Devaluation involves diminishing someone's worth to protect oneself emotionally, while rejection is the direct refusal or dismissal of a person or idea. Explore the nuanced differences between devaluation and rejection in this article.
Table of Comparison
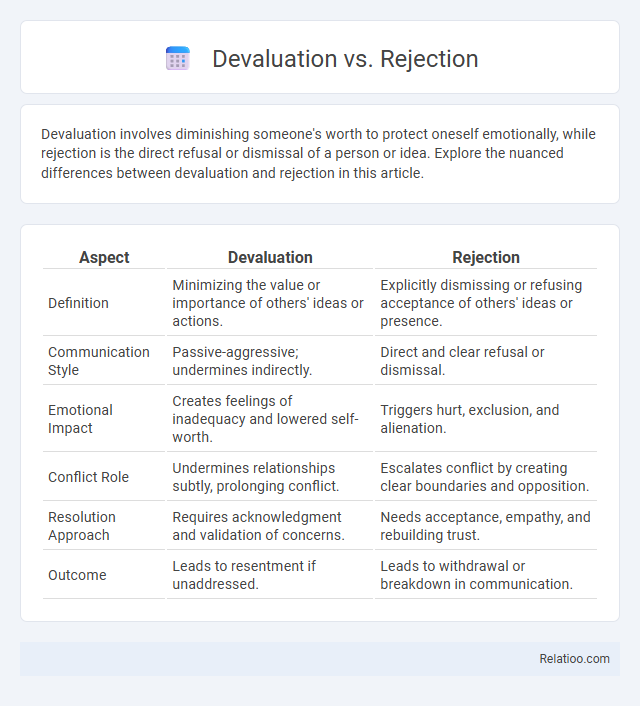
| Aspect | Devaluation | Rejection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimizing the value or importance of others' ideas or actions. | Explicitly dismissing or refusing acceptance of others' ideas or presence. |
| Communication Style | Passive-aggressive; undermines indirectly. | Direct and clear refusal or dismissal. |
| Emotional Impact | Creates feelings of inadequacy and lowered self-worth. | Triggers hurt, exclusion, and alienation. |
| Conflict Role | Undermines relationships subtly, prolonging conflict. | Escalates conflict by creating clear boundaries and opposition. |
| Resolution Approach | Requires acknowledgment and validation of concerns. | Needs acceptance, empathy, and rebuilding trust. |
| Outcome | Leads to resentment if unaddressed. | Leads to withdrawal or breakdown in communication. |
Understanding Devaluation and Rejection
Understanding devaluation involves recognizing it as an unconscious defense mechanism where an individual attributes exaggerated negative qualities to others to reduce perceived threats. Rejection occurs when one dismisses or refuses ideas, people, or emotions, often as a conscious response to protect oneself from discomfort or harm. Both devaluation and rejection impact interpersonal relationships by distorting perceptions and creating emotional distance.
Key Differences Between Devaluation and Rejection
Devaluation involves diminishing the worth of a person or object, often by attributing negative qualities, whereas rejection is the outright dismissal or refusal to accept someone or something. Devaluation subtly undermines value, impacting self-esteem or perception, while rejection is a clear, decisive act of exclusion. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in psychology and interpersonal relationships to address emotional responses effectively.
Psychological Impact of Devaluation
Devaluation in psychological terms refers to the process where an individual attributes exaggerated negative qualities to themselves or others, often leading to diminished self-worth and lowered self-esteem. Unlike rejection, which involves outright dismissal or exclusion, devaluation subtly undermines confidence, causing emotional distress and increased vulnerability to anxiety or depression. Understanding the psychological impact of devaluation helps you recognize harmful patterns that may impair your mental health and interpersonal relationships.
Emotional Consequences of Rejection
Emotional consequences of rejection often include feelings of worthlessness, sadness, and diminished self-esteem, leading to increased vulnerability to anxiety and depression. Rejection triggers activation of brain areas associated with physical pain, intensifying emotional distress and social withdrawal. Persistent rejection can impair interpersonal relationships and contribute to long-term psychological difficulties such as chronic loneliness and low self-worth.
Causes and Triggers for Devaluation
Devaluation often stems from internal fears of abandonment or low self-esteem, triggered by perceived threats to self-worth or unmet emotional needs. Rejection usually arises when an individual feels excluded or dismissed by others, prompting defensive responses to maintain social or emotional boundaries. Devaluation involves attributing excessive negative qualities to others, frequently caused by unresolved insecurities or conflicting feelings within close interpersonal relationships.
Common Situations Involving Rejection
Common situations involving rejection often trigger intense emotional responses where individuals may experience both devaluation and outright rejection simultaneously. You might feel your worth is diminished when your ideas, contributions, or presence are dismissed or invalidated in personal or professional settings. Recognizing the subtle differences in these reactions helps in managing your emotional health and fostering resilience against perceived or real social exclusion.
Devaluation in Relationships vs Rejection
Devaluation in relationships involves diminishing a partner's worth or qualities, often leading to emotional distancing and undermining trust. Rejection, by contrast, is a direct refusal or dismissal that can cause immediate emotional pain but may not erode the ongoing bond as subtly as devaluation. Understanding the distinction between devaluation and rejection highlights how persistent negative judgments can destabilize relationship dynamics more profoundly than occasional dismissals.
Coping Strategies for Devaluation and Rejection
Coping strategies for devaluation include reinforcing self-worth through positive affirmations and seeking support from trusted individuals to counteract negative self-perceptions. In managing rejection, cognitive reframing helps by viewing setbacks as opportunities for growth rather than personal failures. Both approaches benefit from mindfulness and emotional regulation techniques to reduce the impact of external judgments on mental health.
Long-Term Effects on Self-Esteem
Devaluation involves undervaluing your own worth, often leading to persistent feelings of inadequacy that erode long-term self-esteem. Rejection, whether social or personal, can create deep-seated doubts about your belonging and acceptance, significantly damaging your self-confidence over time. Understanding these distinctions helps you develop coping strategies that protect and rebuild self-esteem in the face of emotional challenges.
Building Resilience Against Devaluation and Rejection
Building resilience against devaluation and rejection involves strengthening self-worth through consistent positive affirmations and mindful self-reflection. Cognitive restructuring techniques help individuals challenge internalized negative beliefs and reduce emotional responses linked to devaluation experiences. Developing supportive relationships and practicing emotional regulation enhance adaptive coping mechanisms, fostering long-term psychological resilience.
Infographic: Devaluation vs Rejection
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com