Praise emphasizes affirming a person's qualities or efforts, while positive reinforcement involves providing rewards to increase desirable behaviors. Explore this article to understand how both strategies uniquely impact relationship dynamics and personal growth.
Table of Comparison
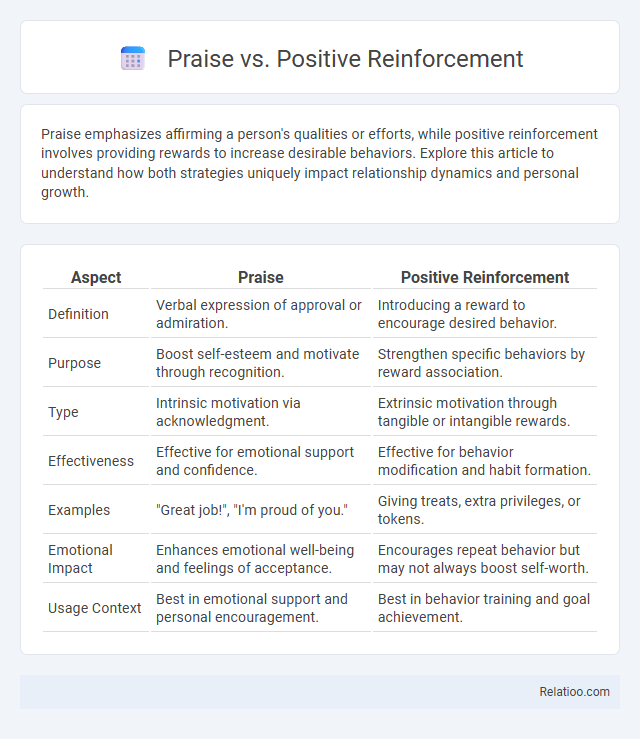
| Aspect | Praise | Positive Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verbal expression of approval or admiration. | Introducing a reward to encourage desired behavior. |
| Purpose | Boost self-esteem and motivate through recognition. | Strengthen specific behaviors by reward association. |
| Type | Intrinsic motivation via acknowledgment. | Extrinsic motivation through tangible or intangible rewards. |
| Effectiveness | Effective for emotional support and confidence. | Effective for behavior modification and habit formation. |
| Examples | "Great job!", "I'm proud of you." | Giving treats, extra privileges, or tokens. |
| Emotional Impact | Enhances emotional well-being and feelings of acceptance. | Encourages repeat behavior but may not always boost self-worth. |
| Usage Context | Best in emotional support and personal encouragement. | Best in behavior training and goal achievement. |
Introduction to Praise and Positive Reinforcement
Praise involves expressing approval or admiration for someone's actions, reinforcing their sense of accomplishment and boosting motivation. Positive reinforcement uses specific rewards or consequences to increase the likelihood of desired behaviors by providing tangible or intangible incentives. Understanding the distinction helps in effectively encouraging and shaping behavior in educational, workplace, and developmental settings.
Defining Praise: What It Means and How It's Used
Praise involves expressing approval or admiration for someone's behavior or achievements, serving as a motivational tool in various settings such as education, parenting, and workplace environments. Unlike positive reinforcement, which specifically encourages desired behaviors through rewards or consequences, praise primarily focuses on verbal acknowledgment to boost self-esteem and foster intrinsic motivation. Effective use of praise targets specific actions or qualities, enhancing its impact on learning, performance, and personal development.
Understanding Positive Reinforcement in Behavior Management
Positive reinforcement in behavior management involves providing a tangible reward or desired stimulus immediately after a specific behavior to increase the likelihood of its recurrence. Unlike simple praise, which is verbal and may not always motivate continued positive behavior, positive reinforcement uses concrete incentives that directly reinforce the action. Your understanding of positive reinforcement can enhance behavior modification by ensuring that the rewards align with the individual's preferences and promote sustained behavioral improvements.
Key Differences Between Praise and Positive Reinforcement
Praise involves expressing approval or admiration for a specific behavior, while positive reinforcement is a behavioral strategy that uses rewards to increase the likelihood of that behavior recurring. Praise is generally verbal and focuses on acknowledgment, whereas positive reinforcement includes tangible rewards or privileges that motivate continued behavior. Key differences lie in praise being a form of social feedback, whereas positive reinforcement directly strengthens behavior through incentives.
Psychological Impacts of Praise vs. Positive Reinforcement
Praise often boosts self-esteem by acknowledging specific qualities, but positive reinforcement strengthens desired behaviors through consistent rewards, shaping habits more effectively. While praise can enhance motivation and emotional well-being, relying solely on it may create dependency on external validation, whereas positive reinforcement fosters intrinsic motivation by linking actions to tangible outcomes. Your understanding of these psychological impacts helps tailor strategies that promote lasting behavioral change and personal growth.
Effectiveness in Shaping Desired Behaviors
Positive reinforcement, which involves providing a reward following a desired behavior, is the most effective method in shaping behaviors because it increases the likelihood of the behavior being repeated. Praise alone, while encouraging, may not always lead to consistent behavior change unless it is specific and linked to the desired action. Your ability to effectively shape desired behaviors improves when praise is combined with tangible positive reinforcement, ensuring motivation and clarity in expectations.
Common Misconceptions and Pitfalls
Praise often gets confused with positive reinforcement, but while praise is generally verbal approval that boosts self-esteem, positive reinforcement specifically strengthens desired behaviors by offering rewards contingent on those behaviors. A common misconception is that any praise automatically acts as positive reinforcement, yet indiscriminate praise can lead to dependency or reduced intrinsic motivation, making it a pitfall in behavior modification strategies. Effective use of positive reinforcement requires clear timing, consistency, and relevance to the behavior, whereas mere praise without these elements risks becoming hollow flattery rather than a tool for behavioral change.
When to Use Praise vs. Positive Reinforcement
Praise is effective for acknowledging specific achievements and boosting immediate motivation, while positive reinforcement involves rewarding desired behaviors to increase their frequency over time. Use praise when you want to express approval and enhance self-esteem following a particular action, and apply positive reinforcement strategically to shape long-term habits or skills by consistently rewarding consistent behaviors. Both techniques are essential in education and behavior management but serve distinct purposes based on the timing and intent of the feedback.
Practical Tips for Parents and Educators
Praise highlights specific achievements, boosting your child's motivation by acknowledging effort and progress. Positive reinforcement strengthens desired behaviors through consistent rewards or encouragement, making actions more likely to recur. Combining both methods with clear, actionable feedback helps parents and educators foster confidence and sustained learning.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Approach for Lasting Change
Positive reinforcement creates lasting behavioral change by consistently rewarding desired actions, making it more effective than simple praise, which may be viewed as superficial or insufficient. Praise can boost motivation temporarily but lacks the structured incentive system of positive reinforcement that encourages repetition and habit formation. For your goals, combining genuine praise with targeted positive reinforcement optimizes both emotional support and sustained improvement.
Infographic: Praise vs Positive Reinforcement
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com