Consent is a mutual, enthusiastic agreement in a relationship, while compliance often involves passive or reluctant agreement without genuine willingness. Explore the key differences and their impact on healthy connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
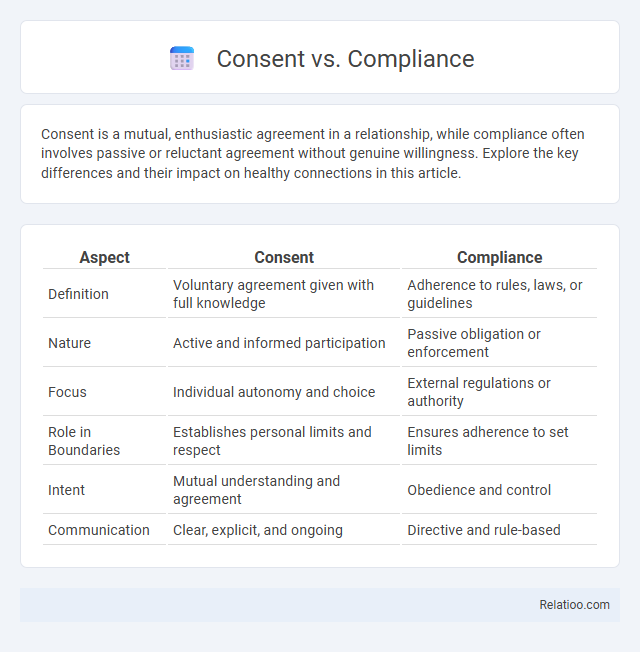
| Aspect | Consent | Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary agreement given with full knowledge | Adherence to rules, laws, or guidelines |
| Nature | Active and informed participation | Passive obligation or enforcement |
| Focus | Individual autonomy and choice | External regulations or authority |
| Role in Boundaries | Establishes personal limits and respect | Ensures adherence to set limits |
| Intent | Mutual understanding and agreement | Obedience and control |
| Communication | Clear, explicit, and ongoing | Directive and rule-based |
Understanding the Meaning of Consent
Consent involves the explicit, informed agreement by an individual to participate in an action or process, ensuring autonomy and respect for personal choice. Compliance refers to adhering to rules or regulations, often mandated by external authorities, which may not require active agreement from the individual. Understanding consent requires recognizing it as a voluntary, enthusiastic, and revocable agreement, distinct from mere compliance or obedience to directives.
Defining Compliance in Different Contexts
Compliance refers to adherence to laws, regulations, and policies within various contexts such as corporate governance, healthcare, and data protection. In regulatory environments, compliance ensures organizations meet mandatory standards to avoid legal penalties and maintain operational integrity. Unlike consent, which is voluntary agreement, compliance often involves obligatory actions imposed by authoritative bodies to safeguard ethical and legal responsibilities.
Key Differences Between Consent and Compliance
Consent involves voluntarily agreeing to a specific action or decision after being fully informed, highlighting personal autonomy and choice. Compliance refers to conforming to rules, regulations, or requests often due to external pressure, authority, or obligation, without necessarily agreeing internally. Understanding the key differences between consent and compliance ensures your actions respect individual freedom rather than mere adherence to imposed requirements.
The Importance of True Consent
True consent ensures that Your agreement is given freely, informed, and reversible, distinguishing it from mere compliance, which may involve passive acquiescence without genuine willingness. Unlike compliance, true consent requires clear communication, understanding, and respect for personal boundaries to protect autonomy and ethical standards. Prioritizing true consent fosters trust, transparency, and mutual respect in any interaction or relationship.
Power Dynamics in Consent and Compliance
Power dynamics play a critical role in differentiating consent from compliance, as consent requires genuine agreement without coercion, whereas compliance often involves submission due to authority or pressure. Your ability to give valid consent depends on a balanced power relationship where free will is respected, contrasting sharply with compliance, which may mask underlying coercion or manipulation. Understanding these distinctions emphasizes the importance of ensuring environments where consent is informed and voluntary, rather than merely compliant.
Examples of Consent vs Compliance in Real Life
Consent involves voluntary agreement, such as a patient signing a medical consent form after understanding treatment risks, while compliance refers to following rules or orders, like an employee adhering to company policies without necessarily agreeing with them. For instance, a child complying with bedtime rules may not consent, whereas an adult agreeing to a contract provides explicit consent. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify legal and ethical responsibilities in scenarios ranging from workplace behavior to medical decisions.
Psychological Impacts of Compliance Without Consent
Compliance without consent often leads to negative psychological impacts such as decreased motivation, heightened stress, and reduced sense of autonomy, which can undermine trust and long-term engagement. Individuals subjected to authoritative demands without voluntary agreement may experience feelings of resentment, helplessness, and diminished self-efficacy. Research in organizational psychology highlights that genuine consent fosters intrinsic motivation, whereas mere compliance prompts extrinsic regulation that harms overall well-being and performance.
Strategies to Promote Genuine Consent
Strategies to promote genuine consent emphasize clear communication, ensuring individuals fully understand their rights and the implications of their agreement. Creating an environment of transparency and trust reduces coercion and distinguishes true consent from mere compliance or acquiescence. Employing ongoing consent practices, such as regular check-ins and the ability to withdraw consent at any time, strengthens ethical engagement and respects personal autonomy.
Legal Implications: Consent vs Compliance
Consent involves explicit, informed agreement from an individual, legally binding and crucial for data protection under regulations like the GDPR. Compliance refers to adhering to laws, regulations, or standards, ensuring your organization meets legal requirements but not necessarily obtaining individual permission. Understanding the legal implications of consent versus compliance helps your business avoid costly penalties and maintain trust by respecting user autonomy and regulatory mandates.
Building a Culture of Consent over Compliance
Building a culture of consent over compliance empowers Your organization to prioritize genuine agreement and ethical decision-making rather than mere rule-following. This approach fosters trust, encourages active participation, and enhances overall workplace wellbeing by valuing individual autonomy and mutual respect. Emphasizing consent ensures policies are embraced authentically, leading to sustainable and positive behavioral change.
Infographic: Consent vs Compliance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com