Honor killing involves the murder of a family member for allegedly bringing dishonor, often related to marriage choices, whereas dowry death occurs when a bride is killed or driven to suicide due to disputes over dowry demands. Explore this article to understand the legal distinctions, cultural contexts, and prevention strategies for both practices.
Table of Comparison
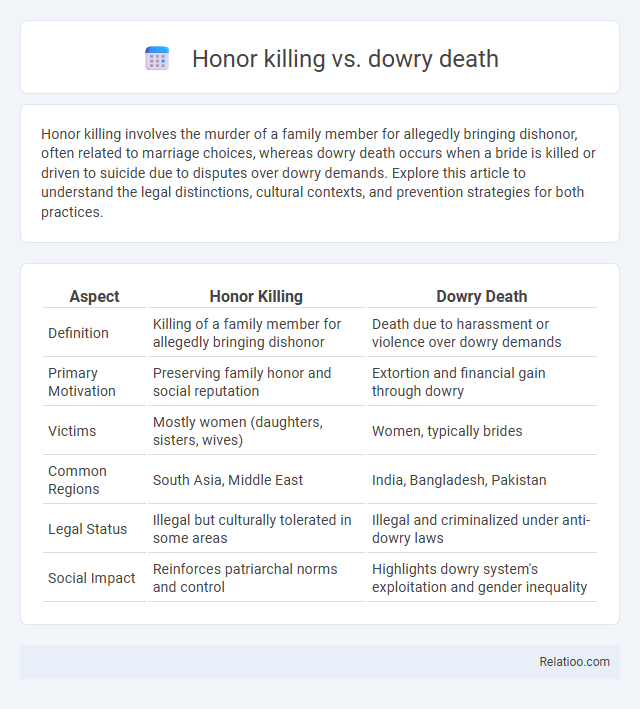
| Aspect | Honor Killing | Dowry Death |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Killing of a family member for allegedly bringing dishonor | Death due to harassment or violence over dowry demands |
| Primary Motivation | Preserving family honor and social reputation | Extortion and financial gain through dowry |
| Victims | Mostly women (daughters, sisters, wives) | Women, typically brides |
| Common Regions | South Asia, Middle East | India, Bangladesh, Pakistan |
| Legal Status | Illegal but culturally tolerated in some areas | Illegal and criminalized under anti-dowry laws |
| Social Impact | Reinforces patriarchal norms and control | Highlights dowry system's exploitation and gender inequality |
Introduction to Honor Killing and Dowry Death
Honor killing involves the murder of a family member, usually a woman, perceived to have brought shame or dishonor upon the family, often due to actions related to marriage, relationships, or behavior. Dowry death occurs when a woman is killed or driven to suicide by her husband or his family over disputes regarding dowry demands, a significant social issue in certain cultures. Understanding these distinct forms of violence can help you recognize the serious cultural and legal challenges involved in combating gender-based crimes.
Defining Honor Killing: Meaning and Context
Honor killing refers to the murder of a family member, usually a woman, perceived to have brought dishonor upon the family, often due to actions related to marriage, relationships, or personal autonomy. Dowry death occurs when a woman is killed or driven to suicide over disputes related to dowry demands made by her husband's family. While both involve gender-based violence rooted in cultural and social practices, honor killing specifically targets perceived violations of family honor, whereas dowry death centers on financial extortion tied to marriage customs.
Dowry Death: Definition and Prevalence
Dowry death refers to the fatal outcome resulting from disputes or torture related to dowry demands in marriages, predominantly seen in South Asian countries like India. According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) of India, dowry deaths account for approximately 7,000 cases annually, highlighting a persistent socio-legal issue. This form of violence is distinct from honor killing, which involves the murder of family members to protect perceived family honor, while both underline severe gender-based violence.
Historical Roots and Cultural Factors
Honor killing and dowry death both stem from deep-rooted cultural traditions, though their historical origins differ significantly. Honor killings have ancient ties to patriarchal societies where family reputation and social standing are paramount, while dowry deaths emerge primarily from South Asian marital customs involving financial transactions. Understanding Your cultural context is crucial, as these practices persist due to entrenched norms and legal challenges despite ongoing social reforms.
Legal Frameworks: Comparative Analysis
Honor killing and dowry death are distinct crimes addressed under different legal frameworks, with honor killing often prosecuted under sections related to murder and culpable homicide in criminal codes across South Asia, while dowry death is specifically addressed under the Indian Penal Code Section 304B. Legal systems in countries like India and Pakistan have enacted stringent provisions, including the Dowry Prohibition Act and specific clauses in their criminal laws to deter such acts, reflecting varying degrees of societal and judicial recognition of these crimes. Comparative analysis reveals that honor killing laws tend to be broader and less specific, whereas dowry death statutes incorporate elements like harassment and demand for dowry, ensuring targeted legal recourse and enhanced punishments.
Societal Impact and Psychological Consequences
Honor killing, dowry death, and domestic violence each exert profound societal impacts, perpetuating gender-based violence and reinforcing detrimental cultural norms. These crimes contribute to sustained cycles of fear, stigma, and social exclusion for victims' families, undermining societal cohesion and human rights. Psychological consequences include severe trauma, anxiety, depression, and long-lasting emotional scars that affect survivors and communities, impeding psychological recovery and social stability.
Gender Dynamics in Honor Killing vs Dowry Death
Honor killing primarily targets women accused of violating family or community norms related to chastity or behavior, reflecting deep-rooted patriarchal control over female autonomy. Dowry death involves the fatal consequences of dowry disputes, typically affecting married women subjected to ongoing harassment or violence from their in-laws, rooted in economic and gender-based power imbalances. Both practices underscore systemic gender inequalities, with honor killing emphasizing cultural control over women's honor and dowry death highlighting exploitation tied to marriage economics and patriarchal entitlement.
Case Studies and Real-life Examples
Case studies of honor killings, such as the 2018 Pakistan incident where a young woman was murdered for marrying without family consent, illustrate the brutal enforcement of social norms tied to family honor. Dowry death cases, like the 2019 Indian tragedy where a bride was burnt due to unpaid dowry demands, highlight the deadly consequences of financial greed and gender discrimination embedded in dowry practices. Real-life examples emphasize cultural, legal, and societal differences but consistently reveal the urgent need for effective legal reforms and awareness campaigns to combat these human rights violations.
Prevention Strategies and Policy Recommendations
Prevention strategies for honor killing and dowry death must address deeply rooted cultural norms and legal enforcement gaps in South Asian countries, where these practices are prevalent. Strengthening legal frameworks, implementing community education programs, and providing protection mechanisms for at-risk individuals form the cornerstone of effective policy recommendations. Your role in advocating for comprehensive reforms and supporting awareness initiatives contributes significantly to eradicating these human rights violations.
Conclusion: Towards Eradicating Gender-based Violence
Eradicating gender-based violence necessitates targeted legal reforms and community-based education addressing both honor killings and dowry deaths, which are rooted in harmful patriarchal norms. Comprehensive strategies integrating victim support, strict enforcement of laws, and public awareness campaigns contribute significantly to reducing these cultural practices. Sustainable change requires collaboration among government agencies, civil society, and local communities to challenge and transform societal attitudes underpinning gender-based violence.
Infographic: Honor killing vs Dowry death
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com