Biological parents typically have stronger legal rights to custody compared to stepparents, who must often seek formal adoption or court approval to gain custody. Explore this article to understand the legal distinctions and factors influencing custody decisions between biological parents and stepparents.
Table of Comparison
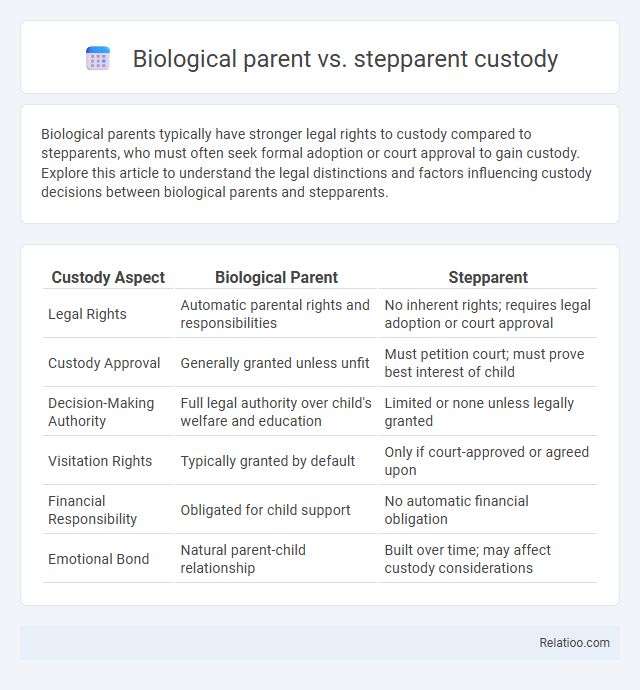
| Custody Aspect | Biological Parent | Stepparent |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Rights | Automatic parental rights and responsibilities | No inherent rights; requires legal adoption or court approval |
| Custody Approval | Generally granted unless unfit | Must petition court; must prove best interest of child |
| Decision-Making Authority | Full legal authority over child's welfare and education | Limited or none unless legally granted |
| Visitation Rights | Typically granted by default | Only if court-approved or agreed upon |
| Financial Responsibility | Obligated for child support | No automatic financial obligation |
| Emotional Bond | Natural parent-child relationship | Built over time; may affect custody considerations |
Overview of Custody: Biological Parent vs Stepparent
Custody laws typically prioritize the rights of the biological parent due to the established legal and genetic connection, but stepparents can seek custody or visitation through court approval, particularly if the biological parent is deemed unfit. Courts evaluate the child's best interests, considering factors like emotional bonds, stability, and the caregiving role played by either the biological parent or stepparent. Your custody arrangement may be influenced by jurisdiction-specific statutes and the strength of the relationship between the child and each caregiver.
Legal Definitions and Custodial Rights
Biological parent custody typically refers to the legal rights and responsibilities granted to a child's birth parents, including decision-making authority and physical care, recognized by family law statutes. Stepparent custody, while less common, may be established through legal agreements or court orders, granting non-biological parents specific rights, often contingent on the biological parent's consent or termination of their rights. Your custodial rights depend heavily on these legal definitions, where biological parents usually have primary entitlement, but stepparents can gain custody rights through adoption or formal guardianship processes.
Factors Courts Consider in Custody Decisions
Courts prioritize the best interests of the child when comparing biological parent vs stepparent custody, evaluating factors such as the stability of the home environment, the child's emotional bonds, and each caregiver's ability to provide for the child's physical and emotional needs. Your child's relationship history, the biological parent's fitness, and the stepparent's role in the child's life are critical elements influencing custody rulings. Courts also assess evidence related to each party's involvement in educational, medical, and extracurricular decisions to ensure the child's overall well-being.
Child’s Best Interests: Key Determinants
Child's best interests remain the paramount consideration in custody disputes involving biological parents and stepparents, with courts assessing factors such as the child's emotional stability, the quality of the parent-child relationship, and the ability to provide a safe and nurturing environment. Legal custody often favors the biological parent unless the stepparent has established a significant caregiving role and demonstrates a capacity to meet the child's developmental and psychological needs. Evaluations prioritize the child's continuity of care, attachment bonds, and minimizing disruption to their daily life and schooling.
Parental Rights: Comparing Biological and Stepparent Claims
Biological parents typically hold primary legal rights to custody based on genetic ties and established parental responsibilities, including decision-making in education, healthcare, and welfare. Stepparents may seek custody or visitation through adoption or court intervention, but their claims often require demonstrating the best interests of the child and the stepparent's established relationship. Custody disputes consider factors such as the biological parent's fitness, the stepparent's role in nurturing the child, and the child's emotional stability to determine parental rights.
The Role of Parental Consent in Stepparent Custody
Parental consent plays a crucial role in stepparent custody cases, often determining whether the stepparent can obtain legal rights without terminating the biological parent's rights. Courts typically require the biological parent's consent unless there is evidence of unfitness or abandonment, emphasizing the protection of the biological parent's fundamental custody rights. Stepparent custody arrangements are thus contingent on navigating complex consent laws and demonstrating the stepparent's ability to act in the child's best interests.
Adoption and Stepparent Custody: Legal Implications
Adoption legally transfers parental rights from the biological parent to the stepparent, establishing full custody and eliminating the biological parent's legal responsibilities. Stepparent custody without adoption often requires court approval and may involve guardianship or custody agreements that do not sever biological parental rights. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for navigating legal processes in family law and ensuring the welfare of the child.
Challenges Faced by Stepparents Seeking Custody
Stepparents seeking custody face significant legal challenges due to the biological parent's primary rights, often requiring proof of unfitness or abandonment. Courts prioritize the child's best interests, complicating stepparents' claims without established parental rights or long-term caregiving history. Navigating custody disputes demands strong legal representation and evidence of a stable, nurturing environment provided by the stepparent.
Psychological Impact on Children: Biological vs Stepparent Custody
Children in biological parent custody often experience greater emotional stability and identity continuity due to established attachments and shared genetic ties. Stepparent custody can introduce challenges such as loyalty conflicts and adjustment difficulties, impacting the child's psychological well-being and sense of security. Research highlights the importance of consistent parenting quality and supportive relationships in mitigating negative psychological effects regardless of parental biological status.
Navigating Custody Disputes: Tips for Blended Families
Navigating custody disputes in blended families requires understanding the legal distinctions between biological parent and stepparent custody rights, as biological parents generally retain primary custody unless a stepparent obtains legal guardianship or adoption. Courts prioritize the child's best interests, considering factors such as the emotional bond with each caregiver and the stability provided by the home environment. Establishing clear communication and mediation can facilitate cooperative co-parenting agreements, reducing conflict and promoting a nurturing atmosphere for all family members.
Infographic: Biological parent vs stepparent custody
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com