Dissonance in relationships arises from conflicting values and poor communication, while resonance occurs when partners share mutual understanding and emotional harmony. Explore how to recognize and cultivate relationship resonance in this article.
Table of Comparison
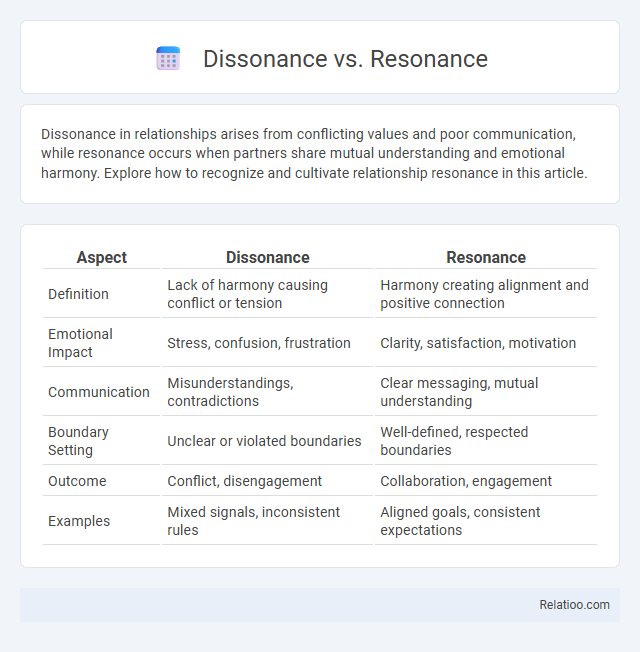
| Aspect | Dissonance | Resonance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lack of harmony causing conflict or tension | Harmony creating alignment and positive connection |
| Emotional Impact | Stress, confusion, frustration | Clarity, satisfaction, motivation |
| Communication | Misunderstandings, contradictions | Clear messaging, mutual understanding |
| Boundary Setting | Unclear or violated boundaries | Well-defined, respected boundaries |
| Outcome | Conflict, disengagement | Collaboration, engagement |
| Examples | Mixed signals, inconsistent rules | Aligned goals, consistent expectations |
Understanding Dissonance and Resonance
Understanding dissonance involves recognizing the tension or clash between conflicting elements, often creating a sense of discomfort or instability in music or communication. Resonance refers to the harmonious reinforcement that amplifies sound waves or ideas, leading to clarity and emotional impact. Your ability to differentiate dissonance from resonance enhances comprehension and expression in both auditory and cognitive contexts.
The Science Behind Dissonance
Dissonance in psychology refers to the mental discomfort experienced when holding conflicting beliefs or behaviors, driving the mind towards resolution to achieve cognitive harmony. Resonance, in contrast, describes the alignment or harmony between ideas, emotions, or frequencies, producing a reinforcing effect on perception or understanding. The science behind dissonance primarily stems from Leon Festinger's Cognitive Dissonance Theory, which explains how people strive for internal consistency by altering beliefs or behaviors to reduce psychological tension.
How Resonance Works in Nature
Resonance occurs when an object vibrates at its natural frequency due to external forces, amplifying the energy transfer between systems in nature, such as the synchronization of tree branches swaying in the wind or the harmonious hum of a singing bowl. In contrast, dissonance refers to a lack of harmonic alignment causing tension or instability, often leading to destructive interference or chaotic vibrations. Understanding how resonance works can help you harness these natural vibrations for applications in engineering, acoustics, and even healing practices.
Psychological Impact: Dissonance vs Resonance
Dissonance creates psychological discomfort by highlighting conflicting beliefs or attitudes, which motivates individuals to resolve the inconsistency and restore mental balance. Resonance, on the other hand, fosters psychological harmony by aligning with Your existing values, emotions, and experiences, enhancing engagement and positive feelings. Understanding the impact of dissonance versus resonance helps in designing messages or environments that either challenge or comfort the psyche effectively.
Musical Applications of Dissonance and Resonance
In musical applications, dissonance creates tension and instability by combining tones with clashing frequencies, which You can use to evoke emotional intensity or anticipation. Resonance enhances sound quality through sympathetic vibrations, enriching your music with fuller, more vibrant tones that amplify harmonic richness. Understanding the balance between dissonance and resonance allows composers to manipulate sonic textures and emotional dynamics effectively in compositions.
Dissonance and Resonance in Communication
Dissonance in communication occurs when conflicting messages create confusion or discomfort, hindering clarity and effective understanding. Resonance, on the other hand, happens when your message aligns harmoniously with the audience's values and emotions, enhancing engagement and retention. Recognizing and managing dissonance while fostering resonance ensures your communication is both impactful and meaningful.
Everyday Examples of Dissonance
Dissonance occurs when your beliefs or actions conflict, causing mental discomfort, such as feeling guilty after eating unhealthy food despite valuing health. Resonance, by contrast, is the harmony between your beliefs and actions, like choosing eco-friendly products that align with your environmental values. Everyday examples of dissonance include procrastination despite wanting to be productive, or purchasing expensive gadgets while aiming to save money.
Harnessing Resonance for Personal Growth
Harnessing resonance for personal growth involves aligning your values, goals, and actions to create meaningful connections and inner harmony. While dissonance represents internal conflict or mismatch, resonance encourages motivation and clarity by reinforcing positive feedback loops between your beliefs and experiences. Cultivating resonance helps you overcome dissonance, fostering emotional balance and sustained self-improvement.
Navigating Dissonance in Relationships
Navigating dissonance in relationships involves recognizing and addressing conflicts that arise from differing values, beliefs, or expectations, which create psychological discomfort. Cultivating resonance through active listening, empathy, and open communication helps transform dissonance into mutual understanding and emotional alignment. Effective conflict resolution strategies and emotional intelligence are key to fostering lasting relational harmony amid inevitable dissonance.
Achieving Balance: Integration of Dissonance and Resonance
Achieving balance between dissonance and resonance involves integrating conflicting ideas and harmonious elements to foster innovation and growth. Effective management of dissonance creates productive tension that challenges existing paradigms, while resonance amplifies shared understanding and emotional connection. This dynamic interplay drives creativity and adaptive problem-solving within organizations and interpersonal relationships.
Infographic: Dissonance vs Resonance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com