Generation X values independence and face-to-face communication in relationships, while Millennials prioritize digital connectivity and emotional expression. Explore these generational dynamics and their impact on modern relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
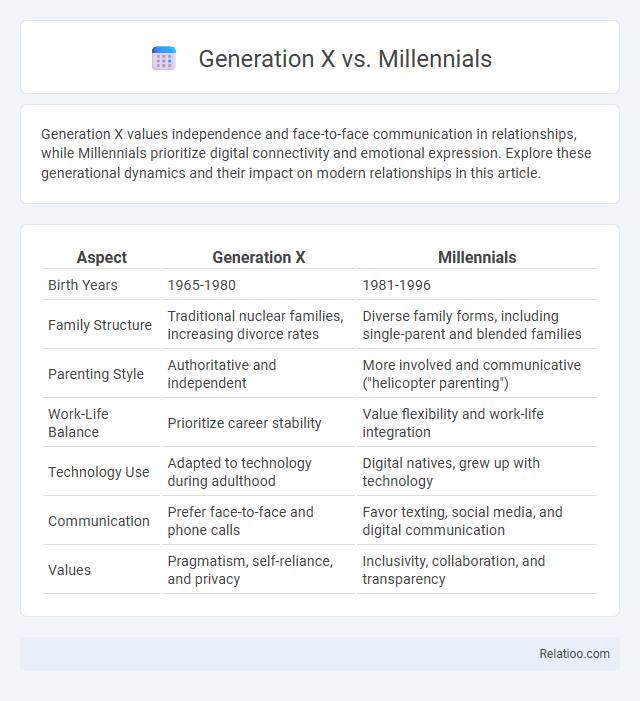
| Aspect | Generation X | Millennials |
|---|---|---|
| Birth Years | 1965-1980 | 1981-1996 |
| Family Structure | Traditional nuclear families, increasing divorce rates | Diverse family forms, including single-parent and blended families |
| Parenting Style | Authoritative and independent | More involved and communicative ("helicopter parenting") |
| Work-Life Balance | Prioritize career stability | Value flexibility and work-life integration |
| Technology Use | Adapted to technology during adulthood | Digital natives, grew up with technology |
| Communication | Prefer face-to-face and phone calls | Favor texting, social media, and digital communication |
| Values | Pragmatism, self-reliance, and privacy | Inclusivity, collaboration, and transparency |
Defining Generation X and Millennials
Generation X, born between 1965 and 1980, is characterized by independence, adaptability, and a pragmatic approach to work and life, often shaped by economic uncertainty and technological transitions. Millennials, born between 1981 and 1996, tend to prioritize digital connectivity, social consciousness, and a desire for work-life balance, influenced by rapidly evolving technology and cultural shifts. Understanding these generational traits helps you navigate the distinct values and communication styles that often define the generational gap in workplaces and social settings.
Key Historical Events Shaping Each Generation
Generation X, born between 1965 and 1980, experienced pivotal events such as the end of the Cold War, the rise of personal computing, and economic recessions that shaped their pragmatic and independent mindset. Millennials, born between 1981 and 1996, were influenced by the 9/11 attacks, the 2008 financial crisis, and the rapid expansion of the internet and social media, fostering adaptability and digital fluency. The generational gap between these cohorts is underscored by differing worldviews formed through distinct historical contexts, technological advancements, and socio-economic challenges.
Core Values and Beliefs
Generation X values independence, self-reliance, and a pragmatic approach to work, emphasizing work-life balance and skepticism towards institutions. Millennials prioritize collaboration, social responsibility, and technological integration, often seeking purpose-driven careers and valuing diversity and inclusion. The generational gap reflects contrasting attitudes toward authority, communication styles, and priorities shaped by distinct socio-economic and technological contexts influencing core beliefs and behaviors.
Attitudes Toward Technology and Innovation
Generation X tends to value practical technology and often favors tools that enhance productivity and work-life balance, while Millennials embrace rapid innovation and integrate digital advancements seamlessly into daily life. The generational gap is evident in attitudes toward technology adoption speed and reliance on digital solutions, with Millennials generally more comfortable with emerging trends like AI and social media. Understanding these differences helps you tailor communication and product development strategies to meet diverse tech expectations across generations.
Workplace Expectations and Career Goals
Generation X values independence and work-life balance, seeking job security and gradual career progression, while Millennials prioritize meaningful work, continuous feedback, and rapid advancement in dynamic environments. The generational gap in workplace expectations often leads to varied communication styles and motivations, impacting teamwork and leadership approaches. Understanding these differences helps you tailor management strategies to enhance collaboration and meet diverse career goals.
Financial Habits and Economic Challenges
Generation X tends to prioritize financial stability and long-term savings, often balancing debt management with retirement planning, while Millennials face heavier economic challenges such as student loan debt and a fluctuating job market, influencing their preference for digital banking and investment in experiences over assets. The generational gap highlights differences in risk tolerance, with Generation X favoring conservative investments and Millennials leaning towards innovative financial technologies like cryptocurrencies and peer-to-peer lending. Economic challenges like the 2008 recession for Gen X and the COVID-19 pandemic for Millennials significantly shape their distinct financial behaviors and priorities.
Educational Trends and Learning Preferences
Generation X prefers traditional classroom settings and values self-directed learning, while Millennials favor interactive, technology-driven educational methods emphasizing collaboration and instant access to information. Your understanding of the generational gap in educational trends reveals that Gen X adapts to structured schedules, whereas Millennials thrive in flexible, digital environments with multimedia content. Recognizing these learning preferences can enhance teaching strategies and improve engagement across both generations.
Social Relationships and Communication Styles
Generation X values direct, face-to-face communication, often preferring phone calls or in-person interactions, while Millennials embrace digital communication through social media and instant messaging, shaping their social relationships to be more virtual and fluid. The generational gap between these groups often leads to misunderstandings in communication preferences, with Gen X viewing Millennials as overly reliant on technology, and Millennials perceiving Gen X as less adaptable to rapid digital changes. Your ability to navigate these differing social styles can enhance cross-generational relationships and improve collaborative communication.
Entertainment and Media Consumption
Generation X tends to prefer traditional media such as television and radio, valuing content that offers nostalgia and depth, while Millennials show a strong preference for digital streaming platforms like Netflix and YouTube, favoring on-demand and interactive content. The generational gap in entertainment consumption is evident as Gen X relies more on scheduled programming, whereas Millennials embrace binge-watching and social media engagement for news and entertainment. Media companies increasingly tailor content strategies to these differences, leveraging social media algorithms and cross-platform accessibility to capture Millennial audiences while maintaining classic formats for Generation X.
Future Outlook: Bridging the Generational Gap
Bridging the generational gap between Generation X and Millennials requires embracing diverse perspectives and leveraging their unique strengths in the evolving workplace. Your organization can foster collaboration by implementing mentorship programs, encouraging open communication, and investing in technology that supports flexible work styles. Future outlooks emphasize adaptability and mutual respect, enabling both generations to innovate and drive sustainable growth together.
Infographic: Generation X vs Millennials
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com