Gesture recognition apps enhance communication by translating physical movements into digital commands, increasing efficiency and accessibility. Explore this article to discover how these technologies compare to traditional manual communication methods.
Table of Comparison
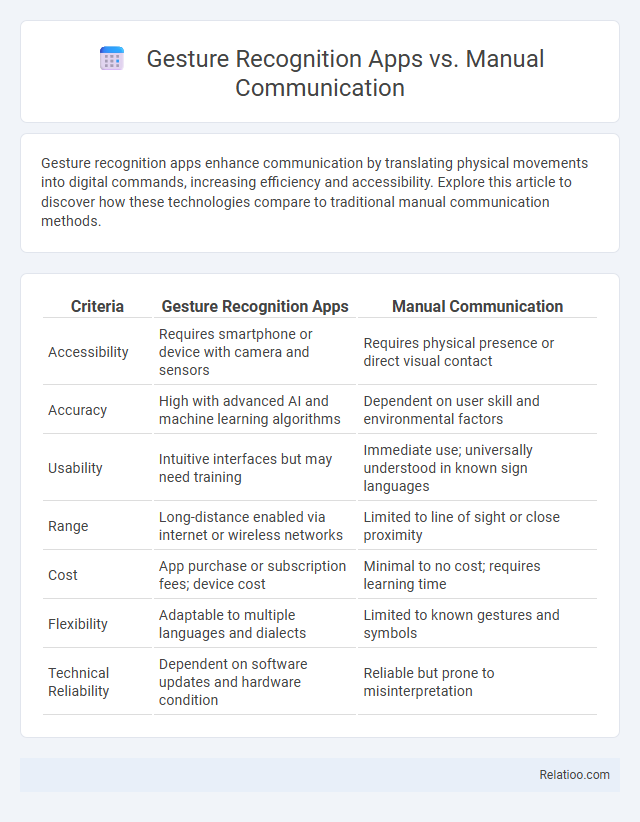
| Criteria | Gesture Recognition Apps | Manual Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Requires smartphone or device with camera and sensors | Requires physical presence or direct visual contact |
| Accuracy | High with advanced AI and machine learning algorithms | Dependent on user skill and environmental factors |
| Usability | Intuitive interfaces but may need training | Immediate use; universally understood in known sign languages |
| Range | Long-distance enabled via internet or wireless networks | Limited to line of sight or close proximity |
| Cost | App purchase or subscription fees; device cost | Minimal to no cost; requires learning time |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to multiple languages and dialects | Limited to known gestures and symbols |
| Technical Reliability | Dependent on software updates and hardware condition | Reliable but prone to misinterpretation |
Introduction to Gesture Recognition Apps
Gesture recognition apps utilize advanced computer vision and machine learning algorithms to interpret human motions as digital commands, enhancing interaction efficiency compared to traditional manual communication. These apps transform dynamic and static gestures into actionable inputs, offering real-time processing that surpasses the limitations of physical sign language or manual cues. By integrating with devices such as smartphones and wearable technology, gesture recognition apps enable hands-free control and accessibility in diverse applications, from gaming to assistive communication.
Overview of Manual Communication Methods
Manual communication methods encompass traditional forms like sign languages, finger spelling, and tactile signing, serving as vital tools for Deaf and hard-of-hearing communities. These methods rely on hand shapes, movements, and facial expressions to convey complex messages without spoken words. You can enhance your understanding by exploring how manual communication remains a powerful, accessible alternative to digital gesture recognition apps, which primarily automate interpreting gestures through technology.
Core Technologies Behind Gesture Recognition
Gesture recognition apps rely heavily on core technologies such as computer vision, machine learning, and sensor fusion to accurately interpret human hand and body movements. Unlike manual communication methods that depend on direct human input and traditional gesture use in sign languages, these apps utilize advanced algorithms and depth-sensing cameras or accelerometers to capture and analyze motion data in real-time. The integration of neural networks and real-time processing frameworks significantly enhances the precision and responsiveness of gesture recognition systems.
Accuracy: Gesture Recognition vs Manual Communication
Gesture recognition apps leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning to interpret hand movements with high precision, often exceeding human error rates found in manual communication. These apps provide consistent accuracy by minimizing misinterpretations that commonly occur in manual gestures due to individual variations or environmental factors. You can rely on gesture recognition technology for more dependable and standardized communication compared to traditional manual methods.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Both Approaches
Gesture recognition apps enhance accessibility by translating sign language into text or speech, enabling communication for individuals with hearing impairments in diverse settings. Manual communication, such as sign language, remains crucial for fostering inclusive, direct interactions within Deaf communities, preserving cultural identity and nuanced expression. Both approaches complement each other by expanding communication options, improving inclusivity in education, workplace environments, and social interactions for people with disabilities.
Speed and Efficiency of Communication
Gesture recognition apps significantly enhance the speed and efficiency of communication by instantly translating physical movements into digital commands, reducing response time compared to manual communication methods. Manual communication, relying on verbal or written exchanges, often suffers from delays, misinterpretations, and slower feedback loops. Pure gestures, while immediate in face-to-face settings, lack scalability and integration into digital platforms, limiting their overall communication efficiency compared to gesture recognition technology.
User Experience and Learning Curve
Gesture recognition apps offer an intuitive user experience by translating physical gestures into digital commands, reducing the need for manual input and enabling hands-free interaction. Manual communication, while straightforward and universally understood, often demands more effort and slower execution compared to gesture-based systems. Gesture recognition apps typically have a moderate learning curve, requiring users to familiarize themselves with specific gestures, whereas manual communication relies on existing knowledge but lacks the efficiency and accessibility provided by technology-driven gesture interfaces.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Gesture recognition apps enhance real-world communication by translating hand movements into digital commands, significantly improving accessibility for individuals with speech or hearing impairments. Manual communication methods like sign language remain essential for direct human interaction, especially in social and educational settings where nuanced expression is vital. Gesture-based interfaces find practical applications in augmented reality, automotive controls, and smart home devices, enabling intuitive, touchless interaction that increases efficiency and safety.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Gesture Recognition Apps face challenges in accurately interpreting diverse hand movements across different lighting and background conditions, often suffering from limited gesture vocabulary and susceptibility to sensor inaccuracies. Manual Communication, while reliable and universally understood through direct human interaction, is limited by the physical presence requirement and slower transmission speed compared to digital counterparts. Natural Gestures, although intuitive and effective for non-verbal cues, lack standardized interpretation and can vary significantly across cultures, leading to potential misunderstandings in communication.
Future Trends in Gesture Recognition and Manual Communication
Future trends in gesture recognition apps emphasize enhanced accuracy through AI-driven machine learning algorithms and expanded integration with augmented reality devices, transforming human-computer interaction. Manual communication methods continue evolving with wearable technologies that capture subtle hand movements, enabling seamless translation between gestures and digital commands. Advances in sensor technology and real-time data processing are driving convergence between gesture recognition apps and manual communication, fostering more intuitive and accessible communication systems globally.
Infographic: Gesture Recognition Apps vs Manual Communication
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com