Consolation offers immediate comfort by alleviating pain or distress, while compassion involves a deeper understanding and ongoing support for someone's suffering. Explore this article to learn how both play essential roles in nurturing meaningful relationships.
Table of Comparison
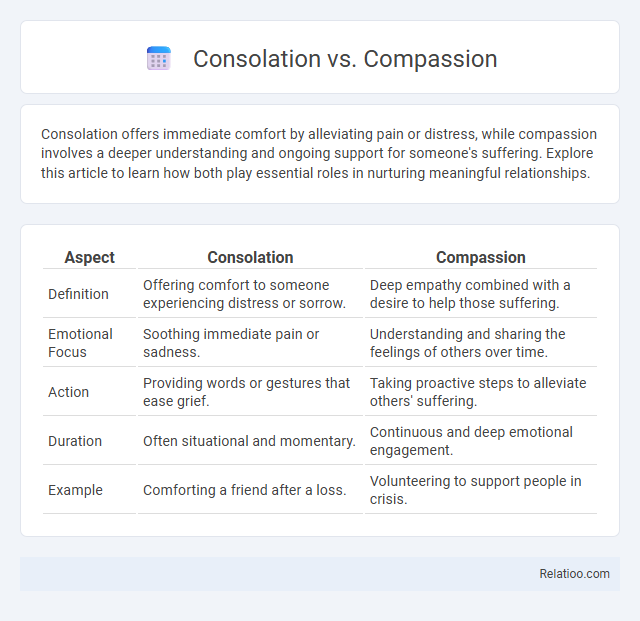
| Aspect | Consolation | Compassion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Offering comfort to someone experiencing distress or sorrow. | Deep empathy combined with a desire to help those suffering. |
| Emotional Focus | Soothing immediate pain or sadness. | Understanding and sharing the feelings of others over time. |
| Action | Providing words or gestures that ease grief. | Taking proactive steps to alleviate others' suffering. |
| Duration | Often situational and momentary. | Continuous and deep emotional engagement. |
| Example | Comforting a friend after a loss. | Volunteering to support people in crisis. |
Understanding Consolation and Compassion
Understanding consolation involves recognizing the act of providing comfort and alleviating someone's grief or distress through supportive words or gestures. Compassion goes deeper by encompassing an empathetic awareness of another person's suffering, driving a genuine desire to help ease their pain. While consolation primarily addresses immediate emotional relief, compassion is rooted in ongoing empathy and active concern for the well-being of others.
The Core Differences: Consolation vs Compassion
Consolation involves offering comfort to alleviate someone's grief or distress, often through words or gestures that aim to soothe emotional pain. Compassion goes deeper, encompassing a genuine understanding and active desire to help someone suffering, which may include both emotional support and practical assistance. Your ability to discern these core differences enhances empathetic interactions and ensures that your support is both meaningful and effective.
Emotional Impact of Consolation
Consolation provides immediate emotional relief by soothing feelings of sadness and loss, often through empathetic listening or comforting gestures. Compassion involves a deeper emotional connection, motivating supportive actions to alleviate suffering beyond words alone. While sympathy expresses understanding, consolation specifically targets the emotional healing process, fostering resilience and hope in moments of distress.
Compassion: Going Beyond Words
Compassion extends beyond consolation by actively engaging with the suffering of others, offering emotional support that transcends mere words. Unlike consolation, which often provides temporary comfort, compassion involves empathetic understanding and a genuine desire to alleviate pain through meaningful actions. Your ability to practice compassion creates deeper connections and fosters healing in challenging moments.
Scenarios Where Consolation is Needed
Scenarios where consolation is needed often involve situations of loss, failure, or deep disappointment, such as the death of a loved one or a personal setback. Your ability to offer consolation provides emotional support by acknowledging pain and providing comfort without necessarily solving the problem. Compassion, while related, is broader and involves empathy and a desire to help, whereas consolation specifically focuses on soothing emotional distress.
When Compassion Makes the Difference
Compassion goes beyond consolation by actively engaging with another's suffering, offering empathy that fosters genuine emotional connection and healing. When you provide compassion, you validate feelings and create a supportive space that transforms pain into hope, unlike mere consolation, which can feel distant or impersonal. Understanding this difference is crucial in situations where your presence and heartfelt concern genuinely make the difference in someone's recovery and emotional resilience.
Psychological Effects: Consolation vs Compassion
Consolation provides relief by acknowledging pain and offering comfort, which can reduce feelings of isolation and promote emotional healing in your moments of distress. Compassion involves a deeper empathic connection that not only comforts but also motivates supportive actions, enhancing emotional resilience and fostering trust. Understanding these psychological effects helps you choose appropriate responses to effectively support others or yourself during difficult times.
Building Stronger Connections Through Compassion
Compassion fosters deeper connections by actively recognizing and addressing others' suffering with empathy, which goes beyond offering mere consolation that often provides temporary relief. Unlike consolation, which may offer comfort through words, compassion involves a heartfelt engagement that builds trust and emotional bonds over time. Prioritizing compassion in relationships cultivates resilience and understanding, strengthening interpersonal connections in meaningful, lasting ways.
Potential Pitfalls of Consolation
Consolation often risks minimizing the feelings of those who are suffering by offering quick reassurances instead of truly acknowledging their pain, which can lead to feelings of isolation or misunderstanding. You may inadvertently silence someone's emotional experience by prioritizing solutions over empathy, contrasting with compassion's deeper, more genuine emotional connection that validates and supports the person's suffering. Understanding the potential pitfalls of consolation allows you to foster more meaningful interactions through compassionate listening and presence.
Cultivating Compassion in Everyday Life
Cultivating compassion in everyday life enhances emotional resilience and deepens social connections by fostering genuine empathy and understanding for others' suffering. Unlike consolation, which provides temporary comfort after distress, compassion involves proactive kindness and a continuous commitment to alleviate pain and support well-being. Practicing compassion regularly cultivates mindfulness, strengthens neural pathways linked to positive emotions, and promotes a more harmonious and supportive community.
Infographic: Consolation vs Compassion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com