Short breaks during work sprints enhance productivity and mental clarity by preventing burnout and maintaining focus. Discover how to balance breaks and work sprints effectively in this article.
Table of Comparison
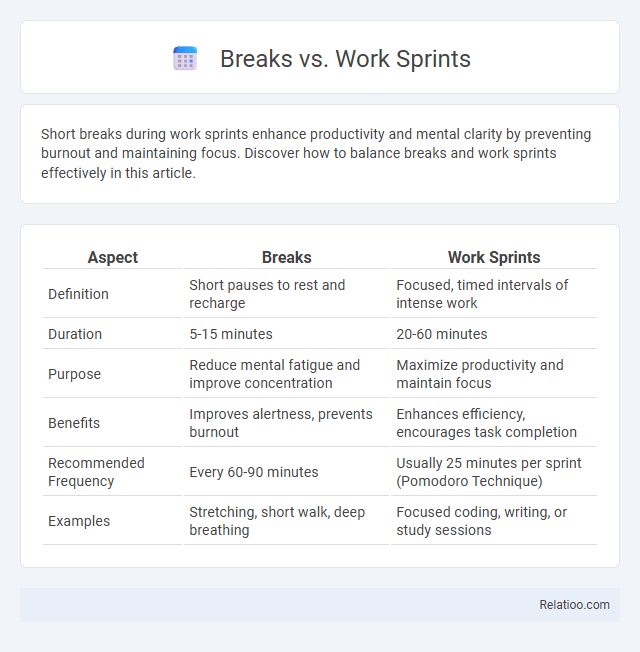
| Aspect | Breaks | Work Sprints |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short pauses to rest and recharge | Focused, timed intervals of intense work |
| Duration | 5-15 minutes | 20-60 minutes |
| Purpose | Reduce mental fatigue and improve concentration | Maximize productivity and maintain focus |
| Benefits | Improves alertness, prevents burnout | Enhances efficiency, encourages task completion |
| Recommended Frequency | Every 60-90 minutes | Usually 25 minutes per sprint (Pomodoro Technique) |
| Examples | Stretching, short walk, deep breathing | Focused coding, writing, or study sessions |
Understanding Work Sprints: Definition and Benefits
Work sprints are focused, time-bound periods where You concentrate intensely on specific tasks to maximize productivity and minimize distractions. This method enhances task completion speed and improves task management by breaking work into manageable intervals, often aligned with techniques like the Pomodoro method. Incorporating work sprints allows for measurable progress and increases overall efficiency while reducing burnout through balanced effort.
The Science Behind Taking Breaks
Taking breaks enhances cognitive function by preventing mental fatigue and improving focus through the brain's natural rest cycles, as supported by neuroscience research on the default mode network. Work sprints, such as the Pomodoro Technique's 25-minute intervals, optimize productivity by balancing intense periods of concentration with short restorative pauses. Rejuvenation activities during breaks, including mindfulness or physical movement, promote neuroplasticity and stress reduction, facilitating sustained attention and overall well-being.
Productivity Impact: Breaks vs Work Sprints
Work sprints, focused bursts of intense work, enhance productivity by capitalizing on peak concentration periods, while breaks provide essential recovery to prevent mental fatigue and maintain overall efficiency. Your productivity improves when balanced sprints are interspersed with short, frequent breaks that replenish cognitive resources and sustain motivation. Research shows that alternating work sprints with strategic breaks optimizes focus, reduces burnout, and increases long-term output compared to continuous work without pauses.
How Breaks Improve Focus and Creativity
Short breaks during work sprints significantly enhance Your cognitive performance by reducing mental fatigue and boosting concentration. These intervals stimulate creative thinking by allowing the brain to rest and process information subconsciously, leading to innovative problem-solving. Regularly scheduled breaks optimize productivity and maintain sustained focus throughout demanding tasks.
The Pomodoro Technique: Structured Sprints and Breaks
The Pomodoro Technique structures your work into focused sprints of 25 minutes followed by 5-minute breaks to optimize productivity and mental clarity. These short, timed sprints increase concentration and reduce burnout by balancing intense work periods with regular rejuvenation intervals. Implementing this method can enhance your time management, maintain motivation, and improve overall work efficiency.
Common Myths About Work Sprints and Breaks
Work sprints are often mistaken for continuous, intense work without pause, but research shows that brief, focused sprints followed by regular breaks improve productivity and mental clarity. A common myth is that skipping breaks leads to more output, yet evidence highlights that rejuvenation periods help prevent burnout and maintain high performance. Your work routine benefits significantly when you balance concentrated sprints with restorative breaks to optimize cognitive function and overall well-being.
Identifying the Right Work Sprint Length For You
Determining the optimal work sprint length depends on individual focus capacity and task complexity, with common sprint durations ranging from 25 to 90 minutes based on techniques like Pomodoro or Ultradian rhythms. Tracking productivity and energy levels during different sprint lengths helps identify the interval that maximizes deep work without causing burnout. Incorporating strategic breaks and rejuvenation periods between sprints enhances cognitive recovery, improving sustained concentration and overall task performance.
Optimal Break Strategies for Maximum Efficiency
Incorporating structured breaks during work sprints enhances cognitive function and sustains productivity by preventing mental fatigue and maintaining focus. Optimal break strategies, such as the Pomodoro Technique with 25-minute work intervals followed by 5-minute breaks, leverage the brain's natural attention span and promote efficient task completion. Rejuvenation periods involving physical movement, hydration, and mindfulness exercises further amplify work efficiency by restoring energy levels and reducing stress.
Work Sprints vs Breaks: Which Boosts Mental Health?
Work sprints, characterized by focused, intensive periods of work, enhance productivity by leveraging deep concentration, while breaks provide essential mental rest that prevents burnout and reduces stress. Balancing your work sprints with regular breaks optimizes cognitive function and supports sustained mental health, enabling sharper focus and improved mood. Prioritizing this balance helps maintain energy levels and enhances overall well-being during demanding tasks.
Creating a Balanced Routine: Integrating Sprints and Breaks
Creating a balanced routine involves integrating focused work sprints with strategic breaks to maximize productivity and mental clarity. Your work sprints should be time-boxed intervals of intense concentration, followed by rejuvenation periods that allow your brain to recover and maintain high performance. Implementing this cycle enhances sustained focus, prevents burnout, and fosters long-term motivation.
Infographic: Breaks vs Work Sprints
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com