Indirect communication conveys messages through hints and non-verbal cues, often to avoid confrontation or preserve harmony. Passive communication involves withholding opinions or feelings, leading to misunderstandings and unresolved conflicts; explore these communication styles in relationships further in this article.
Table of Comparison
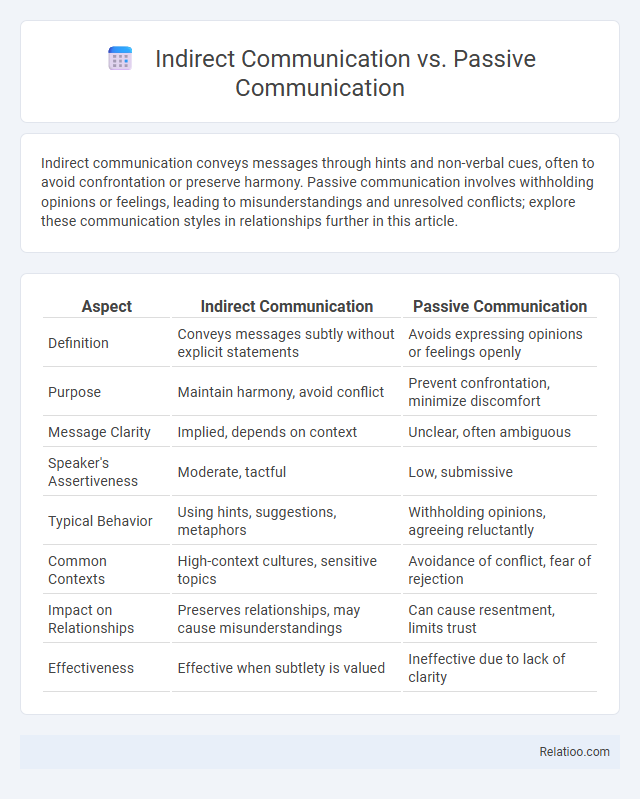
| Aspect | Indirect Communication | Passive Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conveys messages subtly without explicit statements | Avoids expressing opinions or feelings openly |
| Purpose | Maintain harmony, avoid conflict | Prevent confrontation, minimize discomfort |
| Message Clarity | Implied, depends on context | Unclear, often ambiguous |
| Speaker's Assertiveness | Moderate, tactful | Low, submissive |
| Typical Behavior | Using hints, suggestions, metaphors | Withholding opinions, agreeing reluctantly |
| Common Contexts | High-context cultures, sensitive topics | Avoidance of conflict, fear of rejection |
| Impact on Relationships | Preserves relationships, may cause misunderstandings | Can cause resentment, limits trust |
| Effectiveness | Effective when subtlety is valued | Ineffective due to lack of clarity |
Introduction to Communication Styles
Indirect communication involves conveying messages subtly, often relying on context and nonverbal cues, while passive communication typically reflects avoidance of expressing one's opinions or needs openly. Indirectness refers to the broader tendency to hint or imply rather than state directly, influencing how messages are interpreted in various cultural or social contexts. Understanding these communication styles helps you navigate interpersonal interactions more effectively by recognizing when clarity or sensitivity is required.
Defining Indirect Communication
Indirect communication involves conveying messages subtly or non-explicitly to avoid confrontation or maintain harmony, often relying on context and tone rather than direct statements. It differs from passive communication, which reflects a reluctance to express opinions or needs openly, sometimes leading to misunderstandings or unmet needs. Your understanding of indirect communication can enhance interpersonal dynamics by recognizing how implicit cues shape interactions beyond words alone.
What is Passive Communication?
Passive communication involves expressing your thoughts and feelings in a way that avoids direct confrontation or assertiveness, often leading to misunderstanding or unspoken frustration. Unlike indirect communication, which can use subtle hints or context to convey meaning, passive communication typically results in withholding opinions or allowing others to dominate conversations. Understanding passive communication can help you recognize when your needs are being overlooked and encourage healthier, more assertive dialogue.
Key Differences Between Indirect and Passive Communication
Indirect communication involves conveying messages in a subtle or roundabout way, often relying on context and non-verbal cues, whereas passive communication is characterized by a reluctance to express thoughts or feelings openly, leading to avoidance or silence. Key differences lie in the intent and expression: indirect communication aims to maintain harmony by softening requests or criticism, while passive communication reflects a lack of assertiveness and self-expression. Understanding these distinctions helps you improve interpersonal skills and fosters clearer, more effective exchanges.
Common Examples of Indirect Communication
Common examples of indirect communication include using hints or suggestions instead of direct statements, relying on tone of voice, body language, and facial expressions to convey messages, and employing storytelling or metaphors to imply meaning without explicitly stating it. In passive communication, individuals often avoid expressing their true feelings or opinions, leading to vague or unclear messages. Your ability to recognize these patterns helps in interpreting underlying intentions and navigating social interactions more effectively.
Typical Scenarios for Passive Communication
Passive communication typically occurs in scenarios where You avoid expressing thoughts or feelings directly, often to maintain harmony or prevent conflict. For example, in workplace meetings where expressing disagreement might jeopardize relationships or in family settings where criticism is softened to avoid hurting feelings. This communication style results in subtle cues and non-verbal signals that require careful interpretation to understand the underlying message.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Indirect Communication
Indirect communication involves conveying messages subtly, often relying on context and nonverbal cues, which can prevent conflicts and maintain harmony in sensitive situations. However, this style may lead to misunderstandings or ambiguity, as the intended message is not explicit, potentially causing frustration or confusion. Your choice to use indirect communication should balance the need for tact with the clarity required to ensure effective interaction.
Pros and Cons of Passive Communication
Passive communication often avoids direct confrontation, fostering harmony and minimizing immediate conflict in interpersonal interactions. However, it can lead to misunderstandings, suppressed emotions, and unmet needs due to lack of clarity and assertiveness. Over time, passive communication may reduce personal empowerment and hinder effective problem-solving in both personal and professional settings.
Cultural Impacts on Communication Styles
Indirect communication relies on subtle cues and context, often favored in cultures valuing harmony and relational preservation, while passive communication involves withholding direct expression to avoid conflict. Cultural impacts shape these styles significantly; for example, many East Asian and Middle Eastern societies emphasize indirectness to maintain social cohesion, whereas Western cultures may favor more direct approaches. Understanding these distinctions enhances your ability to navigate cross-cultural interactions effectively and interpret messages with cultural sensitivity.
Choosing the Right Communication Approach
Choosing the right communication approach depends on understanding the nuances between indirect, passive communication, and indirectness. Indirect communication conveys messages subtly to maintain harmony, while passive communication often avoids expressing personal needs or opinions, which may lead to misunderstandings. Your effectiveness improves when you tailor your style to context, balancing clarity with tact to ensure your message resonates without causing unintended offense.
Infographic: Indirect vs Passive Communication
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com