Direct communication in relationships involves clear, straightforward expressions of thoughts and feelings, fostering transparency and reducing misunderstandings. Indirect communication relies on hints and nonverbal cues, which can preserve harmony but may lead to ambiguity; explore this article to understand how to balance both for healthier connections.
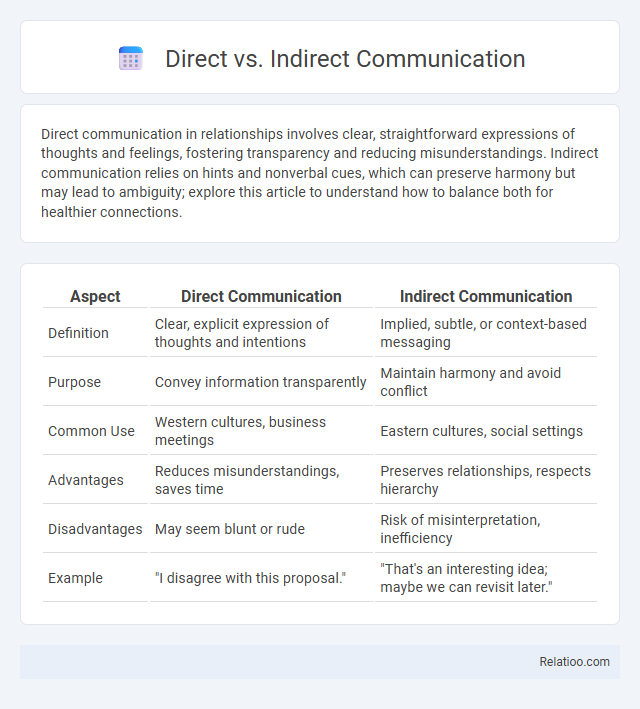
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Direct Communication | Indirect Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clear, explicit expression of thoughts and intentions | Implied, subtle, or context-based messaging |
| Purpose | Convey information transparently | Maintain harmony and avoid conflict |
| Common Use | Western cultures, business meetings | Eastern cultures, social settings |
| Advantages | Reduces misunderstandings, saves time | Preserves relationships, respects hierarchy |
| Disadvantages | May seem blunt or rude | Risk of misinterpretation, inefficiency |
| Example | "I disagree with this proposal." | "That's an interesting idea; maybe we can revisit later." |
Introduction to Direct and Indirect Communication
Direct communication involves explicitly expressing thoughts and feelings through clear, straightforward language, which enhances clarity and reduces misunderstandings in interpersonal interactions. Indirect communication relies on subtlety, context, and non-verbal cues to convey messages, often influenced by cultural norms prioritizing harmony and saving face. Understanding the differences between these styles is crucial for navigating social boundaries and fostering effective cross-cultural communication.
Defining Direct Communication
Direct communication involves explicitly expressing thoughts, feelings, and intentions without ambiguity, ensuring the message is clear and straightforward. It contrasts with indirect communication, where messages are conveyed through hints, context, or nonverbal cues, often to preserve harmony or avoid confrontation. Boundaries in communication refer to the limits set to protect personal space and emotional well-being, influencing how direct or indirect approaches are employed in different cultural or interpersonal contexts.
Understanding Indirect Communication
Indirect communication relies on implicit messages, contextual cues, and nonverbal signals to convey meaning, often prioritizing harmony and relationship preservation over explicit clarity. Understanding indirect communication requires interpreting tone, body language, and situational factors to grasp the underlying intent behind the words. This communication style contrasts sharply with direct communication, which uses straightforward and unambiguous language to express thoughts and boundaries clearly.
Key Differences: Direct vs Indirect Communication
Direct communication involves clear, explicit messages where intentions and expectations are straightforward, making it efficient for delivering precise information. Indirect communication relies on context, tone, and non-verbal cues to convey meaning, often prioritizing harmony and relationship preservation over clarity. Your understanding of these key differences helps navigate social interactions by choosing the appropriate style based on cultural norms and situational boundaries.
Cultural Influences on Communication Styles
Direct communication involves explicit verbal expression of thoughts and feelings, commonly found in low-context cultures such as the United States and Germany, where clarity and transparency are prioritized. Indirect communication, prevalent in high-context cultures like Japan and China, relies on implicit messages, non-verbal cues, and context to convey meaning, emphasizing harmony and saving face. Cultural influences shape communication boundaries, determining how openly individuals share information and navigate social interactions based on values like individualism or collectivism, power distance, and uncertainty avoidance.
Advantages of Direct Communication
Direct communication enhances clarity by reducing misunderstandings and ensuring your message is conveyed precisely. It fosters efficiency in decision-making and problem-solving by allowing quick exchange of essential information. Maintaining clear boundaries through direct communication also promotes respect and minimizes conflicts in personal and professional relationships.
Benefits of Indirect Communication
Indirect communication fosters a deeper understanding of context and emotions, allowing you to navigate sensitive topics with greater diplomacy and minimize conflict. This approach enhances relationship-building by respecting cultural nuances and unspoken social rules, making interactions more harmonious. It also encourages active listening and empathy, improving overall communication effectiveness in both personal and professional settings.
Challenges and Misunderstandings
Direct communication conveys messages explicitly, reducing the risk of misinterpretation but may cause discomfort or conflict in cultures valuing harmony. Indirect communication relies on context and nonverbal cues, often leading to misunderstandings in multicultural settings where explicit clarity is expected. Boundaries in communication, when unclear or ignored, can exacerbate these challenges by blurring personal limits and causing confusion about intentions or responses.
Choosing the Right Communication Style
Choosing the right communication style involves understanding the context and cultural preferences between direct and indirect communication. Direct communication prioritizes clarity and explicitness, ideal for situations requiring straightforward information exchange or decision-making. Indirect communication, often used in high-context cultures, respects social harmony and relies on implicit messages, which helps maintain boundaries and avoid confrontation.
Tips for Bridging Communication Gaps
Direct communication emphasizes clear, explicit messages, while indirect communication relies on context and subtle cues, creating challenges in understanding boundaries between speakers. To bridge these communication gaps effectively, you should practice active listening, clarify ambiguous statements by asking open-ended questions, and respect cultural or personal preferences that influence communication styles. Establishing mutual respect and adapting your approach to fit the preferred style fosters stronger connections and minimizes misunderstandings across diverse interactions.
Infographic: Direct vs Indirect Communication
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com