Allegiance represents a deep commitment to a person or group based on loyalty and shared values, while fidelity emphasizes strict faithfulness and adherence to promises or vows. Discover the nuanced differences and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
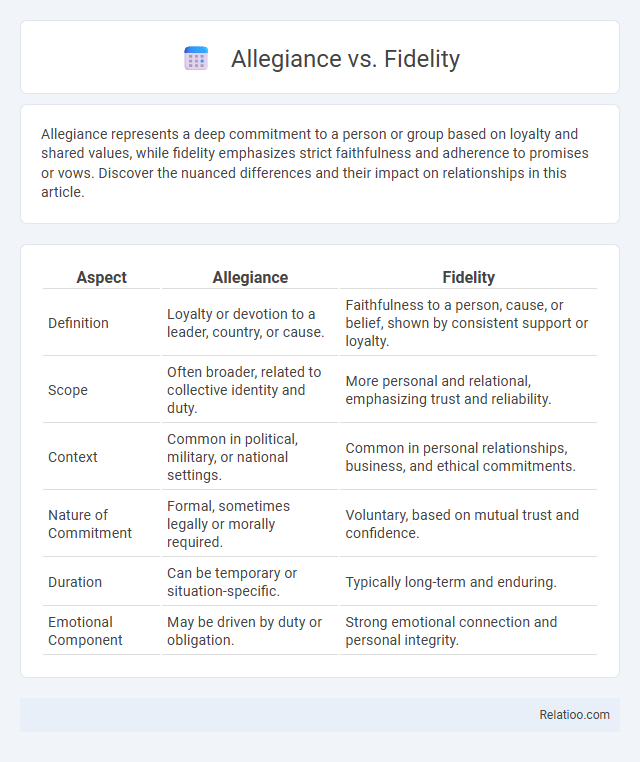
| Aspect | Allegiance | Fidelity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loyalty or devotion to a leader, country, or cause. | Faithfulness to a person, cause, or belief, shown by consistent support or loyalty. |
| Scope | Often broader, related to collective identity and duty. | More personal and relational, emphasizing trust and reliability. |
| Context | Common in political, military, or national settings. | Common in personal relationships, business, and ethical commitments. |
| Nature of Commitment | Formal, sometimes legally or morally required. | Voluntary, based on mutual trust and confidence. |
| Duration | Can be temporary or situation-specific. | Typically long-term and enduring. |
| Emotional Component | May be driven by duty or obligation. | Strong emotional connection and personal integrity. |
Understanding Allegiance and Fidelity: Core Definitions
Allegiance refers to a loyal commitment or duty owed to a sovereign, government, or cause, often implying a deep-rooted bond and obligation. Fidelity denotes faithfulness and accuracy in fulfilling promises or duties, emphasizing trustworthiness and reliability in relationships or responsibilities. Understanding the distinction between allegiance and fidelity is crucial, as allegiance is a broader societal or political loyalty, while fidelity focuses on personal or professional faithfulness and integrity.
Historical Perspectives on Loyalty: Allegiance vs Fidelity
Historical perspectives on loyalty distinguish allegiance as a public, formal commitment to a sovereign or state, often documented through oaths and legal obligations, whereas fidelity emphasizes personal faithfulness and trustworthiness within private or interpersonal relationships. Allegiance historically underpinned feudal societies and monarchies, binding subjects to rulers, while fidelity centered on moral integrity and loyalty in personal bonds, such as between spouses or servants. Understanding these nuances reveals how allegiance structured political order and fidelity maintained social cohesion throughout history.
Emotional Foundations: What Drives Allegiance and Fidelity?
Allegiance stems from deep emotional loyalty often tied to shared identity, values, or group membership, creating a bond rooted in trust and commitment. Fidelity emphasizes unwavering faithfulness and reliability in relationships or duties, driven by strong personal integrity and a sense of moral responsibility. Both allegiances and fidelities are anchored in emotional foundations but differ in focus: allegiance is collective and identity-based, whereas fidelity is individual and principle-based.
Allegiance in Politics and Society
Allegiance in politics and society refers to your loyalty or commitment to a nation, government, or cause, shaping civic identity and social cohesion. It influences political behavior, voting patterns, and national unity, distinguishing it from fidelity, which emphasizes faithfulness often in personal or contractual contexts. Understanding allegiance helps analyze citizen-state relationships and the dynamics of patriotism and social trust.
Fidelity in Personal and Professional Relationships
Fidelity in personal and professional relationships emphasizes loyalty, trustworthiness, and consistency, which build strong, lasting bonds between individuals and organizations. While allegiance often implies a formal or patriotic commitment and allegiance can suggest a broader sense of devotion, fidelity uniquely centers on maintaining faithfulness and reliability in interactions and promises. Your ability to demonstrate fidelity enhances trust and fosters dependable connections in both personal and workplace settings.
Legal Implications: Pledges, Oaths, and Contracts
Allegiance, fidelity, and loyalty differ significantly in their legal implications regarding pledges, oaths, and contracts. Allegiance often involves formal, legally binding commitments to a sovereign state or authority, while fidelity typically relates to contractual obligations requiring faithfulness and honesty, such as fiduciary duties. Loyalty, though morally significant, carries less explicit legal weight unless explicitly codified in contractual or statutory terms.
Allegiance vs Fidelity: Key Differences and Overlaps
Allegiance and fidelity both denote loyalty but differ in scope and usage; allegiance primarily refers to loyalty towards a nation, group, or cause, while fidelity emphasizes faithfulness and accuracy, often in relationships or commitments. Key differences include allegiance's collective or patriotic context versus fidelity's personal or contractual nature. Overlaps occur when both terms imply steadfast devotion, such as in pledges or trustworthiness.
Challenges in Maintaining Allegiance and Fidelity
Maintaining allegiance and fidelity presents challenges such as balancing personal values with organizational goals and navigating conflicts of interest that may arise. Your commitment can be tested by external influences and shifting priorities, requiring consistent communication and trust-building to uphold loyalty. Effective strategies involve transparent decision-making and fostering an environment that values integrity and mutual respect.
Allegiance and Fidelity in Modern Culture
Allegiance and Fidelity are central concepts in modern culture, both emphasizing loyalty but in distinct contexts; Allegiance often relates to loyalty towards a group, nation, or cause, while Fidelity focuses on faithfulness in personal relationships and commitments. In contemporary media and literature, Allegiance symbolizes collective identity and social bonds, whereas Fidelity highlights trust and integrity in interpersonal dynamics. These values shape societal expectations and individual behavior, reflecting evolving cultural norms in loyalty and commitment.
Choosing Between Allegiance and Fidelity: Practical Considerations
Choosing between Allegiance and Fidelity involves evaluating your priorities in trust and loyalty. Allegiance emphasizes unwavering commitment to a person, cause, or nation, while Fidelity highlights faithfulness and accuracy in fulfilling promises or duties. Your decision should consider whether emotional devotion or consistent reliability better supports your goals and relationships.
Infographic: Allegiance vs Fidelity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com