Motivation drives the initial desire to improve relationships, while willpower sustains consistent effort through challenges and setbacks. Discover how to balance motivation and willpower for lasting relationship success in this article.
Table of Comparison
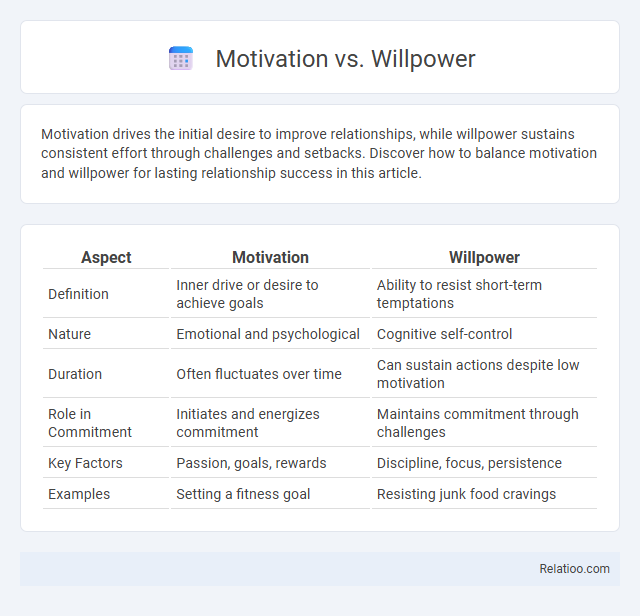
| Aspect | Motivation | Willpower |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inner drive or desire to achieve goals | Ability to resist short-term temptations |
| Nature | Emotional and psychological | Cognitive self-control |
| Duration | Often fluctuates over time | Can sustain actions despite low motivation |
| Role in Commitment | Initiates and energizes commitment | Maintains commitment through challenges |
| Key Factors | Passion, goals, rewards | Discipline, focus, persistence |
| Examples | Setting a fitness goal | Resisting junk food cravings |
Understanding Motivation: What Drives Us
Understanding motivation reveals the underlying psychological and emotional factors that drive human behavior, distinguishing it from willpower, which is the ability to resist short-term temptations to achieve long-term goals. Motivation arises from intrinsic desires or extrinsic rewards, influencing the intensity, direction, and persistence of actions. Strong motivation amplifies willpower by providing clear purpose and meaningful reasons for sustained effort toward personal or professional objectives.
The Science Behind Willpower
Willpower is a finite cognitive resource rooted in brain regions such as the prefrontal cortex, responsible for self-control and decision-making. Scientific studies reveal that willpower operates like a muscle that can be depleted with overuse but also strengthened through practice and adequate rest. Understanding the neurobiological mechanisms and psychological factors behind willpower provides insights into improving self-discipline and achieving long-term goals more effectively than relying solely on motivation.
Key Differences Between Motivation and Willpower
Motivation is the internal drive that initiates behavior toward achieving goals, often influenced by desires, needs, and rewards, whereas willpower is the ability to maintain self-control and resist short-term temptations despite obstacles. Motivation fluctuates based on emotional states and external factors, while willpower relies on cognitive control and conscious effort to persist. Understanding these differences helps in designing strategies for sustained behavior change, where motivation sparks action and willpower sustains it.
How Motivation Influences Behavior
Motivation drives the initiation and persistence of your behavior by providing purpose and direction, while willpower serves as the self-control mechanism that helps you resist temptations and maintain focus. High motivation levels amplify your commitment to goals, making tasks feel more meaningful and increasing the likelihood of consistent effort. Understanding the interplay between motivation and willpower can enhance your ability to sustain productive habits and achieve long-term success.
The Role of Willpower in Achieving Goals
Willpower is the mental strength that enables individuals to resist short-term temptations and persevere in pursuing long-term goals, playing a critical role in goal achievement. Unlike motivation, which can fluctuate based on emotions and external factors, willpower provides consistent self-control and discipline necessary for sustained effort. Studies show that higher levels of willpower correlate with better performance in tasks demanding persistence, highlighting its importance in overcoming obstacles and maintaining focus.
Are Motivation and Willpower Interconnected?
Motivation and willpower are interconnected yet distinct psychological concepts influencing human behavior and goal achievement; motivation provides the initial drive or desire to pursue a goal, while willpower represents the self-control needed to maintain effort despite obstacles or distractions. Neuroscientific studies reveal that motivation activates reward centers in the brain, enhancing persistence, whereas willpower recruits prefrontal cortex regions responsible for executive function and inhibitory control. Understanding their interplay is crucial for developing effective behavioral interventions and strategies for long-term success in areas such as health, education, and productivity.
Factors That Boost Motivation
Motivation thrives on clear goals, intrinsic values, and external rewards, shaping the initial drive to act, while willpower sustains effort through self-control and discipline during challenges. Factors that boost motivation include setting specific, achievable goals, maintaining a positive mindset, and receiving social support, all of which enhance focus and persistence. Understanding the interplay between motivation and willpower helps optimize performance and long-term success by aligning desire with sustained effort.
Strategies to Strengthen Willpower
Willpower represents the ability to resist short-term temptations in order to achieve long-term goals, distinct from motivation, which provides the initial drive, and discipline, which is the consistent application of effort. Effective strategies to strengthen willpower include setting clear, achievable goals, practicing mindfulness to increase self-awareness, and maintaining physical health through adequate sleep, nutrition, and exercise. Research also supports the use of habit formation and reducing decision fatigue by simplifying choices to conserve mental energy for willpower tasks.
Motivation vs Willpower: Which Matters More?
Motivation drives your initial desire to achieve goals by fueling your enthusiasm and purpose, while willpower sustains your focus and discipline during challenging moments. Research shows motivation ignites action, but willpower maintains perseverance when obstacles arise, making both essential for success. Understanding the distinct roles of motivation and willpower helps you balance passion with persistence to reach your objectives effectively.
Practical Tips to Harness Both for Success
Motivation sparks your initial desire to achieve goals, while willpower sustains the effort when motivation fades; combining both effectively increases your chances of success. Practical tips include setting clear, achievable objectives to boost motivation and creating habits or routines that reduce reliance on daily willpower. Tracking progress and using rewards reinforce positive behavior, helping you harness your motivation and willpower for consistent performance.
Infographic: Motivation vs Willpower
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com