Positive Discipline fosters respectful communication and long-term behavioral growth by emphasizing understanding and mutual respect, while Punishment often relies on fear and compliance, risking resentment and damaged trust. Explore this article to learn which approach best supports healthy relationships.
Table of Comparison
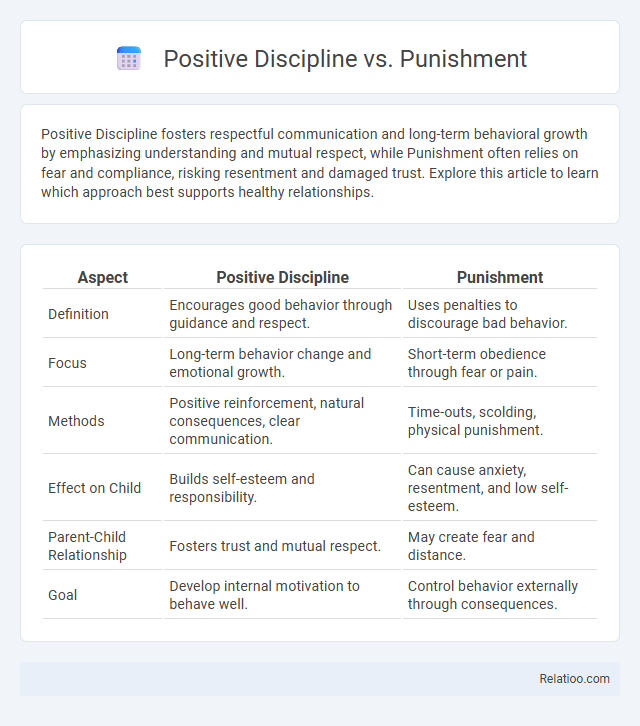
| Aspect | Positive Discipline | Punishment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Encourages good behavior through guidance and respect. | Uses penalties to discourage bad behavior. |
| Focus | Long-term behavior change and emotional growth. | Short-term obedience through fear or pain. |
| Methods | Positive reinforcement, natural consequences, clear communication. | Time-outs, scolding, physical punishment. |
| Effect on Child | Builds self-esteem and responsibility. | Can cause anxiety, resentment, and low self-esteem. |
| Parent-Child Relationship | Fosters trust and mutual respect. | May create fear and distance. |
| Goal | Develop internal motivation to behave well. | Control behavior externally through consequences. |
Understanding Positive Discipline: A Brief Overview
Positive discipline emphasizes teaching and guiding children through mutual respect and encouragement, fostering internal motivation rather than fear. Punishment relies on external consequences to reduce undesired behavior, often causing resistance or resentment in children. Consistent discipline integrates clear rules and expectations with supportive strategies, ensuring children understand boundaries while feeling secure and respected.
Defining Punishment: What It Really Means
Punishment involves imposing a negative consequence to reduce unwanted behavior, often focusing on immediate compliance rather than long-term growth. Positive discipline emphasizes teaching and guiding children to develop self-control and responsibility, fostering a positive relationship and mutual respect. Your consistent approach to discipline, incorporating clear expectations and constructive feedback, ensures a balanced development of behavior while minimizing reliance on punitive measures.
Core Principles of Positive Discipline
Positive Discipline emphasizes mutual respect, encouragement, and teaching skills for long-term behavior change, contrasting with punishment which relies on fear and compliance without fostering internal motivation. Consistency in discipline reinforces clear expectations and predictable consequences, helping children feel secure while learning self-regulation. Core principles of Positive Discipline include effective communication, empathy, and problem-solving to build intrinsic motivation and strengthen parent-child relationships.
Common Methods of Punishment in Parenting
Common methods of punishment in parenting include time-outs, loss of privileges, and verbal reprimands, each aiming to reduce undesirable behavior but often lacking long-term effectiveness. Positive discipline emphasizes teaching and guiding your child to understand consequences and develop self-control through encouragement and clear expectations. Consistency in discipline reinforces boundaries, helping your child internalize appropriate behavior while fostering respect and cooperation.
Impact on Child Behavior: Discipline vs Punishment
Positive discipline encourages understanding and self-regulation by promoting respectful communication and setting clear expectations, which leads to long-term positive behavior changes in children. Punishment often relies on fear or pain, resulting in temporary compliance but potentially fostering resentment or anxiety. Your consistent application of discipline strategies strengthens trust and internal motivation, creating a stable environment that supports healthy emotional development.
Emotional Outcomes: Building Trust or Fear
Positive Discipline fosters emotional safety by promoting trust and mutual respect, which supports healthy psychological development and long-term positive behavior. Punishment often triggers fear and anxiety, undermining self-esteem and damaging the parent-child or teacher-student relationship. Consistent discipline reinforces boundaries and predictability, enhancing emotional regulation and trust while reducing uncertainty and behavioral issues.
Long-Term Effects on Child Development
Positive discipline fosters emotional intelligence and self-regulation in children, leading to healthier relationships and better mental health over time. Punishment often triggers fear and resentment, potentially causing long-term behavioral issues and impaired social skills. Your consistent approach to discipline reinforces predictability and security, which are crucial for a child's ongoing development and confidence.
Effective Strategies for Implementing Positive Discipline
Effective strategies for implementing positive discipline focus on clear communication, setting consistent boundaries, and reinforcing desired behaviors through encouragement and natural consequences rather than punishment. Your approach should emphasize teaching self-regulation and problem-solving skills to foster internal motivation and long-term behavioral change. Consistency in discipline ensures that expectations are predictable, which helps children feel secure and understand the connection between actions and outcomes.
Overcoming Challenges in Shifting from Punishment to Discipline
Overcoming challenges in shifting from punishment to positive discipline requires consistent practice and patience as positive discipline emphasizes teaching and guiding rather than instilling fear. Maintaining discipline consistency helps your child understand boundaries clearly, fostering long-term behavioral changes without resentment. You can support this transition by replacing punitive reactions with empathetic communication and problem-solving strategies that build trust and cooperation.
Expert Recommendations: Choosing the Right Approach
Expert recommendations emphasize Positive Discipline as a sustainable approach that fosters intrinsic motivation, emotional regulation, and respectful communication in children. Punishment often leads to fear-based compliance but can damage trust and long-term behavior change, while consistent discipline ensures clear boundaries and predictable consequences, promoting security and responsibility. Combining Positive Discipline strategies with consistent application aligns with child development principles endorsed by psychologists like Dr. Jane Nelsen and the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Infographic: Positive Discipline vs Punishment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com