Independence is the ability to act without relying on others, while autonomy emphasizes self-governance and making decisions aligned with personal values. Explore how balancing independence and autonomy impacts healthy relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
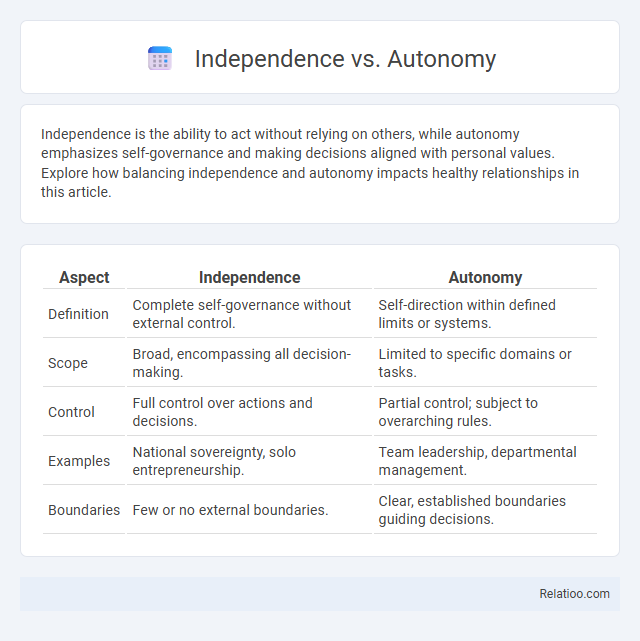
| Aspect | Independence | Autonomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete self-governance without external control. | Self-direction within defined limits or systems. |
| Scope | Broad, encompassing all decision-making. | Limited to specific domains or tasks. |
| Control | Full control over actions and decisions. | Partial control; subject to overarching rules. |
| Examples | National sovereignty, solo entrepreneurship. | Team leadership, departmental management. |
| Boundaries | Few or no external boundaries. | Clear, established boundaries guiding decisions. |
Defining Independence and Autonomy
Independence refers to the state of being self-sufficient and free from external control, allowing you to make decisions without reliance on others. Autonomy emphasizes the capacity for self-governance and the ability to regulate one's own actions within a set framework or system. Understanding the distinction between independence and autonomy helps clarify your degree of freedom versus self-direction.
Historical Perspectives on Independence and Autonomy
Historical perspectives on independence often emphasize the formal political separation of a nation from colonial or foreign rule, highlighted by key events like the American Revolution and India's decolonization in 1947. Autonomy, in contrast, reflects degrees of self-governance within larger political entities, such as the autonomous regions of Catalonia in Spain or the Inuit self-government agreements in Canada, where control over local affairs is granted without full sovereignty. The evolving balance between independence and autonomy has shaped modern statehood and governance, illustrating complex dynamics in national identity and jurisdiction across global history.
Key Differences Between Independence and Autonomy
Independence refers to the state of being self-sufficient and free from external control, while autonomy emphasizes the capacity to make decisions and govern oneself internally, often within a larger system. The key difference lies in independence focusing on external freedom, whereas autonomy centers on internal self-governance and decision-making authority. Understanding this distinction is critical in contexts such as political science, organizational behavior, and personal development, where autonomy enables self-direction despite potential dependencies.
Psychological Impacts of Independence vs Autonomy
Independence typically refers to the ability to make decisions and act without external control, fostering a sense of personal empowerment and self-efficacy crucial for mental well-being. Autonomy, while related, emphasizes the alignment of actions with one's values and intrinsic motivations, promoting psychological satisfaction and authentic self-expression. The psychological impact of independence focuses on control and capability, whereas autonomy enhances internal harmony and motivation, both essential for healthy emotional development and resilience.
Independence in Personal and Social Contexts
Independence in personal and social contexts refers to the ability to make decisions and act without relying on others, fostering self-reliance and confidence. Your independence empowers you to pursue goals, solve problems, and maintain control over your life, while also establishing boundaries in relationships. Unlike autonomy, which emphasizes self-governance within a system, or liberty, which relates to freedom from external constraints, independence centers on personal agency and social responsibility.
The Role of Autonomy in Decision Making
Autonomy plays a crucial role in decision making by allowing individuals to exercise control over their choices, distinguishing it from mere independence or dependence. Unlike independence, which emphasizes freedom from external control, autonomy highlights the capacity to self-govern based on personal values and informed judgment. Your ability to make autonomous decisions fosters responsibility and enhances problem-solving skills essential in complex situations.
Independence vs Autonomy in Leadership
Independence in leadership refers to your ability to make decisions and act without external control, emphasizing self-reliance and personal accountability. Autonomy goes a step further by granting you the freedom to set your own goals and methods within a framework, fostering innovation and adaptability. Understanding the balance between independence and autonomy is crucial for leaders to empower teams while maintaining strategic alignment.
Cultural Views on Independence and Autonomy
Cultural views on independence often emphasize individual self-reliance and decision-making, reflecting values of personal freedom and responsibility prevalent in Western societies. Autonomy, however, is culturally interpreted as the capacity for self-governance within social and familial contexts, highlighting relational interdependence common in collectivist cultures such as those in East Asia. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify how diverse societies prioritize personal agency versus communal harmony in shaping identity and social roles.
Benefits and Challenges of Independence and Autonomy
Independence grants you full self-governance and decision-making power, fostering personal growth and confidence, while autonomy allows for self-directed action within a structured environment, encouraging creativity and responsibility. Benefits of independence include complete control over outcomes and freedom from external influence, but challenges involve the risk of isolation and the burden of sole accountability. Autonomy offers the advantage of support and resource access within a framework, yet it may face limitations due to organizational rules and shared decision-making constraints.
Balancing Independence and Autonomy in Daily Life
Balancing independence and autonomy in daily life involves recognizing independence as the ability to perform tasks without external help, while autonomy emphasizes making personal choices and self-governance. Effective balance requires fostering self-reliance alongside respecting individual decision-making, enabling individuals to maintain control over their actions and environment. This dynamic interplay supports mental well-being, promotes personal growth, and enhances overall life satisfaction in various contexts such as work, relationships, and health.
Infographic: Independence vs Autonomy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com