Shared interests generate deeper emotional connections by fostering active engagement and mutual experiences, while common interests provide a basic foundation for compatibility. Explore how distinguishing between these can enhance your relationship in this article.
Table of Comparison
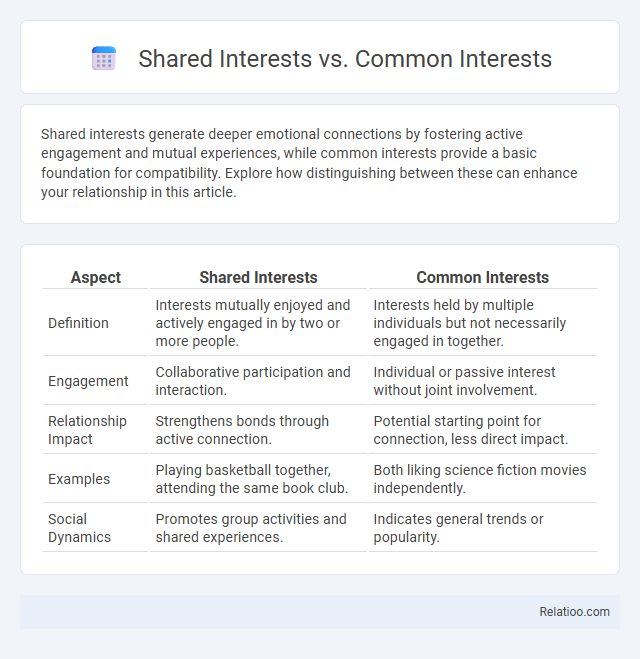
| Aspect | Shared Interests | Common Interests |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interests mutually enjoyed and actively engaged in by two or more people. | Interests held by multiple individuals but not necessarily engaged in together. |
| Engagement | Collaborative participation and interaction. | Individual or passive interest without joint involvement. |
| Relationship Impact | Strengthens bonds through active connection. | Potential starting point for connection, less direct impact. |
| Examples | Playing basketball together, attending the same book club. | Both liking science fiction movies independently. |
| Social Dynamics | Promotes group activities and shared experiences. | Indicates general trends or popularity. |
Understanding Shared Interests
Understanding shared interests involves recognizing the mutual values, passions, or activities that connect individuals, fostering deeper relationships and collaboration. Shared interests differ from common interests, which may be more general or widespread, while newness introduces novel experiences that can either complement or challenge existing connections. Your ability to identify and engage with shared interests enhances communication and strengthens social bonds effectively.
Defining Common Interests
Common interests refer to specific activities, hobbies, or values that two or more individuals consistently enjoy or share, forming a foundation for mutual connection and understanding. Differentiating from shared interests, which may be temporary or superficial, common interests imply a deeper, ongoing alignment that fosters stronger relationships. Recognizing common interests enables more meaningful interactions and long-term bonding in personal and professional contexts.
Key Differences Between Shared and Common Interests
Shared interests involve mutual passions or activities actively enjoyed and pursued together by individuals, fostering stronger personal connections. Common interests refer to general preferences or hobbies that multiple people have independently but may not necessarily engage in collectively. Newness highlights innovative or emerging interests, often driving curiosity and exploration beyond established shared or common interests.
The Role of Shared Interests in Relationships
Shared interests serve as a foundational element in building strong relationships by creating a natural context for meaningful interaction and emotional connection. Your ability to engage in activities or discussions around these shared pursuits fosters trust, mutual understanding, and collaboration, enhancing overall relationship satisfaction. Exploring newness within shared interests can introduce excitement and growth, keeping relationships dynamic and resilient over time.
How Common Interests Shape Communities
Common interests serve as the foundation for cohesive communities by providing shared goals and values that foster trust and cooperation among members. These mutual interests encourage active participation, collaboration, and the development of social bonds, enhancing group identity and stability. Unlike shared or superficial interests, common interests drive sustained engagement and collective action crucial for community growth and resilience.
Benefits of Shared Interests
Shared interests foster deeper connections and stronger bonds by aligning participants' passions and values, enhancing communication and collaboration. These mutual engagements increase trust and empathy, leading to more meaningful and enduring relationships. Unlike common or new interests, shared interests provide a stable foundation for ongoing social interaction and personal growth.
The Importance of Common Interests in Teamwork
Common interests in teamwork foster stronger collaboration by aligning goals and values among team members, enhancing motivation and productivity. Unlike shared or new interests, common interests create a stable foundation for trust and effective communication, crucial for resolving conflicts and achieving consensus. Prioritizing common interests accelerates team cohesion and drives collective success in dynamic work environments.
Examples of Shared vs Common Interests
Shared interests involve activities or topics that individuals actively engage in together, such as playing tennis or cooking classes, fostering a mutual connection through joint participation. Common interests refer to broader, often general preferences like enjoying jazz music or reading mystery novels, which may not require simultaneous involvement but create a basis for conversation and bonding. For example, two friends attending weekly yoga sessions (shared interest) contrasts with their mutual appreciation for classic films discussed separately (common interest).
Navigating Conflicts in Interests
Shared interests create a stable foundation for resolving conflicts by emphasizing mutual understanding, while common interests highlight overlapping goals that facilitate compromise and cooperation. Newness introduces fresh perspectives that can either challenge existing dynamics or inspire innovative solutions to disagreements. Your ability to balance these elements enhances communication and promotes effective conflict navigation in diverse social or professional settings.
Fostering Unity Through Shared and Common Interests
Shared interests create a foundation where Your relationships deepen through mutual activities and passions, fostering unity and collaboration. Common interests extend this connection by highlighting broader, collective values and goals that bind diverse individuals together. Newness introduces fresh perspectives and experiences that invigorate group dynamics, promoting inclusivity and continuous growth.
Infographic: Shared Interests vs Common Interests
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com