Self-confidence strengthens personal relationships by fostering trust and open communication, while feelings of inferiority often lead to insecurity and withdrawal. Discover effective strategies to boost self-confidence and improve your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
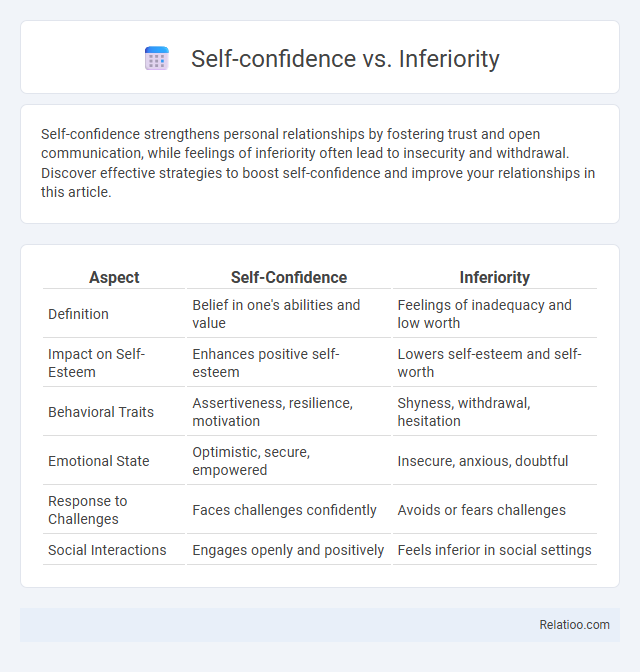
| Aspect | Self-Confidence | Inferiority |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in one's abilities and value | Feelings of inadequacy and low worth |
| Impact on Self-Esteem | Enhances positive self-esteem | Lowers self-esteem and self-worth |
| Behavioral Traits | Assertiveness, resilience, motivation | Shyness, withdrawal, hesitation |
| Emotional State | Optimistic, secure, empowered | Insecure, anxious, doubtful |
| Response to Challenges | Faces challenges confidently | Avoids or fears challenges |
| Social Interactions | Engages openly and positively | Feels inferior in social settings |
Understanding Self-Confidence: Definition and Importance
Self-confidence refers to your belief in your abilities and judgment, enabling you to face challenges with resilience and optimism. Understanding self-confidence is crucial because it directly influences mental health, decision-making, and overall success in personal and professional life. Developing self-confidence mitigates feelings of inferiority, fostering a positive self-image and empowering you to achieve goals more effectively.
Defining Inferiority: Roots and Manifestations
Inferiority stems from deep-seated feelings of inadequacy often rooted in negative early life experiences or unrealistic social comparisons, leading to diminished self-worth. Manifestations include chronic self-doubt, social withdrawal, and a pervasive fear of failure that undermine personal growth. Understanding these origins enables you to address underlying issues and foster genuine self-confidence.
The Psychological Foundations of Self-Confidence
The psychological foundations of self-confidence are rooted in a balanced self-perception and positive self-efficacy, which contrast sharply with feelings of inferiority characterized by persistent self-doubt and perceived inadequacy. Albert Bandura's theory of self-efficacy highlights how mastery experiences and social modeling bolster self-confidence, while Alfred Adler emphasized the role of overcoming inferiority feelings to achieve personal growth. Developing resilience and adaptive coping mechanisms strengthens self-confidence by mitigating the negative impacts of inferiority complexes on mental health and social functioning.
Causes and Triggers of Inferiority Complex
Feelings of inferiority often stem from negative early life experiences such as criticism, neglect, or unrealistic expectations, which sabotage your self-worth and self-confidence. Triggers include comparisons with others, failure, rejection, or social anxiety, which amplify these feelings and reinforce the inferiority complex. Cultivating self-confidence requires recognizing these causes and actively challenging the distorted beliefs that fuel your sense of inferiority.
Self-Confidence vs Inferiority: Key Differences
Self-confidence reflects a positive belief in Your abilities, enabling resilience and proactive decision-making, while inferiority centers on feelings of inadequacy and self-doubt that hinder growth. Self-confidence fosters motivation and healthy risk-taking, contrasting with inferiority's tendency to cause withdrawal and avoidance of challenges. Understanding these key differences helps individuals develop a balanced self-perception and overcome limiting beliefs.
How Self-Confidence Impacts Personal Development
Self-confidence significantly influences personal development by fostering resilience, enhancing decision-making skills, and promoting a positive self-image. When you cultivate self-confidence, you are more likely to take risks, embrace challenges, and recover quickly from setbacks, contrasting sharply with feelings of inferiority that can stunt growth and diminish motivation. This dynamic shapes your ability to pursue goals effectively and build meaningful relationships, ultimately driving continuous improvement and success.
The Negative Effects of Inferiority on Mental Health
Inferiority often leads to diminished self-confidence, which can cause significant mental health challenges, including anxiety and depression. Persistent feelings of inadequacy undermine emotional resilience, resulting in social withdrawal and heightened stress levels. Addressing inferiority is crucial to preventing long-term psychological consequences and promoting overall well-being.
Practical Strategies to Build Self-Confidence
Building self-confidence requires practical strategies such as setting achievable goals, practicing positive self-talk, and seeking constructive feedback. Overcoming feelings of inferiority involves recognizing and challenging negative beliefs, focusing on personal strengths, and engaging in activities that foster skill development. Consistent effort in these areas promotes resilience and a stronger sense of self-worth.
Overcoming Feelings of Inferiority: Actionable Tips
Overcoming feelings of inferiority requires purposeful steps such as setting achievable goals, practicing positive self-talk, and seeking support from trusted individuals. Building self-confidence involves recognizing your unique strengths and celebrating small victories to reinforce a positive self-image. You can transform inferiority into empowerment by consistently challenging negative beliefs and embracing personal growth.
Achieving Balance: Fostering Self-Confidence Without Arrogance
Achieving balance between self-confidence and inferiority involves recognizing personal strengths while acknowledging areas for growth, fostering a healthy self-image without tipping into arrogance. Cultivating self-awareness and humility enables individuals to build resilience and maintain motivation without diminishing others. Effective strategies include setting realistic goals, seeking constructive feedback, and practicing empathy to nurture confidence grounded in authenticity.
Infographic: Self-confidence vs Inferiority
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com