Sarcasm often conveys biting or ironic criticism, while humor aims to entertain and build connection in relationships. Explore how these contrasting communication styles impact relationship dynamics and emotional bonding in this article.
Table of Comparison
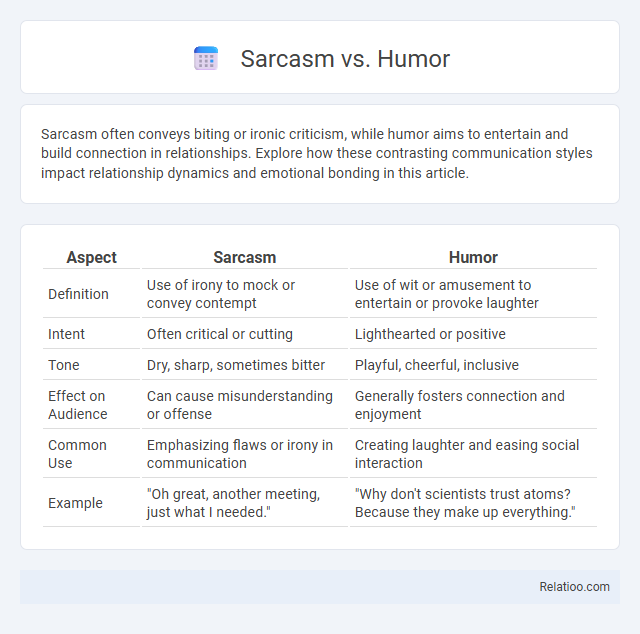
| Aspect | Sarcasm | Humor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of irony to mock or convey contempt | Use of wit or amusement to entertain or provoke laughter |
| Intent | Often critical or cutting | Lighthearted or positive |
| Tone | Dry, sharp, sometimes bitter | Playful, cheerful, inclusive |
| Effect on Audience | Can cause misunderstanding or offense | Generally fosters connection and enjoyment |
| Common Use | Emphasizing flaws or irony in communication | Creating laughter and easing social interaction |
| Example | "Oh great, another meeting, just what I needed." | "Why don't scientists trust atoms? Because they make up everything." |
Understanding Sarcasm: Definition and Examples
Sarcasm involves using irony to mock or convey contempt, often through tone or exaggerated statements that mean the opposite of their literal words. Humor broadly encompasses any content that evokes laughter or amusement, including puns, jokes, and satire, which can be lighthearted or pointed. Your ability to recognize sarcasm relies on understanding context, vocal cues, and social dynamics, distinguishing it from general humor or straightforward statements.
What is Humor? Exploring Its Nuances
Humor is a complex form of communication that involves creating amusement and laughter through various techniques such as wordplay, irony, and surprise. Unlike sarcasm, which often conveys contempt or mockery through sharp remarks, humor aims to entertain and build social bonds by eliciting positive emotions. Understanding your use of humor can enhance social interactions by balancing wit and sensitivity, avoiding misunderstandings often caused by sarcastic expressions.
The Psychological Roots of Sarcasm vs Humor
Sarcasm stems from complex psychological mechanisms involving social cognition and emotional regulation, often used to convey criticism or mockery indirectly, whereas humor relies on cognitive flexibility and positive feelings to create amusement and social bonding. The psychological roots of sarcasm engage theory of mind, requiring the listener to interpret the speaker's underlying intent, which can sometimes lead to misunderstandings or social tension. Humor activates reward centers in the brain, promoting laughter and stress relief, with a focus on playful communication rather than the often sharper, more aggressive edge of sarcasm.
Cultural Differences in Sarcasm and Humor
Cultural differences significantly impact how sarcasm and humor are perceived and expressed, with some cultures valuing indirect, sarcastic remarks while others favor direct, lighthearted humor. Sarcasm often relies on tone and context that may be misunderstood across cultural boundaries, potentially leading to miscommunication or offense. Understanding your audience's cultural background is essential for effectively using sarcasm and humor, ensuring your message is received as intended.
Sarcasm in Everyday Communication
Sarcasm in everyday communication often serves as a nuanced tool to convey irony or criticism while masking true intent, making it distinct from general humor that aims primarily to entertain. Unlike straightforward jokes, sarcasm relies heavily on tone, context, and shared understanding between speakers to be effective and can sometimes lead to misunderstandings or perceived hostility. Recognizing sarcasm in daily conversations enhances interpersonal communication skills by allowing individuals to navigate complex social cues and emotional subtleties more adeptly.
Benefits and Risks of Using Sarcasm
Sarcasm can enhance communication by adding wit and emphasizing points, fostering social bonding and creative expression when interpreted correctly. However, it carries risks such as misunderstandings, offending others, and damaging relationships due to its often ambiguous tone and potential to be perceived as hostility. Balancing sarcasm with clear context and audience awareness is crucial to harnessing its benefits while minimizing harm in social and professional interactions.
The Positive Impact of Humor on Relationships
Humor strengthens relationships by fostering emotional bonds and reducing stress, creating a positive atmosphere where individuals feel more connected and understood. Unlike sarcasm, which can sometimes create misunderstandings or hurt feelings due to its often ambiguous tone, humor promotes clear, shared enjoyment and trust. The positive impact of humor in relationships includes enhanced communication, increased empathy, and greater resilience during conflicts.
Sarcasm vs Humor: Effects on Mental Health
Sarcasm often involves a sharp, sometimes cutting tone that can lead to misunderstandings and increased stress, impacting mental health negatively by fostering feelings of confusion or hostility. Humor, in contrast, generally promotes positive emotions, social bonding, and stress relief, contributing to improved psychological well-being and resilience. Research indicates that while humor enhances mental health by reducing anxiety and depression, excessive sarcasm may exacerbate emotional distress and social isolation.
Decoding Sarcasm: Tips for Recognizing Tone
Decoding sarcasm involves understanding subtle vocal cues, such as exaggerated intonation and pauses, which differentiate it from straightforward humor. Recognizing tone requires attention to context, facial expressions, and discrepancies between spoken words and underlying meaning. Developing these skills enhances the ability to distinguish sarcasm from humor and literal speech in communication.
Choosing the Right Context: When to Use Humor or Sarcasm
Choosing the right context for humor or sarcasm depends on understanding your audience's sensitivity and the situation's tone. Humor fosters positive interactions and lightens moods, while sarcasm can create sharp wit but risks offending if misapplied. Your awareness of these nuances ensures effective communication without unintended misunderstandings.
Infographic: Sarcasm vs Humor
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com