Manipulative communication involves controlling or influencing others through deceit, while passive-aggressive communication expresses negative feelings indirectly through subtle resistance or sarcasm. Discover effective strategies to identify and address these harmful behaviors in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
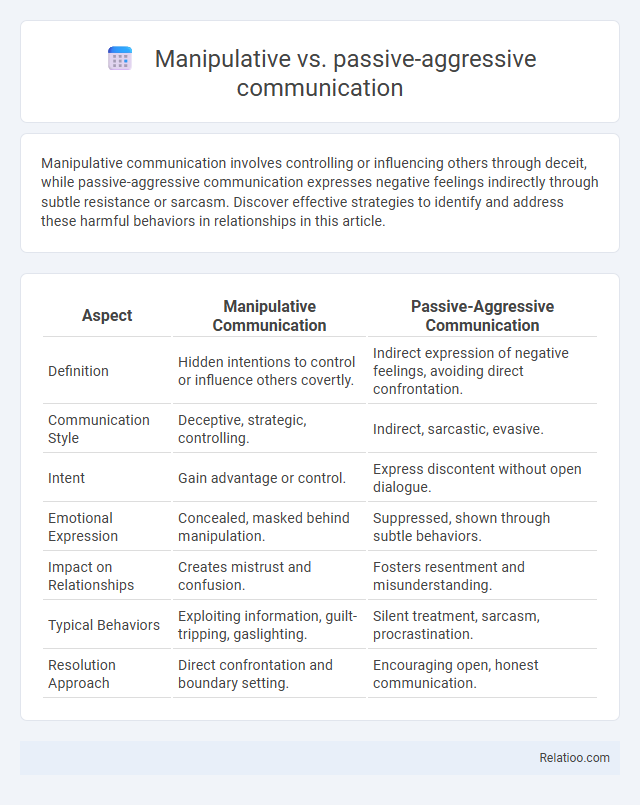
| Aspect | Manipulative Communication | Passive-Aggressive Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hidden intentions to control or influence others covertly. | Indirect expression of negative feelings, avoiding direct confrontation. |
| Communication Style | Deceptive, strategic, controlling. | Indirect, sarcastic, evasive. |
| Intent | Gain advantage or control. | Express discontent without open dialogue. |
| Emotional Expression | Concealed, masked behind manipulation. | Suppressed, shown through subtle behaviors. |
| Impact on Relationships | Creates mistrust and confusion. | Fosters resentment and misunderstanding. |
| Typical Behaviors | Exploiting information, guilt-tripping, gaslighting. | Silent treatment, sarcasm, procrastination. |
| Resolution Approach | Direct confrontation and boundary setting. | Encouraging open, honest communication. |
Understanding Manipulative Communication
Manipulative communication involves influencing others through deceptive, controlling, or exploitative tactics to achieve personal goals, often disregarding others' feelings and autonomy. Understanding manipulative communication helps you recognize behaviors like guilt-tripping, gaslighting, or hidden agendas that mask true intentions. Identifying these patterns allows for healthier interactions and boundaries compared to passive or passive-aggressive communication styles.
Defining Passive-Aggressive Communication
Passive-aggressive communication involves expressing negative feelings indirectly rather than openly addressing them, often through sarcasm, procrastination, or subtle sabotage. This style contrasts with manipulative communication, which aims to control or influence others covertly, and direct confrontation approaches. Understanding passive-aggressive communication is crucial for identifying hidden conflicts and improving interpersonal dynamics in personal and professional relationships.
Key Differences Between Manipulative and Passive-Aggressive Styles
Manipulative communication involves covert control and exploitation to influence others for personal gain, characterized by strategic deception and calculated interactions. Passive-aggressive communication expresses negative feelings indirectly through subtle resistance, sarcasm, or procrastination, often masking true emotions behind a facade of compliance. Key differences lie in intent and expression: manipulation targets control with hidden agendas, while passive-aggressiveness conveys displeasure through indirect, nonconfrontational behaviors.
Common Traits of Manipulative Communicators
Manipulative communicators often use deceit and exploitation to control or influence others, disguising their true intentions behind charm or false concern. Your interactions with these individuals may involve guilt-tripping, gaslighting, or strategic ambiguity to gain power without direct confrontation. Common traits include inconsistency between words and actions, emotional exploitation, and a persistent refusal to take responsibility for negative outcomes.
Recognizable Signs of Passive-Aggressive Behavior
Recognizable signs of passive-aggressive behavior include subtle sabotage, such as procrastination or intentional inefficiency, silent treatment, and indirect expressions of anger like sarcasm or backhanded compliments. You may notice patterns where individuals avoid direct confrontation but communicate hostility through nonverbal cues, chronic forgetfulness, or deliberate resistance to requests. Understanding these behaviors helps identify passive-aggressive communication distinct from manipulative tactics, which are often more overt in controlling or influencing others.
Psychological Impact on Relationships
Manipulative communication often erodes trust by fostering confusion and resentment, leading to power imbalances in relationships. Passive-aggressive communication creates indirect hostility and unresolved conflicts, causing emotional distance and frustration between individuals. Both styles damage psychological safety, reducing intimacy and mutual respect essential for healthy interpersonal dynamics.
Real-Life Examples: Manipulative vs Passive-Aggressive
Manipulative communication involves tactics like guilt-tripping or deceit to control others, such as a coworker pretending to need help to avoid tasks, while passive-aggressive communication manifests through indirect resistance, like giving silent treatment or sarcastic remarks after being asked to complete a project. Your ability to recognize these behaviors in real life, such as a friend who subtly criticizes your choices versus one who openly demands favors under false pretenses, helps maintain healthy boundaries and effective interactions. Understanding these differences promotes clearer communication and reduces emotional misunderstandings.
Consequences in the Workplace and Personal Life
Manipulative communication often leads to mistrust and damaged relationships in both workplace and personal life, resulting in reduced collaboration and increased conflict. Passive-aggressive communication creates confusion and frustration, as indirect hostility undermines clear dialogue and problem-solving efforts. Both styles contribute to unhealthy environments, decreased productivity, and emotional stress for all parties involved.
Strategies for Effective and Assertive Communication
Manipulative communication often involves covert tactics to control or influence others, while passive-aggressive communication expresses negative feelings indirectly, causing ambiguity and frustration. Your strategy for effective and assertive communication should focus on clear, honest expression of thoughts and needs, using "I" statements to own your feelings without blaming others. Establishing boundaries and practicing active listening helps maintain respect and reduces misunderstandings in any interaction.
Transforming Unhealthy Patterns for Better Interaction
Manipulative communication exploits others' emotions or vulnerabilities to control outcomes, while passive-aggressive communication masks dissent through indirect resistance and subtle sabotage. Transforming these unhealthy patterns involves fostering assertiveness and emotional intelligence to encourage honest, respectful exchanges. Developing clear boundaries and promoting transparent dialogue enhances trust and mitigates conflict, leading to healthier interpersonal interactions.
Infographic: Manipulative vs Passive-aggressive communication
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com