The Pursuer-Widow dynamic often creates communication imbalances where the pursuer seeks closeness while the withdrawer distances themselves. Explore strategies to navigate and improve this challenging relationship pattern in this article.
Table of Comparison
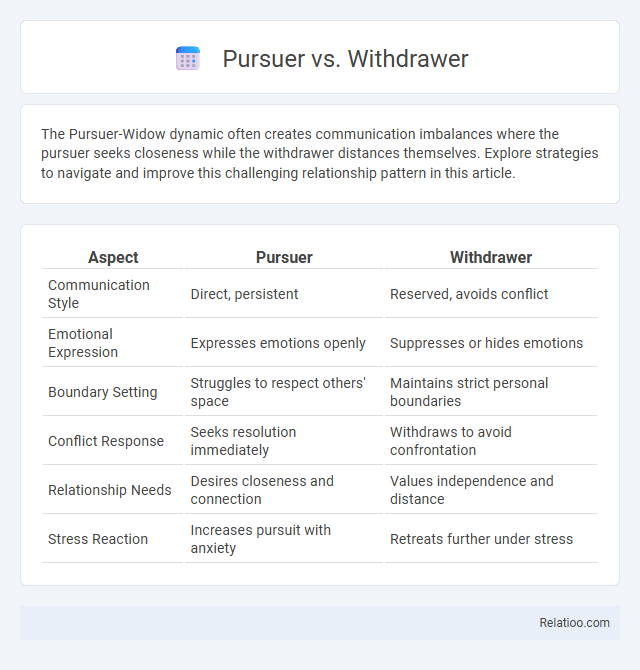
| Aspect | Pursuer | Withdrawer |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Style | Direct, persistent | Reserved, avoids conflict |
| Emotional Expression | Expresses emotions openly | Suppresses or hides emotions |
| Boundary Setting | Struggles to respect others' space | Maintains strict personal boundaries |
| Conflict Response | Seeks resolution immediately | Withdraws to avoid confrontation |
| Relationship Needs | Desires closeness and connection | Values independence and distance |
| Stress Reaction | Increases pursuit with anxiety | Retreats further under stress |
Understanding the Pursuer-Withdrawer Dynamic
The Pursuer-Withdrawer dynamic often emerges in relationships where one partner seeks closeness and continuous communication, while the other retreats to manage stress or avoid conflict. This pattern can lead to escalating tension as the pursuer's efforts trigger the withdrawer's need for space, creating a cycle of frustration and miscommunication. Recognizing these roles helps couples develop healthier interaction strategies by balancing the pursuer's need for connection with the withdrawer's need for autonomy.
Origins of Pursuer and Withdrawer Roles
The origins of pursuer and withdrawer roles often stem from early attachment patterns where one partner seeks connection and reassurance while the other retreats to avoid perceived pressure. These behaviors are rooted in differing emotional needs and coping mechanisms developed during childhood, influencing how individuals respond to conflict and intimacy. Understanding these origins helps identify the dynamic's impact on communication and relationship satisfaction.
Key Traits of a Pursuer
The key traits of a Pursuer include a strong desire for closeness, frequent initiation of conversations, and persistent efforts to resolve conflicts. You tend to seek reassurance and emotional connection, often feeling anxious when your partner withdraws or avoids discussions. This dynamic frequently leads to the classic Pursuer-Withdrawer cycle, where your active engagement contrasts with your partner's distance.
Key Traits of a Withdrawer
A Withdrawer often exhibits key traits such as emotional distancing, avoidance of conflict, and reluctance to engage in discussions, especially during tense moments. Your tendency to retreat or shut down can create frustration for the Pursuer, who seeks connection and resolution. Understanding these withdrawal patterns can help improve communication and foster healthier relationship dynamics.
Common Triggers for Pursuer-Withdrawer Patterns
Common triggers for Pursuer-Withdrawer patterns often include emotional withdrawal, perceived rejection, and communication breakdowns. Pursuers tend to demand connection and reassurance, feeling abandoned when Withdrawers pull away or silence conversations. Withdrawers, overwhelmed by conflict or fear of vulnerability, retreat to protect themselves, which escalates the cycle of pursuit and withdrawal.
Impact on Relationship Satisfaction
The dynamic between pursuer and withdrawer often creates a communication imbalance, leading to decreased relationship satisfaction as unmet emotional needs generate frustration. When both partners become pursuers, conflict intensifies, resulting in heightened tension and diminished trust. Your ability to recognize these patterns can improve emotional connection and foster a healthier, more satisfying relationship.
Communication Breakdown in Pursuer-Withdrawer Cycles
In Pursuer-Withdrawer cycles, communication breakdown occurs when the pursuer seeks constant engagement while the withdrawer retreats to avoid conflict, creating a repetitive loop of frustration and silence. Your efforts to express needs can feel ignored, making it difficult to resolve underlying issues as each party reinforces opposing communication styles. Recognizing these patterns is essential to breaking the cycle and fostering empathetic, balanced dialogue that addresses both partners' emotional needs.
Strategies to Break the Pursuer-Withdrawer Pattern
Effective strategies to break the pursuer-withdrawer pattern include improving communication by encouraging open, non-defensive dialogue and promoting emotional regulation for both parties. The pursuer should practice patience and reduce criticism, while the withdrawer can work on expressing needs and staying engaged during conflicts. Implementing mutual empathy exercises and seeking professional couples counseling further supports overcoming this cycle.
When to Seek Professional Help
Persistent conflict patterns between pursuers and withdrawers often indicate deeper relationship issues requiring professional intervention. When communication breaks down consistently, emotional distance grows, or one partner avoids resolution leading to repeated cycles of pursuit and withdrawal, couples therapy can provide tools for healthier interaction. Seeking help early prevents escalation and fosters constructive dialogue by addressing underlying attachment dynamics effectively.
Building Healthy Relationship Dynamics
Understanding the Pursuer vs Withdrawer dynamic is essential for building healthy relationship dynamics, as it highlights how one partner's approach to conflict--seeking closeness and resolution (Pursuer)--contrasts with the other's tendency to retreat and avoid confrontation (Withdrawer). Effective communication strategies, including active listening and establishing safe emotional spaces, help balance these opposing interaction styles and promote mutual understanding. Couples who develop awareness of these patterns and practice patience can transform conflict into opportunities for deeper connection and trust.
Infographic: Pursuer vs Withdrawer
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com