Traditional families typically consist of two biological parents and their children, emphasizing stable, long-term bonds. Blended families blend members from previous relationships, creating unique dynamics that require adaptive communication and trust-building; discover effective strategies for both family types in this article.
Table of Comparison
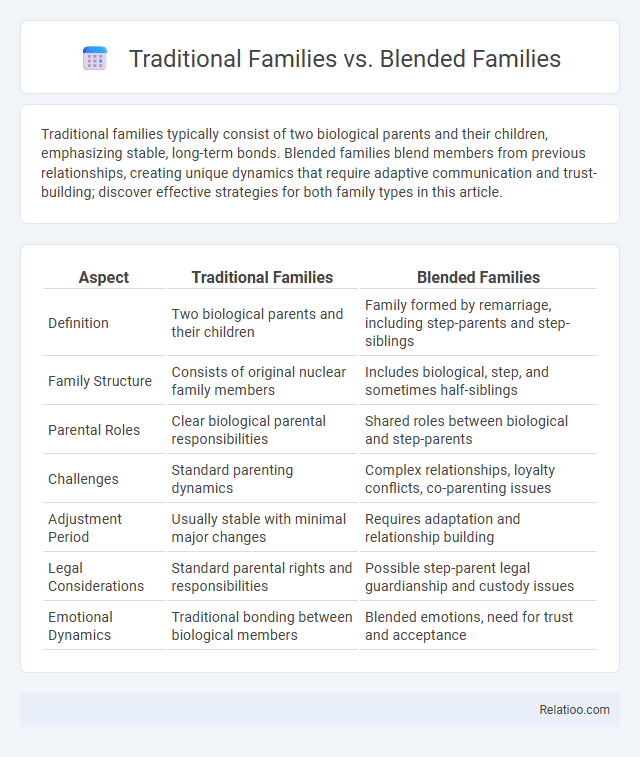
| Aspect | Traditional Families | Blended Families |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two biological parents and their children | Family formed by remarriage, including step-parents and step-siblings |
| Family Structure | Consists of original nuclear family members | Includes biological, step, and sometimes half-siblings |
| Parental Roles | Clear biological parental responsibilities | Shared roles between biological and step-parents |
| Challenges | Standard parenting dynamics | Complex relationships, loyalty conflicts, co-parenting issues |
| Adjustment Period | Usually stable with minimal major changes | Requires adaptation and relationship building |
| Legal Considerations | Standard parental rights and responsibilities | Possible step-parent legal guardianship and custody issues |
| Emotional Dynamics | Traditional bonding between biological members | Blended emotions, need for trust and acceptance |
Understanding Traditional and Blended Family Structures
Traditional families typically consist of two married parents and their biological children, emphasizing stability and clear generational roles, while blended families combine members from previous relationships, often requiring adaptive parenting and conflict resolution strategies. Understanding the dynamics of blended family structures involves recognizing diverse family roles and the importance of communication to foster cohesion and shared family values. Family values in both structures center on support, respect, and commitment, shaping the emotional and social development of all members.
Historical Evolution of Family Dynamics
Traditional families, characterized by nuclear structures with clearly defined roles, dominated societal norms for centuries, emphasizing stability and inherited family values. Blended families emerged as social mobility and divorce rates increased in the late 20th century, reflecting evolving dynamics where parental roles and household compositions became more diverse. Family values have continuously adapted, influenced by cultural shifts, legal changes, and economic factors, highlighting the historical evolution from rigid roles to more inclusive and flexible family systems.
Core Characteristics of Traditional Families
Traditional families are primarily characterized by a structure involving two married parents and their biological children, emphasizing stability, clear roles, and generational continuity. Family values in this model often center around commitment, respect for authority, and shared cultural or religious beliefs that guide behavior and decision-making. Understanding these core characteristics helps you appreciate how traditional families differ in dynamics and expectations from blended families, which combine members from previous relationships.
Defining Features of Blended Families
Blended families consist of spouses and children from previous relationships, creating a complex family dynamic distinct from traditional families where all members share biological or legal ties. The defining features of blended families include navigating step-parenting roles, managing relationships between step-siblings, and blending family traditions while maintaining individual family values. Understanding these unique challenges helps you foster strong bonds and preserve core family values in a blended household.
Cultural Perspectives on Family Types
Traditional families often emphasize multigenerational bonds and clear roles rooted in cultural heritage, while blended families reflect modern societal shifts creating diverse family dynamics. Family value varies significantly, influenced by cultural perspectives that shape expectations, roles, and support systems within each family type. Your understanding of these differences enriches appreciation for how cultural context defines the meaning and function of family across communities.
Challenges Faced by Traditional Families
Traditional families often encounter challenges such as rigid gender roles, communication gaps, and difficulty adapting to societal changes. These families may struggle with balancing work-life priorities and addressing mental health stigma within a conventional framework. The emphasis on preserving longstanding family values can create resistance to progressive family dynamics, impacting emotional well-being and relationship flexibility.
Unique Challenges in Blended Families
Blended families face unique challenges such as navigating complex relationships, managing loyalties between biological and stepfamily members, and addressing differing parenting styles. These dynamics often require strong communication and flexibility to foster family cohesion and uphold shared family values. Understanding your role within a blended family can help in creating a supportive environment that honors each member's needs.
Parenting Styles and Child Development
Traditional families often emphasize authoritative parenting, promoting structure and clear boundaries that support consistent child development outcomes such as academic achievement and social competence. Blended families may adopt more flexible parenting styles, balancing integration of stepchildren while addressing diverse emotional needs to foster resilience and adaptability in children. Family values in both settings prioritize nurturing environments that shape children's emotional security and identity formation, although approaches differ to accommodate unique family dynamics.
Emotional and Social Impacts on Children
Traditional families often provide children with a stable environment grounded in consistent routines and clear parental roles, fostering a strong sense of security and belonging. Blended families introduce diverse emotional dynamics that can challenge children's adaptability but also enhance social skills through exposure to varied relationships and conflict resolution experiences. Your children's emotional resilience and social development are influenced significantly by how family values are upheld and communicated within these differing family structures.
Building Harmony and Resilience in Modern Families
Traditional families often rely on generational roles and cultural heritage to build harmony, while blended families emphasize adaptability and open communication to foster resilience. Core family values such as trust, respect, and support serve as foundational elements that strengthen bonds across diverse family structures. Prioritizing emotional connection and problem-solving skills enables modern families to navigate complexities and maintain lasting unity.
Infographic: Traditional Families vs Blended Families
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com