False agreement occurs when parties incorrectly assume shared understanding, while consensus requires genuine, mutual agreement based on clear communication and aligned expectations. Explore this article to learn how distinguishing between false agreement and true consensus can strengthen your relationships.
Table of Comparison
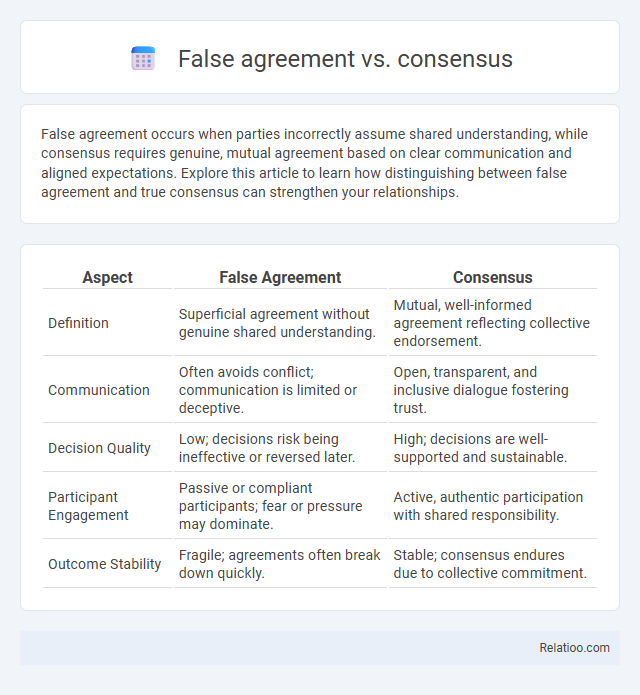
| Aspect | False Agreement | Consensus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Superficial agreement without genuine shared understanding. | Mutual, well-informed agreement reflecting collective endorsement. |
| Communication | Often avoids conflict; communication is limited or deceptive. | Open, transparent, and inclusive dialogue fostering trust. |
| Decision Quality | Low; decisions risk being ineffective or reversed later. | High; decisions are well-supported and sustainable. |
| Participant Engagement | Passive or compliant participants; fear or pressure may dominate. | Active, authentic participation with shared responsibility. |
| Outcome Stability | Fragile; agreements often break down quickly. | Stable; consensus endures due to collective commitment. |
Understanding False Agreement
False agreement occurs when individuals mistakenly believe their opinion or understanding aligns with a group's consensus despite actual disagreement, leading to inaccurate perceptions of unanimity. Unlike true consensus, which reflects genuine collective agreement, false agreement results from social pressures or miscommunication that obscure dissenting views. Recognizing false agreement is crucial for fostering authentic dialogue and making informed decisions based on accurate representations of group opinions.
Defining True Consensus
True consensus occurs when all participants genuinely agree on a decision or opinion, reflecting authentic shared understanding without coercion or misunderstanding. False agreement happens when individuals outwardly agree due to pressure, misunderstanding, or desire to conform but internally dissent. Your aim should be to foster true consensus by encouraging open communication and verifying all viewpoints are honestly represented rather than settling for superficial or false agreement.
Key Differences Between False Agreement and Consensus
False agreement occurs when parties superficially express agreement without genuine consensus, often leading to misunderstandings or conflicts later. Consensus represents a true mutual understanding where all involved actively agree on the decision or viewpoint. Key differences include the authenticity of agreement, with false agreement masking disagreement, while consensus reflects collective commitment.
Causes of False Agreement in Groups
False agreement in groups often arises from social pressure, conformity bias, and overestimation of shared beliefs, leading individuals to mistakenly perceive unanimity. Groupthink and desire for harmony suppress dissenting opinions, causing members to align with a perceived majority despite private disagreement. Cognitive biases such as pluralistic ignorance further reinforce false consensus by obscuring true individual views within the group dynamic.
The Dangers of Mistaking False Agreement for Consensus
Mistaking false agreement for consensus can severely undermine decision-making processes and organizational trust. False agreement occurs when individuals pretend to agree due to social pressure or fear of conflict, whereas consensus represents genuine, collective support and alignment on a decision. You risk flawed outcomes, unresolved conflicts, and reduced team cohesion if false agreement is mistaken for true consensus, making it crucial to foster transparent communication and validate genuine agreement in group settings.
Psychological Factors Behind False Agreement
False agreement occurs when individuals mistakenly believe others share their opinions or behaviors, often influenced by cognitive biases like the false consensus effect. Psychological factors such as social identity, need for validation, and conformity pressure drive this misperception, causing you to overestimate agreement within your social group. Understanding these influences can help you distinguish true consensus from false agreement, improving interpersonal communication and decision-making accuracy.
Strategies to Identify False Agreement
Strategies to identify false agreement involve carefully analyzing communication patterns for discrepancies between vocal affirmations and actual behaviors or decisions. False agreement often arises when individuals say "yes" to maintain harmony but secretly disagree, making it essential to seek explicit confirmation and observe nonverbal cues. You can prevent misunderstandings by fostering an environment that encourages open dialogue and verifying consensus through clear, shared expectations.
Building Genuine Consensus: Best Practices
Building genuine consensus involves facilitating open dialogue where all participants' perspectives are acknowledged and integrated, preventing false agreement characterized by superficial or coerced conformity. Effective consensus requires active listening, transparent communication, and a shared commitment to collective goals, ensuring Your team members feel heard and valued. Employing techniques such as structured decision-making and iterative feedback helps distinguish true agreement from pseudo-consensus, enhancing trust and long-term collaboration.
Real-World Examples of False Agreement vs Consensus
False agreement occurs when parties mistakenly believe they share the same opinion, as seen in groupthink scenarios in corporate board meetings where dissenting views are suppressed. Consensus is a genuine, collective decision-making process exemplified by successful environmental policy agreements like the Paris Climate Accord, where all participants actively contribute to a shared solution. Real-world cases such as the Challenger disaster highlight false agreement, where engineers' concerns were ignored, contrasting with consensus-driven decisions in Switzerland's direct democracy system fostering transparent policy development.
Enhancing Decision-Making Through Authentic Consensus
False agreement undermines decision quality by masking true opinions, leading to groupthink and poor outcomes. Consensus fosters authentic collaboration where diverse views are genuinely integrated, enhancing collective decision-making strength. Authentic consensus ensures decisions reflect true agreement, reducing errors and promoting sustainable, effective solutions.
Infographic: False agreement vs Consensus
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com