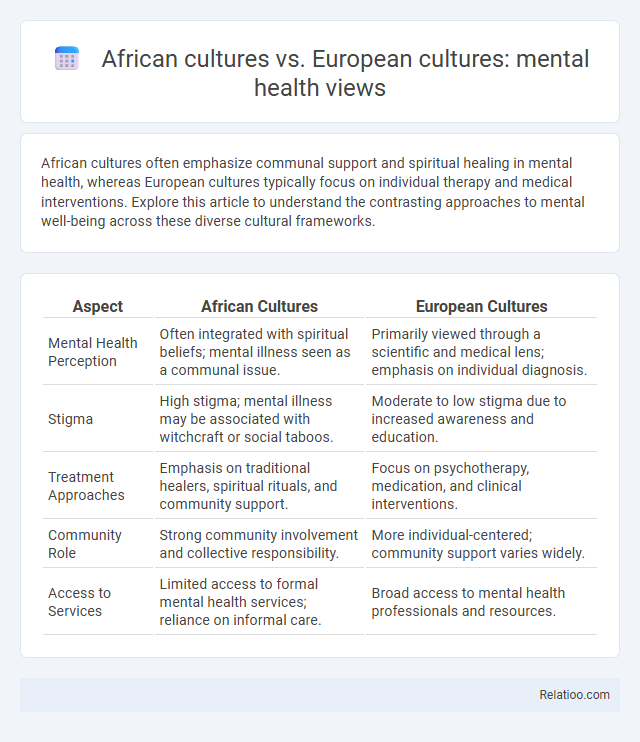
African cultures often emphasize communal support and spiritual healing in mental health, whereas European cultures typically focus on individual therapy and medical interventions. Explore this article to understand the contrasting approaches to mental well-being across these diverse cultural frameworks.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | African Cultures | European Cultures |
|---|---|---|
| Mental Health Perception | Often integrated with spiritual beliefs; mental illness seen as a communal issue. | Primarily viewed through a scientific and medical lens; emphasis on individual diagnosis. |
| Stigma | High stigma; mental illness may be associated with witchcraft or social taboos. | Moderate to low stigma due to increased awareness and education. |
| Treatment Approaches | Emphasis on traditional healers, spiritual rituals, and community support. | Focus on psychotherapy, medication, and clinical interventions. |
| Community Role | Strong community involvement and collective responsibility. | More individual-centered; community support varies widely. |
| Access to Services | Limited access to formal mental health services; reliance on informal care. | Broad access to mental health professionals and resources. |
Historical Context of Mental Health in Africa and Europe
African cultures traditionally interpret mental health through spiritual and communal lenses, often attributing conditions to ancestral or supernatural forces, which influences the persistent stigma surrounding mental illness. European views, shaped by the Enlightenment and medical advancements, shifted toward biological and psychological explanations, reducing some stigma but also institutionalizing treatment practices. Your understanding of mental health stigma benefits from recognizing these historical contexts that shape divergent attitudes and approaches across African and European societies.
Traditional Beliefs and Stigma Surrounding Mental Health
Traditional African cultures often interpret mental health issues through spiritual or supernatural lenses, attributing conditions to ancestral displeasure or witchcraft, which reinforces stigma and hinders seeking professional care. European cultures typically approach mental health from medical and psychological perspectives, though stigma persists due to misunderstandings and societal prejudices. The divergence in cultural frameworks significantly impacts mental health stigma, with traditional beliefs in African societies perpetuating silence and exclusion, whereas European contexts increasingly promote awareness and destigmatization.
Family and Community Roles in Mental Health Support
In African cultures, mental health support is deeply rooted in collective family and community involvement, where extended family members often play active roles in caregiving and decision-making, emphasizing social cohesion and spiritual healing practices. European cultures tend to approach mental health with a more individualistic perspective, focusing on professional healthcare services and psychological therapy, often resulting in less direct family participation. This divergence influences the prevalence and nature of mental health stigma, with African views sometimes blending traditional beliefs that can both support and hinder openness, while European contexts face stigma around personal disclosure despite clinical advancements.
Spirituality and Religious Approaches to Mental Wellness
African cultures often integrate spirituality and ancestral beliefs into mental health practices, viewing wellness as a balance between the physical, spiritual, and communal realms. European cultures tend to emphasize medical and psychological models, sometimes leading to a more clinical approach to mental health care. Your understanding of mental health stigma can deepen by recognizing how African spirituality fosters communal support, while European perspectives may inadvertently contribute to stigma through reliance on institutional treatment.
Perceptions of Mental Illness: Myths and Realities
African cultures often interpret mental illness through spiritual or communal lenses, attributing symptoms to supernatural causes, which can intensify stigma and hinder access to professional care. European cultures tend to approach mental health from a clinical and psychological perspective, promoting awareness but still facing challenges such as stigma linked to misunderstanding and fear. Your understanding of these differing cultural perceptions is crucial for addressing mental health stigma by separating myths from realities and fostering more compassionate, informed attitudes.
Access to Mental Health Care: Barriers and Opportunities
African cultures often emphasize communal support and spiritual healing in mental health, which can create barriers to accessing formal mental health care due to stigma and lack of resources. European cultures generally prioritize medical and psychological treatments, facilitating better access to mental health services but still facing challenges from societal stigma and systemic inequalities. Improving access requires culturally sensitive interventions in Africa and policy reforms in Europe to reduce stigma and increase resource availability.
The Influence of Colonialism on Mental Health Perspectives
Colonialism profoundly shaped mental health perspectives by imposing European medical models on African cultures, often dismissing traditional healing practices and spiritual beliefs. Your understanding of mental health stigma must consider that European views historically framed African expressions of distress as primitive or pathological, amplifying stigma in colonized societies. This legacy continues to influence mental health systems, creating disparities in recognition and treatment across African and European contexts.
Modernization and Changing Attitudes Toward Mental Health
African cultures historically link mental health to spiritual and communal contexts, often leading to stigma rooted in traditional beliefs. European cultures, influenced by biomedical models, increasingly advocate for psychological interventions, reducing stigma through modern healthcare frameworks. Modernization fosters shifting attitudes in both regions, promoting mental health awareness and integrating diverse cultural perspectives to challenge stigma effectively.
Mental Health Education and Public Awareness in Africa vs Europe
African cultures often emphasize communal support and spiritual approaches in mental health, whereas European cultures typically prioritize clinical treatment and psychological therapies, impacting Mental Health Education and Public Awareness strategies. In Africa, limited resources and traditional beliefs contribute to stigma, hindering public awareness campaigns, while Europe benefits from widespread educational programs and government policies promoting mental health literacy. Efforts to reduce stigma in African contexts increasingly involve integrating cultural sensitivity and community leaders, contrasting with Europe's more institutionalized mental health education frameworks.
Integrating Indigenous and Western Mental Health Practices
African cultures emphasize community and spiritual healing, integrating ancestral knowledge with modern mental health care, while European cultures often prioritize clinical and individual therapeutic approaches. Mental health stigma persists in both regions but manifests differently, with African societies sometimes associating mental illness with supernatural causes and European communities focusing on medical diagnoses. Combining Indigenous African healing rituals with Western psychological methods can foster holistic mental health care, reducing stigma and enhancing treatment efficacy.
Infographic: African cultures vs European cultures mental health views
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com