The distinction between an Imam and a Sheikh lies in their roles: an Imam leads prayers and offers religious guidance in a mosque, while a Sheikh is often a respected scholar or elder with broader authority in Islamic law and community teaching. Explore this article to understand the nuanced relationship and responsibilities of Imams and Sheikhs.
Table of Comparison
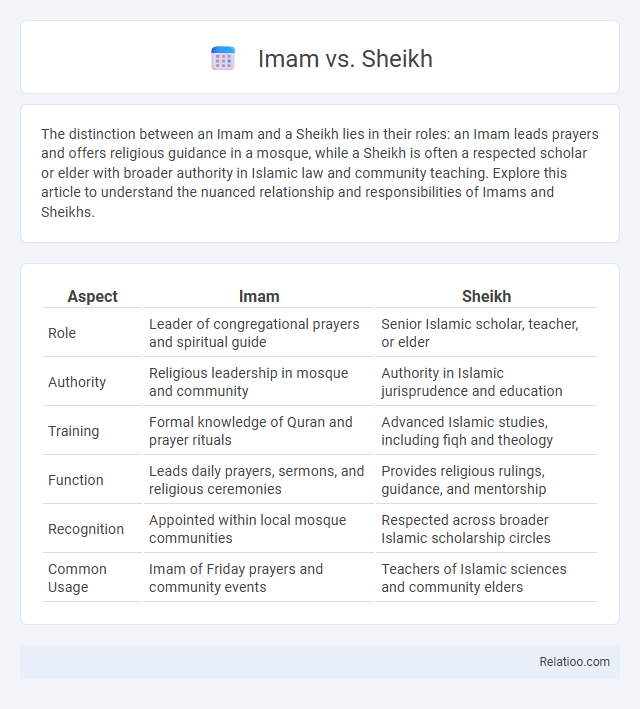
| Aspect | Imam | Sheikh |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Leader of congregational prayers and spiritual guide | Senior Islamic scholar, teacher, or elder |
| Authority | Religious leadership in mosque and community | Authority in Islamic jurisprudence and education |
| Training | Formal knowledge of Quran and prayer rituals | Advanced Islamic studies, including fiqh and theology |
| Function | Leads daily prayers, sermons, and religious ceremonies | Provides religious rulings, guidance, and mentorship |
| Recognition | Appointed within local mosque communities | Respected across broader Islamic scholarship circles |
| Common Usage | Imam of Friday prayers and community events | Teachers of Islamic sciences and community elders |
Definition of Imam and Sheikh
An Imam is a leader in Islamic worship who leads prayers, delivers sermons, and provides spiritual guidance to the community, often recognized for religious knowledge and piety. A Sheikh is a respected elder or scholar in Islam, commonly acknowledged for deep understanding of Islamic law, theology, or traditions, and may also serve as a teacher or advisor. Your choice between an Imam, Sheikh, or officiant depends on whether you seek formal religious leadership, scholarly expertise, or a general presiding figure for ceremonies.
Historical Origins of Imam and Sheikh
The terms Imam and Sheikh have distinct historical origins rooted in Islamic culture; Imam traditionally refers to a leader of prayer and community in mosque settings, originating from the Arabic word meaning "leader" or "guide." Sheikh, deriving from the Arabic word for "elder," historically signifies respect for wisdom, age, or leadership within tribal and religious contexts. Officiant, a broader term used globally, usually denotes a person authorized to conduct ceremonies and lacks the specific religious and cultural connotations tied to Imam and Sheikh in Islamic tradition.
Roles and Responsibilities
An Imam leads Islamic prayers, delivers sermons, and provides spiritual guidance within a mosque, often interpreting religious texts and overseeing community rituals. A Sheikh, recognized for deep scholarly knowledge or leadership in Islamic law and theology, serves as a teacher, advisor, or respected authority in religious and social matters. An Officiant, commonly seen in interfaith or civil ceremonies, performs official rites like weddings or funerals, ensuring legal and procedural compliance rather than specific religious instruction.
Religious Authority and Leadership
Imam, Sheikh, and Officiant represent distinct roles within religious contexts, each embodying varying levels of spiritual authority and leadership. An Imam is primarily recognized in Islam as a prayer leader and religious scholar, guiding communal worship and interpreting Islamic law. A Sheikh often denotes a respected elder or scholar with deep religious knowledge and leadership stature, while an Officiant broadly refers to an individual authorized to lead ceremonies across diverse religious traditions, emphasizing formal authorization over spiritual hierarchy.
Educational Background and Training
Imams typically undergo extensive Islamic studies at religious seminaries or universities, focusing on Quranic interpretation, jurisprudence, and theology. Sheikhs often hold advanced scholarly titles earned through years of specialized education and mentorship, emphasizing deep knowledge in Islamic law, history, and spiritual guidance. Your choice between an Imam, Sheikh, or officiant should consider their formal training and educational credentials to ensure authoritative and knowledgeable leadership.
Significance in Islamic Communities
Imam, Sheikh, and Officiant serve distinct roles within Islamic communities, each with specific significance tied to leadership and religious guidance. An Imam primarily leads congregational prayers, offers spiritual teachings, and interprets Islamic law, making them central to daily worship and religious education. A Sheikh holds scholarly status, often providing advanced theological insight and community leadership, while an Officiant typically conducts ceremonies such as weddings or funerals, ensuring religious rites are properly observed.
Variations Across Islamic Sects
Imam, Sheikh, and Officiant roles differ significantly across Islamic sects due to varying religious interpretations and community needs. In Sunni Islam, an Imam primarily leads prayers and offers religious guidance, while a Sheikh is often a respected scholar or teacher, and an Officiant may conduct ceremonies without necessarily being a religious authority. In Shia Islam, the Imam holds a more central theological position with spiritual and political authority, whereas the term Sheikh may refer to senior clerics, and Officiants perform ritual duties depending on local customs, highlighting the diversity you encounter within Islamic practices.
Imam vs Sheikh: Key Differences
An Imam is a religious leader in Islam who leads prayers, delivers sermons, and provides spiritual guidance to the community, often with formal religious education. A Sheikh typically refers to a respected elder or scholar, sometimes holding authority in religious, tribal, or social contexts, emphasizing knowledge, wisdom, or leadership beyond just prayer leadership. While an Imam's role is primarily within mosque rituals and Islamic worship, a Sheikh's influence can extend to broader social, educational, and advisory functions.
Title Usage in Different Cultures
Imam typically refers to a Muslim religious leader responsible for leading prayers and providing spiritual guidance within Islamic communities, widely used in Middle Eastern, South Asian, and North African cultures. Sheikh denotes a respected elder or Islamic scholar, often signifying authority, wisdom, or nobility across Arab nations and some Muslim societies. Officiant is a broader, non-denominational term employed globally to describe an individual authorized to conduct religious or civil ceremonies, such as weddings or funerals, without specifying a particular faith tradition.
Contemporary Relevance and Challenges
Imams, Sheikhs, and Officiants each hold distinct roles in religious and community leadership, with imams primarily leading Islamic prayers and guiding religious practices, sheikhs often serving as respected scholars or elders, and officiants conducting ceremonies across various faiths. Contemporary relevance lies in their adaptation to multicultural, interfaith environments, addressing modern ethical dilemmas and social issues while maintaining spiritual authority. Your engagement with these leaders reflects a dynamic balance between tradition and contemporary societal challenges, including inclusion, technological integration, and evolving community needs.
Infographic: Imam vs Sheikh
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com