Allegiance signifies a broader, voluntary loyalty to a group or cause, while fealty specifically denotes a sworn, personal loyalty often tied to a hierarchical obligation. Explore the subtle distinctions and historical contexts of allegiance versus fealty in this article.
Table of Comparison
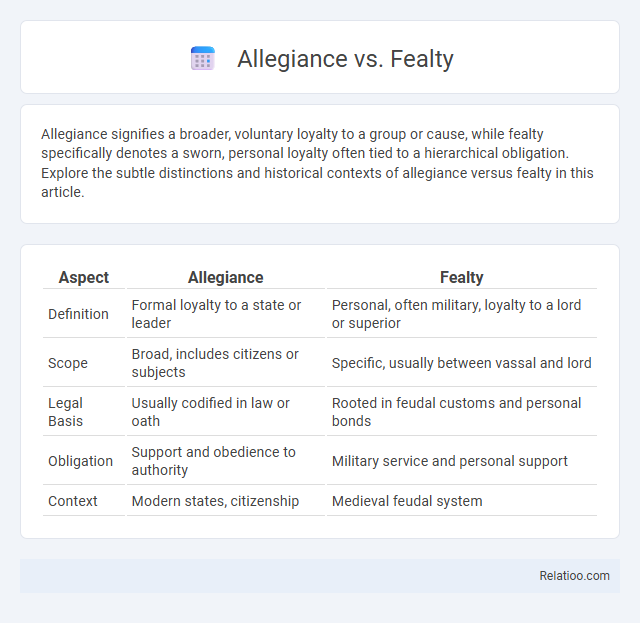
| Aspect | Allegiance | Fealty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal loyalty to a state or leader | Personal, often military, loyalty to a lord or superior |
| Scope | Broad, includes citizens or subjects | Specific, usually between vassal and lord |
| Legal Basis | Usually codified in law or oath | Rooted in feudal customs and personal bonds |
| Obligation | Support and obedience to authority | Military service and personal support |
| Context | Modern states, citizenship | Medieval feudal system |
Understanding Allegiance and Fealty: Key Definitions
Allegiance is a binding loyalty or commitment to a sovereign, state, or cause, often formalized through oaths or declarations, while fealty is a specific type of allegiance historically tied to the medieval relationship between a vassal and a lord, emphasizing duties and service. Understanding the distinctions between allegiance and fealty helps clarify the nature of your obligations and loyalty within political or social hierarchies. Recognizing these terms' key definitions enables more precise communication about loyalty, authority, and responsibility in various contexts.
Historical Origins of Allegiance and Fealty
Allegiance and fealty both originated in the medieval feudal system, where allegiance referred to the loyalty owed by subjects to their sovereign or lord, while fealty was a more specific oath of fidelity between a vassal and their immediate lord. Allegiance historically represented a broader, more encompassing loyalty to a monarch or state, often formalized through ceremonies and legal obligations. Your understanding of medieval political relationships can deepen by recognizing that fealty emphasized personal loyalty and service, whereas allegiance underscored a collective duty to the ruling authority.
Allegiance in Modern Governance
Allegiance in modern governance signifies the formal loyalty and commitment a citizen owes to their country, serving as the foundation for social order and legal obligations. Unlike fealty, which historically implied personal loyalty to a lord or monarch, allegiance encompasses a broader, institutional relationship between individuals and state authority. Your understanding of allegiance helps clarify civic duties, including obeying laws and participating in democratic processes, thereby reinforcing national unity and stability.
Fealty in Medieval Society
Fealty in medieval society was a solemn oath of loyalty sworn by a vassal to a lord, symbolizing personal commitment and military service within the feudal system. Unlike general allegiance, which denotes loyalty to a nation or ruler, fealty specifically emphasized the hierarchical relationship and mutual obligations between lord and vassal, often involving land grants or protection. This bond of fealty ensured political stability and social order during the Middle Ages, reinforcing the structure of medieval governance and land tenure.
Legal Implications of Allegiance and Fealty
Allegiance signifies a broader, often formal loyalty to a nation or sovereign, legally establishing duties such as obedience to laws and military service, whereas fealty traditionally denotes a personal, sworn loyalty to a lord or superior, creating specific legal obligations tied to medieval or feudal contexts. Legal implications of allegiance include citizenship responsibilities, such as tax payment and defense obligations, enforceable under constitutional and international law. Fealty, though largely historical, imposed contractual duties of service and protection within feudal systems, influencing property rights and vassal-lord relationships under common law traditions.
Differences Between Allegiance and Fealty
Allegiance refers to a general loyalty or commitment to a sovereign, government, or cause, while fealty specifically denotes a sworn loyalty that includes obligations of service and support, primarily in a feudal or hierarchical context. The key difference lies in fealty's formal and often legal binding, involving personal vows between a lord and vassal, whereas allegiance can be broader, including abstract or national loyalty without such formal ties. Understanding these distinctions helps you accurately describe relationships of loyalty based on the nature and context of the commitment.
The Role of Loyalty in Allegiance and Fealty
Loyalty plays a central role in both allegiance and fealty, serving as the binding force between individuals and their leaders or sovereigns. Allegiance denotes a broader, often formal commitment to a state or authority, emphasizing civic duty and national unity. Fealty specifically refers to the personal vow of loyalty and service made by a vassal to a lord within a feudal system, highlighting a hierarchical and reciprocal relationship rooted in trust and obligation.
Allegiance vs Fealty in Popular Culture
Allegiance represents a formal loyalty or commitment to a group, nation, or cause, while fealty historically refers to the sworn loyalty between a vassal and lord, often found in medieval contexts. In popular culture, fealty is frequently depicted in fantasy and historical dramas as a personal oath binding individuals to rulers, contrasting with allegiance, which tends to emphasize collective or national identity. Understanding the distinction between these terms enhances your appreciation of how loyalty dynamics are portrayed across different storytelling genres.
Symbolism and Rituals of Allegiance and Fealty
Symbols of allegiance often include flags, anthems, or oaths demonstrating loyalty to a nation or leader, while fealty involves more personal rituals such as kneeling or hand-kissing, symbolizing a vassal's direct commitment to a lord. Rituals of allegiance typically occur during formal ceremonies, reinforcing collective identity and national unity, whereas fealty ceremonies emphasize hierarchical bonds and mutual obligations within a feudal system. Understanding these distinctions helps you appreciate how allegiance fosters broad societal loyalty, while fealty reflects intimate, personal devotion through symbolic acts.
Relevance of Allegiance and Fealty Today
Allegiance and fealty historically denote loyalty, with allegiance emphasizing commitment to a state or cause, while fealty specifically signifies sworn loyalty to a lord or ruler. In contemporary contexts, allegiance remains highly relevant as a foundational principle in citizenship, national identity, and legal responsibilities, whereas fealty has largely become symbolic or ceremonial within modern institutions. The evolution of political and social structures underscores allegiance's ongoing significance in fostering collective unity and civic duty.
Infographic: Allegiance vs Fealty
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com