Suppression occurs when a third variable reduces the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable, while mediation explains the process through which an independent variable influences a dependent variable via a mediator. Explore this article to understand key differences between suppression and mediation in relationship dynamics.
Table of Comparison
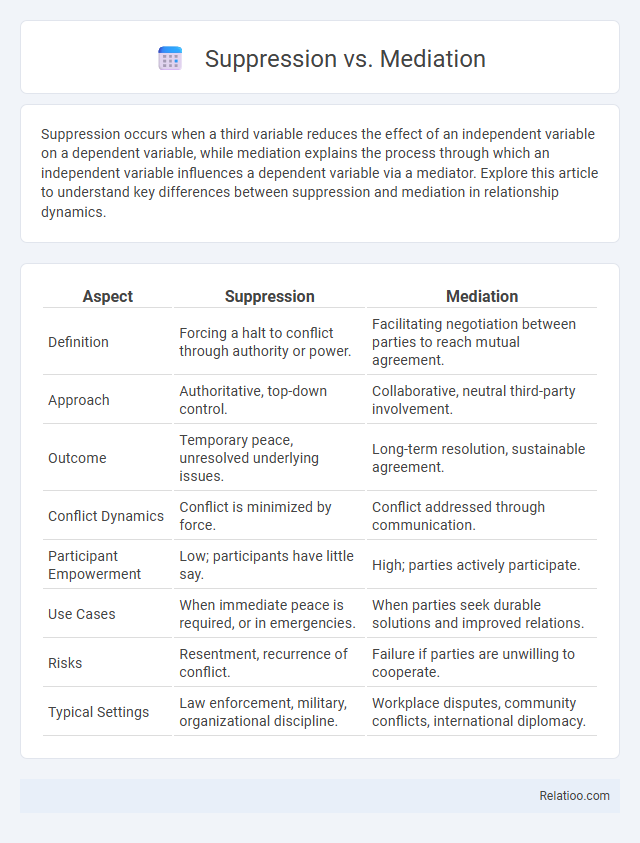
| Aspect | Suppression | Mediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Forcing a halt to conflict through authority or power. | Facilitating negotiation between parties to reach mutual agreement. |
| Approach | Authoritative, top-down control. | Collaborative, neutral third-party involvement. |
| Outcome | Temporary peace, unresolved underlying issues. | Long-term resolution, sustainable agreement. |
| Conflict Dynamics | Conflict is minimized by force. | Conflict addressed through communication. |
| Participant Empowerment | Low; participants have little say. | High; parties actively participate. |
| Use Cases | When immediate peace is required, or in emergencies. | When parties seek durable solutions and improved relations. |
| Risks | Resentment, recurrence of conflict. | Failure if parties are unwilling to cooperate. |
| Typical Settings | Law enforcement, military, organizational discipline. | Workplace disputes, community conflicts, international diplomacy. |
Understanding Suppression and Mediation
Suppression and mediation are key concepts in statistical analysis used to explain relationships between variables. Understanding suppression involves recognizing how a third variable enhances the predictive validity of an independent variable by controlling for irrelevant variance, while mediation explains the process through which an independent variable influences a dependent variable via a mediator. Your ability to distinguish these effects improves the accuracy of interpreting complex data patterns in research.
Defining Suppression in Research
Suppression in research refers to a statistical phenomenon where the inclusion of a suppressor variable increases the predictive validity of another independent variable by controlling for irrelevant variance. It contrasts with mediation, which explains the mechanism through which an independent variable influences a dependent variable, and moderation, which affects the strength or direction of this relationship. Identifying suppression effects is crucial for accurately interpreting regression analyses and understanding complex variable interrelations.
What is Mediation?
Mediation is a statistical method used to understand the mechanism through which an independent variable influences a dependent variable by introducing a third variable called the mediator. This process explains how or why an effect occurs, indicating an indirect relationship that accounts for the connection between the predictor and outcome variables. In comparison, suppression involves a third variable that increases the predictive validity of another variable by controlling for irrelevant variance, while suppression and mediation differ in whether the third variable explains (mediation) or clarifies (suppression) the relationship.
Key Differences Between Suppression and Mediation
Suppression involves consciously blocking or minimizing awareness of specific thoughts or feelings, whereas mediation refers to a neutral third party facilitating communication and conflict resolution between disputing parties. Key differences include suppression being an internal psychological defense mechanism aimed at controlling unwanted emotions, while mediation is an external process designed to achieve mutual agreement and understanding. Suppression often leads to unresolved stress or emotional buildup, whereas mediation promotes collaborative problem-solving and restores relationships.
The Role of Variables in Suppression
In suppression, the suppressor variable increases the predictive validity of another variable by controlling for irrelevant variance, enhancing the relationship between the predictor and outcome. Unlike mediation, where the mediator explains the mechanism underlying the relationship between independent and dependent variables, the suppressor's role is to clarify or reveal the direct association by removing confounding influences. Understanding suppression requires identifying variables that suppress irrelevant noise, thereby improving model accuracy and interpretability in statistical analyses.
Mediation Analysis: Methods and Approaches
Mediation analysis methods focus on understanding the mechanism by which an independent variable influences a dependent variable through a mediator. Techniques such as the causal steps approach, the Sobel test, and bootstrapping are commonly used to assess indirect effects and quantify mediation strength. Your ability to accurately interpret mediation results depends on selecting appropriate statistical tools that address assumptions like linearity, independence, and sample size.
Identifying Suppression Effects in Data
Identifying suppression effects in data requires analyzing how the inclusion of a third variable changes the relationship between the independent and dependent variables, often revealing hidden or counterintuitive correlations. Suppression occurs when a suppressor variable increases the predictive validity of another variable by controlling for irrelevant variance, unlike mediation which explains the mechanism of influence and moderation which alters the strength or direction of an effect. Statistical techniques such as multiple regression analysis and Sobel tests help detect suppression by comparing coefficients before and after including potential suppressor variables.
Practical Applications of Mediation
Practical applications of mediation involve resolving disputes efficiently by facilitating open communication and mutual agreement between parties without resorting to legal battles or suppressing emotions. You benefit from mediation's ability to maintain relationships and reduce litigation costs while allowing all voices to be heard and needs addressed. Unlike suppression, which involves avoiding or denying issues, and mediation, which encourages resolution, mediation serves as a constructive tool for practical conflict management in business, family, and community disputes.
Challenges in Distinguishing Suppression from Mediation
Distinguishing suppression from mediation presents significant challenges due to their overlapping statistical effects and conceptual differences in psychological research. Suppression occurs when a variable increases the predictive validity of another by controlling irrelevant variance, whereas mediation explains the mechanism through which an independent variable influences an outcome. Your understanding can be enhanced by carefully analyzing the direction and significance of indirect and direct effects using rigorous statistical methods like structural equation modeling and bootstrapping techniques.
Implications for Research and Practice
Suppression occurs when a variable increases the predictive validity of another variable by controlling for irrelevant variance, impacting the clarity of research findings and model accuracy. Mediation explains the mechanism through which an independent variable affects a dependent variable, essential for understanding causal pathways and refining intervention strategies. Distinguishing these effects enhances the precision of statistical models and informs evidence-based decision-making in both research and applied settings.
Infographic: Suppression vs Mediation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com