Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding during conversations, while empathetic listening adds emotionally connecting by genuinely sharing and understanding the speaker's feelings. Discover more insights on enhancing your relationships through these listening techniques in this article.
Table of Comparison
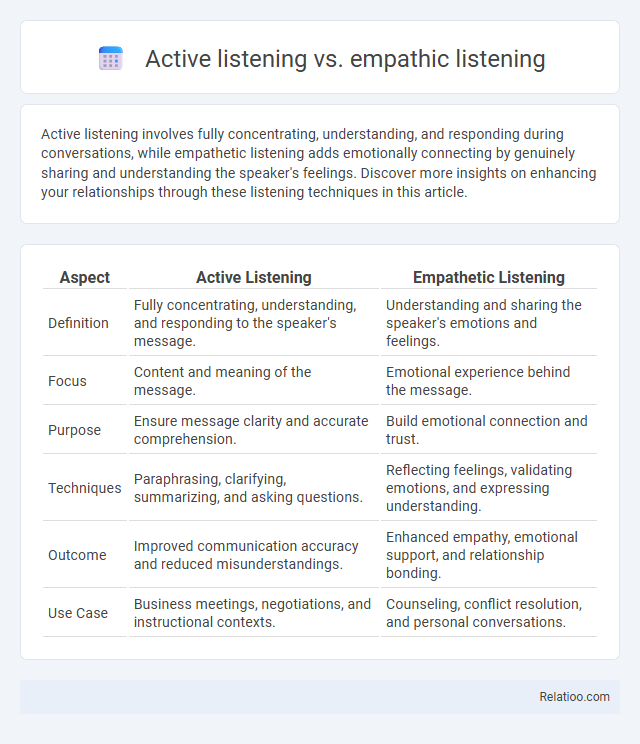
| Aspect | Active Listening | Empathetic Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to the speaker's message. | Understanding and sharing the speaker's emotions and feelings. |
| Focus | Content and meaning of the message. | Emotional experience behind the message. |
| Purpose | Ensure message clarity and accurate comprehension. | Build emotional connection and trust. |
| Techniques | Paraphrasing, clarifying, summarizing, and asking questions. | Reflecting feelings, validating emotions, and expressing understanding. |
| Outcome | Improved communication accuracy and reduced misunderstandings. | Enhanced empathy, emotional support, and relationship bonding. |
| Use Case | Business meetings, negotiations, and instructional contexts. | Counseling, conflict resolution, and personal conversations. |
Understanding Active Listening
Active listening involves fully concentrating on the speaker, understanding their message, and responding thoughtfully, which enhances effective communication. Empathetic listening goes deeper by recognizing and sharing the speaker's emotions, fostering trust and connection. Your skill in active listening improves relationships by ensuring accurate comprehension and meaningful feedback.
Defining Empathetic Listening
Empathetic listening involves fully understanding and sharing the feelings of the speaker, making your response emotionally supportive and validating. Unlike active listening, which prioritizes accurately receiving and clarifying information, empathetic listening focuses on connecting with the speaker's emotional experience. Your ability to practice empathetic listening builds trust and deepens interpersonal relationships by showing genuine care.
Key Differences Between Active and Empathetic Listening
Active listening involves fully concentrating on the speaker, understanding their message, and providing feedback to ensure clarity, emphasizing verbal and non-verbal cues. Empathetic listening goes beyond comprehension by seeking to deeply understand the speaker's feelings and emotional context, fostering emotional connection and support. The key difference lies in empathetic listening prioritizing emotional resonance, while active listening focuses more on accurately processing and responding to the communicated information.
Core Principles of Active Listening
Active listening centers on fully concentrating, understanding, and responding thoughtfully to the speaker, involving skills such as paraphrasing, asking clarifying questions, and providing feedback to ensure accurate comprehension. Empathetic listening goes beyond by connecting emotionally, aiming to understand the speaker's feelings and perspectives without judgment. Your ability to practice core principles of active listening--such as maintaining eye contact, minimizing distractions, and validating the speaker's message--enhances communication effectiveness and trust-building in any interaction.
The Emotional Depth of Empathetic Listening
Empathetic listening delves deeper into emotional understanding by fully engaging with the speaker's feelings and perspectives, unlike active listening which mainly focuses on accurately receiving and reflecting information. This depth allows empathetic listeners to respond with genuine compassion, fostering trust and emotional connection. The emotional depth of empathetic listening enhances interpersonal relationships by validating emotions and encouraging open communication.
Benefits of Active Listening in Communication
Active listening enhances communication effectiveness by promoting clear understanding, reducing misunderstandings, and fostering trust between speakers. It requires full attention and engagement, allowing individuals to accurately interpret both verbal and non-verbal cues, which leads to more meaningful interactions. This skill not only improves problem-solving and conflict resolution but also strengthens relationships in both personal and professional contexts.
Advantages of Empathetic Listening in Relationships
Empathetic listening enhances emotional connection by allowing individuals to truly understand and validate their partner's feelings, fostering trust and intimacy. This type of listening reduces misunderstandings and conflict by promoting open communication and emotional safety. It supports relationship resilience by encouraging compassionate responses that meet emotional needs, strengthening bonds over time.
Common Misconceptions About Listening Styles
Common misconceptions about listening styles often confuse active listening with empathetic listening, assuming they serve the same purpose; however, active listening emphasizes understanding and responding to the content, while empathetic listening focuses on sensing emotions and building emotional connection. Many believe that active listening is entirely objective, but it involves selective attention and nonverbal feedback that shapes your interpretation. Recognizing these distinctions helps you improve communication by applying the appropriate listening style in different contexts.
When to Use Active vs. Empathetic Listening
Active listening is most effective in situations requiring clear understanding, problem-solving, or when providing feedback, as it involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to the speaker's message. Empathetic listening is essential during emotionally charged conversations or conflicts, emphasizing understanding the speaker's feelings and perspective to build trust and foster emotional support. Choosing between active and empathetic listening depends on the context: active listening for clarity and task-oriented interactions, empathetic listening for emotional connection and support.
Tips for Developing Effective Listening Skills
Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to the speaker, with tips including maintaining eye contact, avoiding interruptions, and summarizing key points to confirm understanding. Empathetic listening goes deeper by recognizing and validating the speaker's emotions, which can be developed by practicing patience, reflecting feelings, and asking open-ended questions. Developing effective listening skills combines these practices by staying present, showing genuine interest, and regularly seeking feedback to enhance communication and build trust.
Infographic: Active listening vs Empathetic listening
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com