Justice emphasizes adherence to laws and moral principles, while fairness prioritizes equitable treatment based on individual circumstances. Explore the nuanced differences between justice and fairness in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
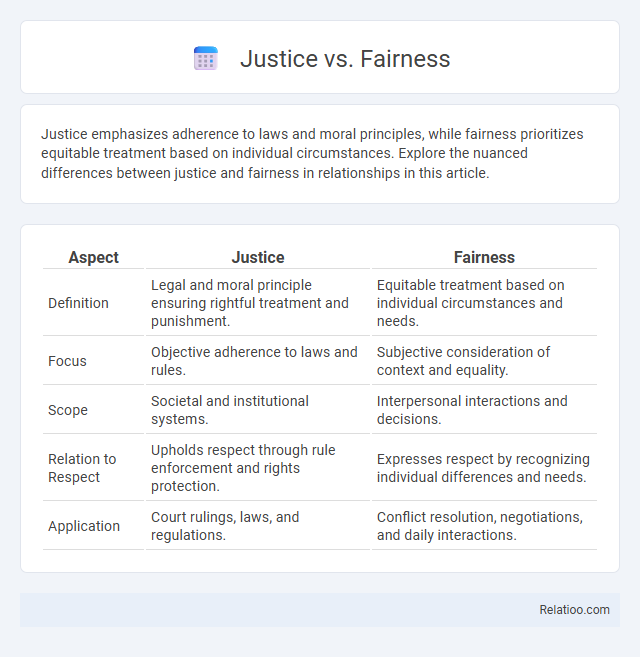
| Aspect | Justice | Fairness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal and moral principle ensuring rightful treatment and punishment. | Equitable treatment based on individual circumstances and needs. |
| Focus | Objective adherence to laws and rules. | Subjective consideration of context and equality. |
| Scope | Societal and institutional systems. | Interpersonal interactions and decisions. |
| Relation to Respect | Upholds respect through rule enforcement and rights protection. | Expresses respect by recognizing individual differences and needs. |
| Application | Court rulings, laws, and regulations. | Conflict resolution, negotiations, and daily interactions. |
Defining Justice and Fairness
Justice involves the administration of law based on principles of equality, impartiality, and moral rightness, ensuring that individuals receive what they are due under legal frameworks. Fairness emphasizes equitable treatment and unbiased decisions tailored to context, often addressing subjective perceptions of what is right or reasonable in social interactions. Differentiating justice and fairness highlights justice as a systemic, rule-based concept, whereas fairness centers on relational and situational equity.
Historical Perspectives on Justice vs Fairness
Historical perspectives on justice vs fairness reveal distinct philosophical roots: justice often aligns with legal and moral principles established by societal laws, while fairness emphasizes equitable treatment based on situational context. Classical philosophers such as Aristotle distinguished distributive justice as giving each individual their due, contrasting with fairness, which accounts for individual circumstances and needs. Over time, legal systems have primarily codified justice, whereas evolving social movements highlight fairness to address systemic inequalities and promote inclusivity.
Key Philosophical Theories
Justice embodies the principle of moral rightness based on laws, ethics, and equity, rooted in theories like Rawls' theory of justice advocating fairness as impartiality. Fairness emphasizes equitable treatment and balance, often guided by Aristotelian distributive justice, ensuring individuals receive proportional rewards or resources. Your understanding deepens by distinguishing fairness as a subset of justice, where justice encompasses legal and ethical dimensions, and fairness focuses on equal opportunity and consistency.
Justice in Legal Systems
Justice in legal systems emphasizes the impartial application of laws to ensure accountability, protect individual rights, and maintain social order. It relies on established legal principles and procedures to deliver consistent and objective outcomes, contrasting with fairness, which centers on subjective perceptions of equity and moral rightness. Understanding justice in law involves recognizing its role in balancing societal norms with individual liberties to promote legitimacy and trust in legal institutions.
Fairness in Social Contexts
Fairness in social contexts refers to the equitable treatment and access to resources, opportunities, and rights for all individuals regardless of their background or status. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing diverse needs and social inequalities to create inclusive policies and practices that promote social cohesion and justice. Social fairness often requires addressing systemic biases and fostering empathy to ensure marginalized groups receive appropriate support and representation.
Common Misconceptions
Justice is often confused with fairness, but justice refers to the legal and moral principles governing right and wrong, while fairness centers on equitable treatment and impartiality in everyday interactions. A common misconception is that fairness always aligns with justice; however, fairness can be more subjective and situational, reflecting personal or cultural values rather than universal legal standards. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate conflicts and ethical dilemmas with greater clarity and balanced judgment.
Justice vs Fairness in Everyday Life
Justice in everyday life emphasizes adherence to laws and ethical principles to ensure impartial treatment, while fairness centers on equitable distribution of resources and opportunities based on individual circumstances. Justice often involves formal systems and legal frameworks enforcing rights and responsibilities, whereas fairness is more flexible, addressing situational nuances and personal needs. Understanding the distinction between justice and fairness helps navigate conflicts and promote social harmony by balancing rule-based judgments with empathetic considerations.
Case Studies: Justice and Fairness in Action
Case studies in justice and fairness reveal how legal systems differentiate between equitable treatment and strict rule enforcement, emphasizing outcomes versus procedures. For instance, restorative justice programs in New Zealand highlight fairness by addressing victims' and offenders' needs, fostering reconciliation beyond mere punishment. Similarly, discrimination lawsuits in the U.S. showcase justice efforts to correct systemic inequities, balancing individual rights with societal norms.
Striking a Balance: Integrating Both Values
Striking a balance between justice and fairness requires recognizing justice as the application of laws and rules, while fairness emphasizes equity and impartiality in treatment. Your approach should integrate legal standards with compassion, ensuring outcomes respect both societal order and individual circumstances. This balance fosters trust in institutions by aligning objective justice with subjective fairness.
The Importance of Justice and Fairness for Society
Justice ensures the enforcement of laws and the protection of rights, creating a stable social order essential for societal progress. Fairness emphasizes impartial treatment and equitable distribution of resources, fostering trust and cooperation among community members. Together, justice and fairness uphold social cohesion by balancing legal frameworks with ethical considerations that meet individuals' needs and societal values.
Infographic: Justice vs Fairness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com