Boundaries define personal limits to protect emotional well-being, while borders often signify external geographical or political divisions. Explore how understanding boundaries versus borders can improve relationship dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
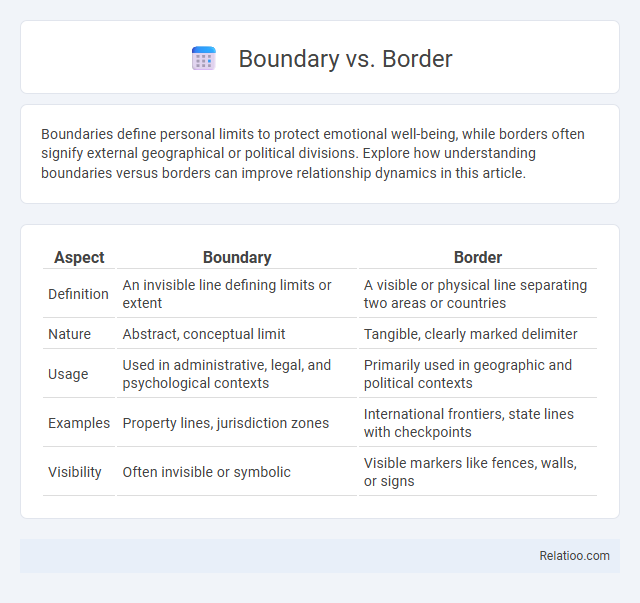
| Aspect | Boundary | Border |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An invisible line defining limits or extent | A visible or physical line separating two areas or countries |
| Nature | Abstract, conceptual limit | Tangible, clearly marked delimiter |
| Usage | Used in administrative, legal, and psychological contexts | Primarily used in geographic and political contexts |
| Examples | Property lines, jurisdiction zones | International frontiers, state lines with checkpoints |
| Visibility | Often invisible or symbolic | Visible markers like fences, walls, or signs |
Understanding Boundaries and Borders
Understanding boundaries and borders involves recognizing that boundaries typically refer to invisible lines defining personal, emotional, or social spaces, while borders are often physical, geopolitical demarcations between countries or regions. Your awareness of boundaries helps manage relationships and personal interactions effectively, preventing conflicts and respecting individual limits. Borders, by contrast, determine jurisdictional control and influence economic, legal, and cultural exchanges across nations.
Definition of Boundaries
Boundaries are defined as invisible lines that demarcate personal space, social norms, or responsibilities, often reflecting psychological or emotional limits rather than physical separations. Unlike borders, which are tangible and geopolitical lines marking territories between countries or regions, boundaries operate on relational and conceptual levels to establish acceptable behavior or interaction zones. Limits refer to the maximum extent or capacity of an object or concept, often measurable, while boundaries emphasize the distinction in identity or domain within social or personal contexts.
Definition of Borders
Borders define the official lines that separate countries or states, often recognized through treaties or legal agreements. Unlike boundaries, which may be informal or cultural demarcations, borders are tangible and enforceable markers of territorial sovereignty. Your understanding of geographic and political divisions improves when distinguishing borders as precise, internationally acknowledged borders that impact governance and jurisdiction.
Key Differences Between Boundaries and Borders
Boundaries define the edges of your personal space, beliefs, or responsibilities, establishing invisible lines that regulate behavior and interactions, while borders typically refer to physical or political divisions between countries or regions. Limits are the maximum extent of something, often quantifiable, whereas boundaries embody psychological or social constraints that shape relationships and personal autonomy. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate both tangible separations and intangible personal or social parameters effectively.
Historical Perspectives on Boundaries and Borders
Historical perspectives reveal that boundaries often represent socially constructed lines marking cultural or political territories, while borders denote formalized, legally recognized separations between nations or regions. Limits refer to more abstract or quantitative thresholds, such as resource capacity or governance reach, rather than physical demarcations. Understanding these distinctions allows you to navigate the complexities of territorial identity and state sovereignty throughout history.
The Psychological Impact of Boundaries
Boundaries define personal emotional and psychological spaces, fostering a sense of safety and self-respect essential for mental well-being. Unlike borders or limits, which denote physical or measurable separations, boundaries operate on an internal level to protect individual values and reduce stress. Establishing clear psychological boundaries enhances interpersonal relationships by preventing emotional exhaustion and promoting healthy communication.
The Geopolitical Significance of Borders
Borders define the official geopolitical divisions between sovereign states, often marked by treaties and patrolled checkpoints, serving as crucial points for national security and immigration control. Boundaries represent conceptual or natural separations that may not be formally recognized but influence cultural, economic, or environmental zones. Limits specify the maximum extent of jurisdictions or regulations within a defined territory, underpinning legal and administrative governance in localized contexts.
Boundaries in Relationships and Society
Boundaries in relationships and society define personal space, emotional limits, and acceptable behavior, distinguishing them from borders or physical limits that separate geographic areas. Your ability to set clear boundaries fosters respect, trust, and healthy interactions by preventing misunderstandings and emotional harm. Understanding the difference between boundaries, borders, and limits empowers you to navigate social dynamics effectively and maintain personal well-being.
Borders in International Relations
Borders in international relations define recognized geographical lines separating sovereign states, crucial for maintaining national security and regulating cross-border movement of people, goods, and services. Unlike boundaries, which can be conceptual or cultural divisions, borders have legal status established through treaties and international law, often marked physically by fences or checkpoints. Effective border management involves balancing sovereignty, diplomacy, and economic interests while addressing challenges like migration, smuggling, and territorial disputes.
Conclusion: Boundaries vs Borders
Boundaries represent clear, defined lines that separate properties or territories, often legally recognized and permanent. Borders are broader, sometimes flexible zones that differentiate countries or regions, influenced by political or cultural context. Understanding the distinction helps you grasp how spatial divisions impact governance, identity, and personal space.
Infographic: Boundary vs Border
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com