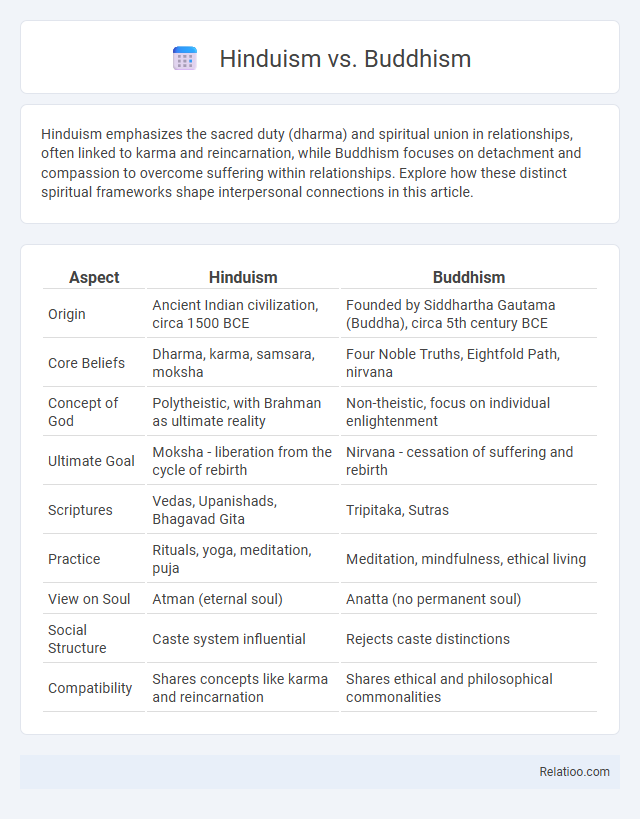
| Aspect | Hinduism | Buddhism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Indian civilization, circa 1500 BCE | Founded by Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha), circa 5th century BCE |
| Core Beliefs | Dharma, karma, samsara, moksha | Four Noble Truths, Eightfold Path, nirvana |
| Concept of God | Polytheistic, with Brahman as ultimate reality | Non-theistic, focus on individual enlightenment |
| Ultimate Goal | Moksha - liberation from the cycle of rebirth | Nirvana - cessation of suffering and rebirth |
| Scriptures | Vedas, Upanishads, Bhagavad Gita | Tripitaka, Sutras |
| Practice | Rituals, yoga, meditation, puja | Meditation, mindfulness, ethical living |
| View on Soul | Atman (eternal soul) | Anatta (no permanent soul) |
| Social Structure | Caste system influential | Rejects caste distinctions |
| Compatibility | Shares concepts like karma and reincarnation | Shares ethical and philosophical commonalities |
Introduction to Hinduism and Buddhism
Hinduism centers on concepts like dharma, karma, and moksha, emphasizing the cycle of rebirth and spiritual liberation through various paths such as devotion, knowledge, and meditation. Buddhism, founded by Siddhartha Gautama, focuses on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, guiding you toward enlightenment by overcoming suffering and attachment. Both religions share beliefs in karma and reincarnation but differ in their views on the self, with Hinduism embracing an eternal soul (atman) and Buddhism rejecting a permanent self (anatman).
Historical Origins and Development
Hinduism, originating over 4,000 years ago in the Indus Valley, is rooted in Vedic traditions emphasizing dharma, karma, and moksha as core beliefs shaping spiritual growth. Buddhism, founded by Siddhartha Gautama in the 6th century BCE, centers on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path to alleviate suffering and attain nirvana. Understanding these historical origins and developmental contrasts helps Your comprehension of their distinct approaches to spirituality and enlightenment.
Core Beliefs and Philosophies
Hinduism centers on the concepts of dharma (duty), karma (action and consequence), and moksha (liberation from the cycle of rebirth), emphasizing the eternal soul (atman) and its unity with the ultimate reality (Brahman). Buddhism focuses on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, teaching the cessation of suffering through mindfulness, ethical conduct, and mental discipline, rejecting a permanent soul in favor of anatta (non-self). Your understanding of these philosophies highlights the contrasting views on self, liberation, and the path to spiritual awakening inherent in each tradition.
Concepts of God and Divinity
Hinduism embraces a diverse pantheon with a supreme reality called Brahman, manifesting in many gods and goddesses representing different aspects of the divine. Buddhism generally rejects the notion of a creator god, emphasizing instead the concept of enlightenment through personal spiritual development and the understanding of impermanence and non-self. Core beliefs in Hinduism center around dharma, karma, and moksha, while Buddhism focuses on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path to achieve Nirvana, illustrating distinct approaches to divinity and ultimate liberation.
Sacred Texts and Scriptures
Hinduism's sacred texts include the Vedas, Upanishads, and Bhagavad Gita, which provide spiritual guidance and philosophical insights. Buddhism centers on the Tripitaka and Mahayana Sutras, emphasizing the teachings of the Buddha and the path to enlightenment. Your understanding of these religions deepens by exploring their core scriptures that shape beliefs and practices uniquely.
Practices, Rituals, and Worship
Hinduism emphasizes diverse practices including puja (worship) at temples, meditation, and rituals like yajna (fire sacrifices) aimed at honoring deities such as Vishnu and Shiva. Buddhism centers on meditation, mindfulness, and monastic disciplines to attain enlightenment, with rituals like chanting and offerings performed in temples or monasteries. Core beliefs in both religions guide worship: Hinduism's dharma and karma influence ritual practices, while Buddhism's Four Noble Truths and Eightfold Path shape meditation and ethical conduct.
Views on Karma and Reincarnation
Hinduism teaches that karma directly influences your dharma and ultimate moksha, emphasizing a continuous cycle of rebirth based on accumulated actions. Buddhism views karma as intentional actions shaping samsara, with reincarnation tied to overcoming suffering through enlightenment and Nirvana. Both religions recognize reincarnation, but Hinduism centers on uniting with Brahman, while Buddhism focuses on liberation from the cycle of rebirth.
Paths to Enlightenment and Liberation
Hinduism emphasizes multiple paths to enlightenment, including Bhakti (devotion), Karma (action), and Jnana (knowledge), aiming for Moksha, the liberation from the cycle of rebirth (samsara). Buddhism focuses on the Noble Eightfold Path, guiding ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom to achieve Nirvana, the cessation of suffering and liberation from samsara. Both religions share the core belief in overcoming ignorance and attachment to attain spiritual freedom but differ in their metaphysical views and practices guiding that liberation.
Influence on Society and Culture
Hinduism's complex rituals, caste system, and festivals deeply shape social hierarchies and cultural norms across South Asia, promoting a diverse yet structured societal framework. Buddhism emphasizes personal enlightenment, compassion, and mindfulness, which foster social harmony and ethical conduct, influencing art, meditation practices, and education worldwide. Understanding these core beliefs allows you to appreciate how both religions continue to impact cultural values, community dynamics, and individual behavior in modern societies.
Key Similarities and Major Differences
Hinduism and Buddhism share core beliefs in karma, dharma, and the cycle of rebirth (samsara), emphasizing ethical living and spiritual progress toward liberation (moksha or nirvana). Major differences include Hinduism's devotion to a supreme god or gods and the caste system, whereas Buddhism rejects the notion of a permanent self (anatman) and caste, focusing instead on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path as a way to end suffering. Both religions originated in India and have deeply influenced East and Southeast Asian cultures, but their practices and doctrines reflect distinct approaches to spirituality and enlightenment.
Infographic: Hinduism vs Buddhism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com