Allegiance involves a deep, voluntary commitment to shared values and goals, whereas obedience is the act of following orders or rules often without personal agreement. Explore the nuances between allegiance and obedience to understand how they shape relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
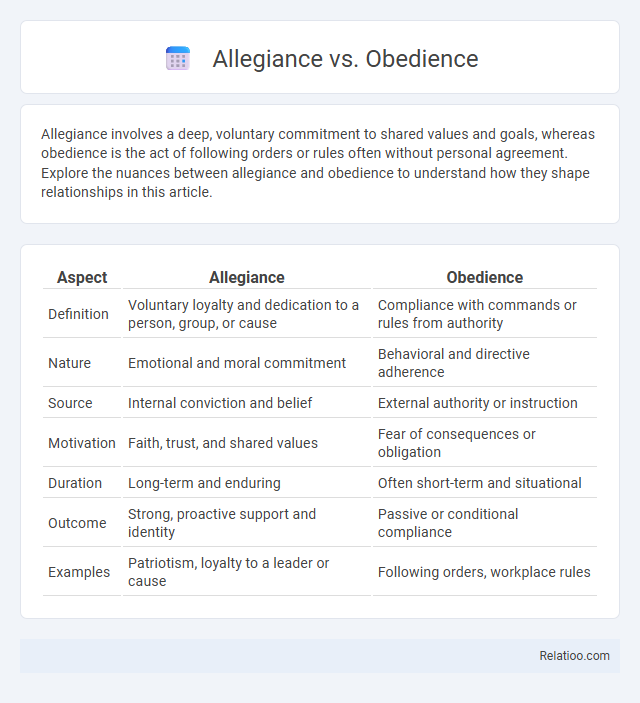
| Aspect | Allegiance | Obedience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary loyalty and dedication to a person, group, or cause | Compliance with commands or rules from authority |
| Nature | Emotional and moral commitment | Behavioral and directive adherence |
| Source | Internal conviction and belief | External authority or instruction |
| Motivation | Faith, trust, and shared values | Fear of consequences or obligation |
| Duration | Long-term and enduring | Often short-term and situational |
| Outcome | Strong, proactive support and identity | Passive or conditional compliance |
| Examples | Patriotism, loyalty to a leader or cause | Following orders, workplace rules |
Defining Allegiance and Obedience
Allegiance refers to your loyalty and commitment to a person, group, or cause, often reflecting a deep, enduring bond. Obedience involves following orders or rules imposed by an authority, emphasizing compliance rather than emotional loyalty. Understanding the distinction clarifies how allegiance embodies voluntary dedication, while obedience entails enforced adherence to directives.
Historical Perspectives on Allegiance and Obedience
Historical perspectives on allegiance emphasize loyalty to a sovereign or nation as a foundational social contract, often rooted in feudal or monarchical systems where subjects pledged fidelity to rulers. Obedience, by contrast, is frequently examined through socio-psychological lenses, highlighting compliance with authority as essential to maintaining order and governance in both authoritarian and democratic contexts. The distinction between allegiance and obedience reveals nuanced dynamics in power relationships, with allegiance reflecting a voluntary and enduring commitment, while obedience involves immediate responsiveness to commands.
Psychological Foundations of Loyalty and Compliance
Allegiance is a deep-rooted psychological commitment to a group or cause, driven by identity and shared values, whereas obedience emphasizes compliance with authority often motivated by external pressures or fear of consequences. Psychological foundations of loyalty involve intrinsic motivation, emotional bonding, and social identity, fostering voluntary allegiance, while obedience reflects learned behavior shaped by socialization and authority legitimacy. Understanding these distinctions clarifies how loyalty sustains group cohesion and obedience maintains social order through hierarchical structures.
Differences Between Allegiance and Obedience
Allegiance represents a deep loyalty or commitment to a person, group, or cause, often rooted in shared values or identity, while obedience involves following orders or rules regardless of personal beliefs. You demonstrate allegiance through voluntary support and dedication, whereas obedience requires compliance, sometimes even without understanding or agreement. Understanding these differences is crucial for distinguishing between genuine loyalty and mere adherence to authority.
Allegiance in Social and Political Contexts
Allegiance in social and political contexts represents a committed loyalty to a nation, group, or cause, often signifying a deeper, voluntary bond than mere obedience. Your sense of allegiance shapes civic identity and influences participation in democratic processes, reflecting shared values and collective goals. Unlike obedience, which demands compliance with authority, allegiance embodies a proactive dedication that strengthens social cohesion and political stability.
Obedience in Hierarchical Structures
Obedience in hierarchical structures ensures compliance with authority, facilitating order and discipline within organizations. Unlike allegiance, which denotes loyalty and commitment to a person or cause, obedience emphasizes the execution of commands regardless of personal agreement. This dynamic is critical for maintaining control and achieving coordinated action in military, corporate, and institutional settings.
The Role of Morality in Allegiance and Obedience
Morality plays a critical role in shaping allegiance and obedience, as allegiance involves a voluntary commitment to a group or cause based on shared ethical values, whereas obedience often requires compliance with authority regardless of personal moral judgments. Your moral framework influences how you distinguish between rightful allegiance, which aligns with ethical principles, and blind obedience, which may lead to harmful actions. Understanding this distinction helps ensure that loyalty supports just causes without compromising your integrity.
Case Studies: Allegiance vs Obedience in Action
Case studies of allegiance versus obedience reveal that allegiance involves a deep-seated loyalty to a group or cause, whereas obedience often reflects compliance with authority. In scenarios where individuals face moral dilemmas, your allegiance may prompt resistance against unjust orders, highlighting the conflict between personal values and imposed obedience. Understanding these dynamics through real-world examples helps clarify how allegiance can drive ethical decision-making beyond mere obedience.
Consequences of Blind Obedience and Misplaced Allegiance
Blind obedience often results in unethical decisions and harmful consequences due to a lack of critical thinking, putting Your values and judgment at risk. Misplaced allegiance can lead to loyalty towards harmful individuals or groups, causing personal and social harm, while true allegiance demands a thoughtful commitment grounded in integrity. Understanding the distinction between allegiance and obedience helps prevent exploitation and fosters responsible, ethical behavior.
Fostering Healthy Allegiance Over Enforced Obedience
Fostering healthy allegiance means cultivating genuine loyalty and commitment rather than relying on enforced obedience, which often breeds resentment and disengagement. Your leadership approach should emphasize building trust, mutual respect, and shared values to inspire allegiance that motivates voluntary cooperation and long-term dedication. Prioritizing allegiance enhances organizational cohesion and performance by aligning individual purpose with collective goals.
Infographic: Allegiance vs Obedience
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com