Biological child relationships often involve innate genetic bonds and shared family history, while stepchild relationships require intentional emotional connection and trust-building. Explore key differences and strategies for strengthening these bonds in this article.
Table of Comparison
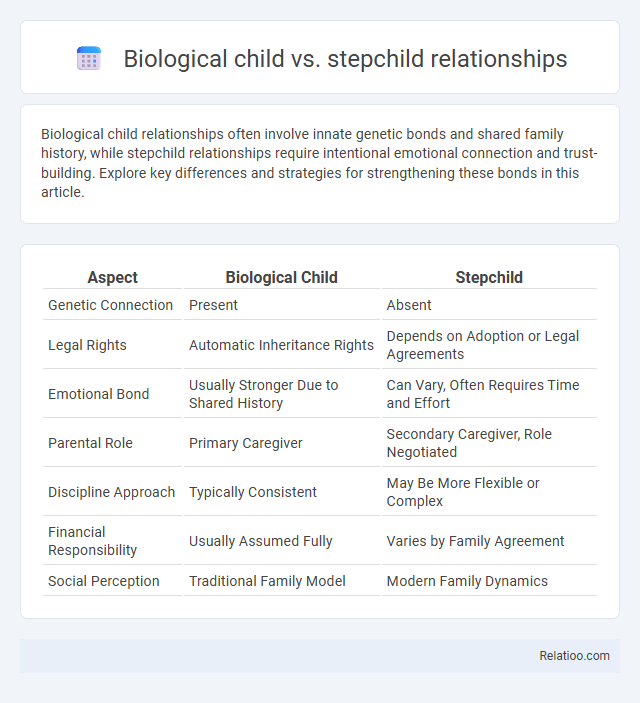
| Aspect | Biological Child | Stepchild |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Connection | Present | Absent |
| Legal Rights | Automatic Inheritance Rights | Depends on Adoption or Legal Agreements |
| Emotional Bond | Usually Stronger Due to Shared History | Can Vary, Often Requires Time and Effort |
| Parental Role | Primary Caregiver | Secondary Caregiver, Role Negotiated |
| Discipline Approach | Typically Consistent | May Be More Flexible or Complex |
| Financial Responsibility | Usually Assumed Fully | Varies by Family Agreement |
| Social Perception | Traditional Family Model | Modern Family Dynamics |
Understanding Biological and Stepchild Dynamics
Understanding biological and stepchild dynamics involves recognizing the unique emotional bonds and challenges inherent in each relationship type. Biological connections often come with inherent genetic ties and shared history, whereas stepchild relationships require cultivating trust, respect, and effective communication to build a strong family bond. Your family's unity depends on valuing both biological ties and chosen relationships, fostering empathy and patience to nurture meaningful connections.
Emotional Bonds: Nature vs Nurture
Emotional bonds in biological child and stepchild relationships are shaped by both genetic connections and shared experiences, with nurture often playing a crucial role in strengthening family ties beyond biology. You can cultivate deep affection and trust through consistent care, communication, and empathy, regardless of genetic links. Research shows that nurturing environments significantly impact the quality of family bonds, highlighting that emotional attachment stems more from interaction than ancestry.
Parental Roles: Biological Parents vs Stepparents
Biological parents typically engage in parenting roles grounded in genetic ties and legal responsibilities, which influence emotional bonding and child development. Stepparents often navigate complex relational dynamics, requiring intentional efforts to build trust and establish parental authority without innate biological connection. Both biological and stepparents contribute uniquely to a child's upbringing, highlighting that family bonds can transcend genetics through consistent support, care, and emotional investment.
Trust Building in Blended Families
Biological child and stepchild relationships often require intentional efforts to build trust and establish a strong family bond in blended families. Trust-building hinges on consistent communication, respect for individual boundaries, and shared experiences that foster emotional connection between you and your children. Prioritizing empathy and patience helps bridge the gap between biological ties and chosen family, creating a harmonious and supportive home environment.
Conflict Resolution: Biological Child vs Stepchild
Conflict resolution in biological child vs stepchild relationships often requires tailored communication strategies to address feelings of loyalty and acceptance. Your approach should emphasize empathy and fairness, ensuring both children feel valued while managing potential rivalry or resentment. Establishing clear family roles and consistent boundaries fosters a harmonious family bond despite genetic differences.
Navigating Loyalty Conflicts
Navigating loyalty conflicts between biological child and stepchild relationships requires understanding the distinct emotional dynamics each bond entails, as biological ties often carry innate expectations of loyalty, while stepchildren seek acceptance and equal regard. Family bond strength improves when communication fosters empathy, acknowledges feelings without favoritism, and creates inclusive experiences that reinforce unity. Strategies such as setting clear boundaries, encouraging open dialogue, and validating each child's unique role diminish rivalry and cultivate harmonious family cohesion.
Communication Strategies for Stepfamilies
Effective communication strategies for stepfamilies emphasize building trust and understanding between you, your biological child, and stepchildren by encouraging open, honest dialogue and active listening. Consistent family meetings and shared activities foster emotional connections and help navigate complex feelings, promoting a cohesive family bond. Establishing clear boundaries and respecting each individual's role supports long-term harmony and strengthens relationships within the blended family structure.
Impact of Divorce and Remarriage on Children
Divorce and remarriage can significantly affect both biological and stepchild relationships, often leading to complex family dynamics and emotional challenges for Your children. Biological children may experience feelings of loss or loyalty conflicts, while stepchildren might struggle with acceptance and identity within the new family structure. Strong family bonds, built on trust and open communication, are crucial in mitigating these impacts and fostering a supportive, cohesive environment for all children involved.
Legal Rights: Biological Children and Stepchildren
Biological children have automatic legal rights related to inheritance, custody, and decision-making, whereas stepchildren often require legal actions such as adoption or guardianship to establish similar rights. Your ability to secure legal recognition for stepchildren may involve formal processes that differ significantly from the inherent rights granted to biological offspring. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for protecting familial bonds and ensuring equitable legal standing within blended families.
Fostering Healthy Relationships in Blended Families
Fostering healthy relationships in blended families requires understanding that both biological children and stepchildren contribute uniquely to the family bond. Building trust and open communication helps bridge differences, allowing your family to develop a supportive and nurturing environment. Prioritizing consistent emotional support and shared family activities strengthens these connections, promoting unity regardless of biological ties.
Infographic: Biological child vs Stepchild relationships
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com