Consent requires informed, enthusiastic agreement given freely without pressure, while permission often implies a more passive approval that may lack full understanding. Explore the critical differences between consent and permission in this article.
Table of Comparison
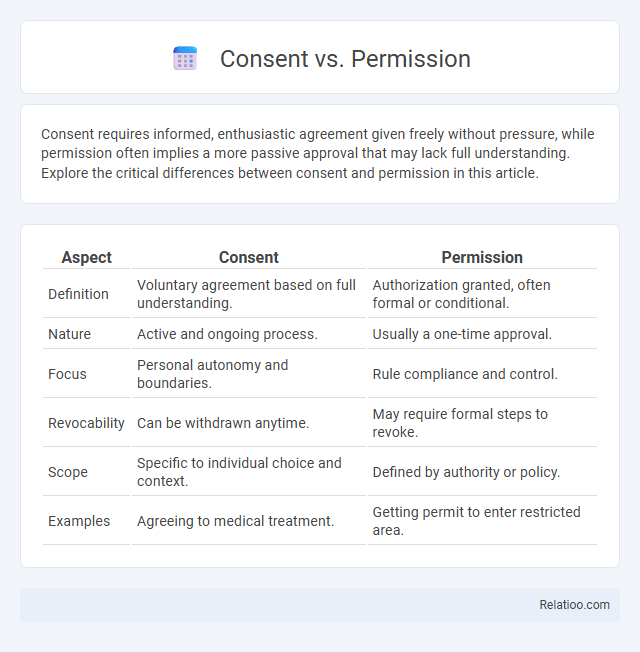
| Aspect | Consent | Permission |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary agreement based on full understanding. | Authorization granted, often formal or conditional. |
| Nature | Active and ongoing process. | Usually a one-time approval. |
| Focus | Personal autonomy and boundaries. | Rule compliance and control. |
| Revocability | Can be withdrawn anytime. | May require formal steps to revoke. |
| Scope | Specific to individual choice and context. | Defined by authority or policy. |
| Examples | Agreeing to medical treatment. | Getting permit to enter restricted area. |
Understanding the Difference: Consent vs Permission
Understanding the difference between consent and permission is crucial for clear communication and respectful interactions. Consent refers to an informed and voluntary agreement given by you, emphasizing autonomy and personal choice, while permission often implies an authority granting approval for an action. Differentiating these concepts helps establish boundaries and ensures ethical decision-making in personal and professional contexts.
Defining Consent in Various Contexts
Consent involves an explicit agreement to participate or allow an action based on informed understanding, often requiring clear communication and voluntary acceptance. Permission generally implies authorization granted by a person or authority, which may or may not involve full awareness or informed choice. In legal, medical, and interpersonal contexts, consent emphasizes autonomy, ensuring all parties comprehend implications and agree without coercion, distinguishing it from mere permission or informal consent.
What Does Permission Truly Mean?
Permission means granting explicit approval for a specific action, emphasizing authority and control over what is allowed. Unlike consent, which involves mutual agreement and understanding, permission often implies a hierarchical relationship where one party authorizes another. Your clarity on permission ensures respect for boundaries and proper legal or ethical adherence.
Legal Perspectives on Consent and Permission
Legal perspectives distinguish consent as a voluntary, informed agreement given by an individual with full understanding of the implications, whereas permission typically refers to authorization granted by an authority or controlling entity. Consent requires clear communication and can be withdrawn at any time, emphasizing personal autonomy and legal protection, while permission may be conditional and subject to specific terms set by the granting party. Your rights are primarily safeguarded through explicit consent in contracts, medical procedures, and data privacy laws, underscoring the critical legal value of consent over mere permission.
The Role of Power Dynamics in Consent and Permission
Consent involves a voluntary agreement between parties with equal power, emphasizing autonomy and mutual respect, whereas permission often reflects an unequal power dynamic where one party grants approval over another's actions. Power dynamics shape consent by ensuring it is freely given without coercion, while permission typically implies hierarchical authority and potential obligation. Understanding these distinctions highlights the ethical importance of genuine consent in relationships, contrasting with permission, which may mask control and limit true agency.
Cultural Influences on Consent and Permission
Cultural influences significantly shape the understanding and practice of consent and permission, as norms around autonomy, authority, and communication vary widely across societies. In collectivist cultures, permission often reflects respect for hierarchical relationships and community consensus, whereas consent emphasizes individual autonomy more prominently in individualistic cultures. These cultural variations impact how consent is negotiated and respected in social, legal, and interpersonal contexts, highlighting the need for culturally sensitive approaches in policies and interactions.
Importance of Clear Communication
Clear communication is essential to distinguish between consent, permission, and agreement, ensuring all parties fully understand the scope and implications of their interactions. Consent involves a voluntary, informed, and explicit agreement, often in personal or legal contexts, while permission typically refers to authorization granted by a controlling authority. Precise language eliminates misunderstandings and protects rights by setting transparent boundaries and expectations.
Real-World Examples: Consent vs Permission
Consent involves voluntarily agreeing to an action with full awareness of its implications, such as a patient signing a medical consent form before surgery. Permission typically refers to obtaining approval or authorization from someone in authority, like a child asking a parent for permission to attend a party. Understanding the difference helps you navigate situations where explicit agreement (consent) is required versus when only authorization (permission) is necessary, ensuring clarity and respect in interactions.
Consequences of Ignoring Consent or Permission
Ignoring consent or permission can lead to serious legal consequences, including lawsuits and fines that can damage reputations and financial standing. Non-compliance with consent requirements in sectors like healthcare, data privacy, and employment may result in regulatory penalties or criminal charges. Ethical violations caused by disregarding informed consent erode trust, harm relationships, and undermine organizational integrity.
Best Practices: Ensuring Respect and Boundaries
Best practices for ensuring respect and boundaries emphasize obtaining explicit consent rather than mere permission, as consent involves mutual understanding and active agreement, reflecting genuine autonomy. Your approach should prioritize clear communication, ongoing dialogue, and respect for personal limits to foster trust and prevent misunderstandings. Implementing these principles safeguards personal integrity and establishes a foundation for ethical interactions.
Infographic: Consent vs Permission
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com