Protective space ensures emotional safety and trust in a relationship, while social space fosters external connections and shared experiences. Discover how balancing these spaces strengthens bonds in this article.
Table of Comparison
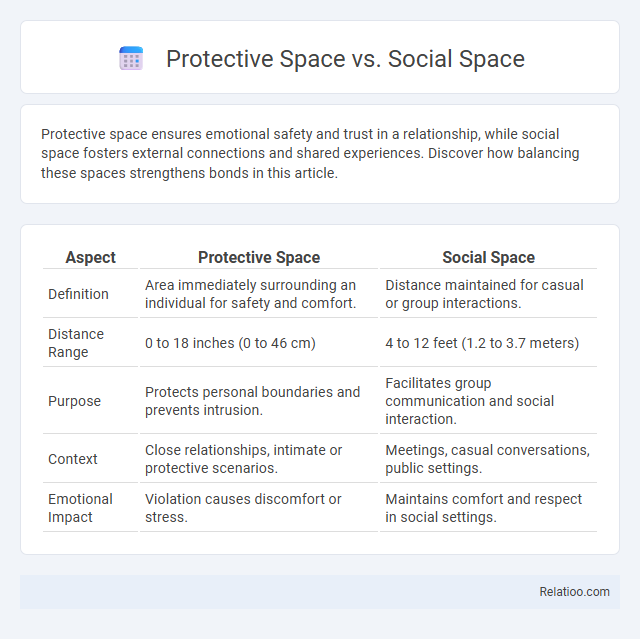
| Aspect | Protective Space | Social Space |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Area immediately surrounding an individual for safety and comfort. | Distance maintained for casual or group interactions. |
| Distance Range | 0 to 18 inches (0 to 46 cm) | 4 to 12 feet (1.2 to 3.7 meters) |
| Purpose | Protects personal boundaries and prevents intrusion. | Facilitates group communication and social interaction. |
| Context | Close relationships, intimate or protective scenarios. | Meetings, casual conversations, public settings. |
| Emotional Impact | Violation causes discomfort or stress. | Maintains comfort and respect in social settings. |
Understanding Protective Space: Definition and Importance
Protective space refers to an environment designed to shield individuals from physical or emotional harm, ensuring safety and privacy. It is crucial in contexts such as healthcare, workplaces, and urban planning, where maintaining personal boundaries enhances well-being and reduces stress. Understanding protective space helps in creating supportive environments that promote trust and security while balancing accessibility and social interaction.
Social Space Explained: Purpose and Dynamics
Social space refers to the area where interpersonal interactions occur, characterized by shared norms, communication, and mutual understanding. Its purpose is to facilitate connection, collaboration, and social bonding while maintaining respect for individual boundaries within a group. Your ability to navigate social space effectively strengthens relationships and supports positive social dynamics.
Key Differences Between Protective and Social Spaces
Protective spaces prioritize safety, privacy, and control, often featuring barriers and limited access to prevent intrusion, while social spaces encourage interaction, openness, and community engagement through shared environments. Protective spaces are typically found in secure facilities, private homes, or restricted zones, contrasting with social spaces like parks, plazas, or communal areas designed to foster communication and collaboration. The key difference lies in their functional intent: protective spaces aim to shield occupants or assets from harm or disturbance, whereas social spaces facilitate connection and socialization among individuals.
Psychological Impact of Space on Individuals
Protective space fosters a sense of safety and control, reducing stress and promoting mental well-being by creating physical and emotional boundaries that shield individuals from potential threats. Social space facilitates interpersonal interactions and connectivity, enhancing feelings of belonging and community support, which are crucial for psychological health and resilience. The dynamic balance between protective and social spaces influences individual anxiety levels, social comfort, and overall cognitive functioning, highlighting the need for environments that support both security and sociability.
Protective Space in Public and Private Settings
Protective space in both public and private settings refers to areas designed to ensure individual safety and privacy, often incorporating physical barriers, surveillance systems, and controlled access to prevent unauthorized intrusion. In public spaces, protective measures include designated safe zones, emergency call stations, and clear visibility to deter crime and promote a sense of security. Private settings emphasize protective space through secured property boundaries, alarm systems, and personal privacy protocols to maintain confidentiality and prevent physical or digital breaches.
Social Space: Fostering Connection and Interaction
Social space fosters connection and interaction by providing environments designed for communal engagement and shared experiences, enhancing social cohesion and communication. Unlike protective space, which prioritizes safety and personal boundaries, social spaces encourage openness, collaboration, and the exchange of ideas. These areas, such as parks, plazas, or community centers, play a crucial role in building relationships and supporting collective well-being.
Design Considerations for Protective and Social Spaces
Design considerations for protective and social spaces prioritize safety, functionality, and user comfort by integrating thoughtful layout, material selection, and accessibility features. Protective spaces require strategic elements such as physical barriers, secure entry points, and surveillance systems to ensure personal security, while social spaces emphasize openness, flexibility, and inviting atmospheres to encourage interaction and community engagement. Your design approach should balance these elements to create environments that support both protection and social connectivity effectively.
Challenges in Balancing Protective and Social Needs
Balancing protective space and social space presents challenges such as maintaining personal boundaries while fostering meaningful interactions, as excessive protective space can lead to isolation, whereas insufficient boundaries may cause discomfort or vulnerability. Navigating these challenges requires adaptive strategies to ensure safety without compromising social connectivity, especially in environments where privacy and collaboration coexist. Individuals and organizations must address conflicting needs by implementing flexible spatial design and communication practices that respect both protection and social engagement.
Case Studies: Effective Use of Both Spaces
Case studies demonstrate that effective use of protective space--designed to ensure privacy and safety--and social space, which facilitates interaction and community engagement, significantly enhances urban living quality. For instance, the High Line in New York balances protected areas with open social spaces, encouraging both personal retreat and social activity. Similarly, Barcelona's superblocks redesign integrates protective zones within active social hubs, reducing traffic-related hazards while fostering community interaction.
Future Trends in Space Design and Social Interaction
Future trends in space design emphasize adaptive environments that blend Protective Space, Social Space, and Personal Protective Space to enhance user well-being and interaction. Integrating smart technologies and modular layouts encourages dynamic transitions between privacy and social engagement, optimizing functionality for remote work, collaboration, and mental health. Advances in biophilic design and AI-driven personalization are shaping spaces that respond proactively to occupants' needs, fostering healthier, more connected communities.
Infographic: Protective Space vs Social Space
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com