Individualistic cultures prioritize personal goals and independence in relationships, while collectivistic cultures emphasize group harmony and family obligations. Explore this article to understand how cultural values shape relationship dynamics and communication styles.
Table of Comparison
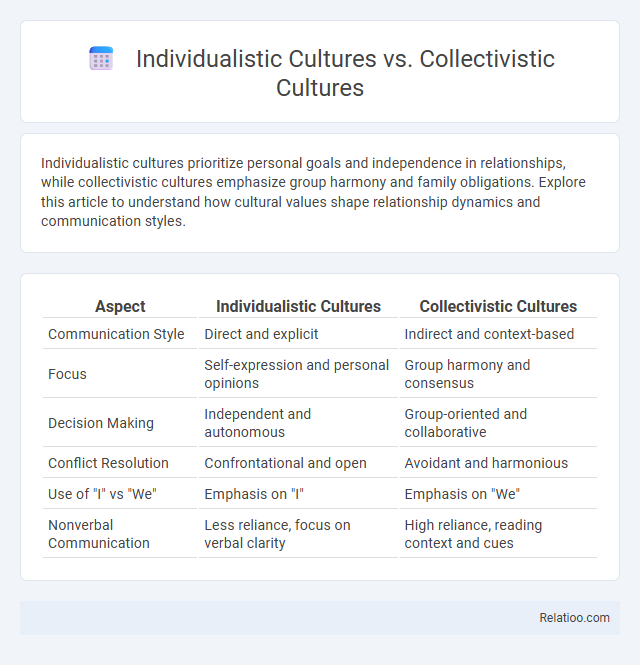
| Aspect | Individualistic Cultures | Collectivistic Cultures |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Style | Direct and explicit | Indirect and context-based |
| Focus | Self-expression and personal opinions | Group harmony and consensus |
| Decision Making | Independent and autonomous | Group-oriented and collaborative |
| Conflict Resolution | Confrontational and open | Avoidant and harmonious |
| Use of "I" vs "We" | Emphasis on "I" | Emphasis on "We" |
| Nonverbal Communication | Less reliance, focus on verbal clarity | High reliance, reading context and cues |
Defining Individualistic and Collectivistic Cultures
Individualistic cultures prioritize personal goals, independence, and self-expression, emphasizing individual achievements and personal rights. Collectivistic cultures value group harmony, interdependence, and community well-being, where individuals often define themselves through social connections and shared responsibilities. Understanding these cultural frameworks helps you avoid stereotyping by recognizing behaviors shaped by cultural values rather than making generalized assumptions.
Key Characteristics of Individualistic Societies
Individualistic cultures emphasize personal autonomy, self-expression, and individual achievements, often valuing independence over group harmony. These societies prioritize personal goals, decision-making freedom, and direct communication styles, fostering innovation and self-reliance. In contrast, collectivistic cultures focus on group cohesion, social roles, and interdependence, where stereotyping can arise from generalized beliefs about group behavior and identity.
Core Values in Collectivistic Societies
Core values in collectivistic societies emphasize group harmony, interdependence, and loyalty, shaping behaviors that prioritize family and community over individual desires. These cultural norms contrast with individualistic cultures that value autonomy and self-expression, often leading to misunderstandings and stereotyping when viewed through differing cultural lenses. Your awareness of these fundamental differences helps avoid simplistic stereotypes and fosters deeper cross-cultural understanding and respect.
Personal Identity and Group Identity
Individualistic cultures emphasize personal identity, autonomy, and self-expression, promoting individuals to define themselves by unique traits and personal achievements. Collectivistic cultures prioritize group identity, social harmony, and interdependence, encouraging individuals to align their values and behaviors with family, community, or societal goals. Stereotyping in these contexts often arises from oversimplified assumptions, where individualistic traits may be misunderstood in collectivistic societies and vice versa, impacting cross-cultural communication and perception.
Communication Styles: Direct vs Indirect
Individualistic cultures prioritize direct communication, emphasizing clarity and personal expression to convey messages explicitly in interpersonal interactions. Collectivistic cultures favor indirect communication styles, often using context, nonverbal cues, and subtlety to maintain group harmony and avoid confrontation. Stereotyping these communication styles risks oversimplifying diverse behaviors, potentially leading to misunderstandings and reduced intercultural effectiveness.
Decision-Making Processes and Authority
Individualistic cultures prioritize personal autonomy and self-expression, influencing decision-making processes that emphasize individual choice and personal responsibility. Collectivistic cultures, by contrast, value group harmony and consensus, leading to decision-making that often involves group input and respect for hierarchical authority. Your ability to recognize these cultural dynamics can help avoid stereotyping, ensuring respectful and effective communication across diverse cultural contexts.
Family and Social Relationships
In individualistic cultures, family and social relationships emphasize personal autonomy and self-expression, promoting independence and individual goals over group priorities. Collectivistic cultures prioritize family cohesion, interdependence, and communal harmony, valuing group decisions and loyalty across extended family networks. Stereotyping often misrepresents these cultural dynamics by oversimplifying individual behaviors and reinforcing biased assumptions about family roles and social obligations.
Work Ethic and Motivation
Individualistic cultures prioritize personal achievement and self-motivation, driving individuals to set personal goals and take initiative in the workplace. Collectivistic cultures emphasize group harmony and team success, motivating employees through shared responsibilities and collective rewards. Understanding how your work ethic aligns with these cultural values helps prevent stereotyping and fosters more effective collaboration.
Conflict Resolution and Social Harmony
Individualistic cultures emphasize personal autonomy and direct communication, often leading to confrontational conflict resolution styles that prioritize individual interests. Collectivistic cultures value group cohesion and indirect communication, promoting harmony through consensus and avoidance of open conflict. Stereotyping between these cultural orientations can hinder effective conflict resolution by creating misunderstandings about intentions and communication styles, ultimately disrupting social harmony.
Global Implications and Cross-Cultural Challenges
Navigating individualistic and collectivistic cultures requires understanding their core values: personal autonomy versus group harmony, which affects communication, decision-making, and conflict resolution in global interactions. Stereotyping risks oversimplifying these cultural differences, leading to misinterpretations and reduced collaboration effectiveness in multinational teams. Your ability to recognize and adapt to these nuances enhances cross-cultural competence, fostering more inclusive and productive international partnerships.
Infographic: Individualistic Cultures vs Collectivistic Cultures
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com